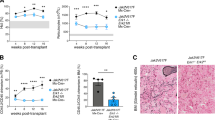
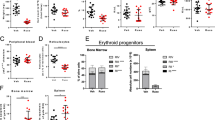
Abstract
Janus tyrosine kinase 2 (JAK2) mediates downstream signaling of cytokine receptors in all hematological lineages, yet constitutively active JAK2 mutants are able to drive selective expansion of particular lineage(s) in myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN). The molecular basis of lineage specificity is unclear. Here, we show that three activating JAK2 mutants with similar kinase activities in vitro elicit distinctive MPN phenotypes in mice by differentially expanding erythroid vs granulocytic precursors. Molecularly, this reflects the differential binding of JAK2 mutants to cytokine receptors EpoR and GCSFR in the erythroid vs granulocytic lineage and the creation of unique receptor/JAK2 complexes that generate qualitatively distinct downstream signals. Our results demonstrate that activating JAK2 mutants can differentially couple to selective cytokine receptors and change the signaling repertoire, revealing the molecular basis for phenotypic differences elicited by JAK2 (V617F) or mutations in exon 12. On the basis of these findings, receptor-JAK2 interactions could represent new targets of lineage-specific therapeutic approaches against MPN, which may be applicable to other cancers with aberrant JAK-STAT signaling.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas SJ, Snowden JA, Zeidler MP, Danson SJ . The role of JAK/STAT signalling in the pathogenesis, prognosis and treatment of solid tumours. Br J Cancer 2015; 113: 365–371.
Vainchenker W, Constantinescu SN . JAK/STAT signaling in hematological malignancies. Oncogene 2013; 32: 2601–2613.
Villarino AV, Kanno Y, Ferdinand JR, O'Shea JJ . Mechanisms of Jak/STAT signaling in immunity and disease. J Immunol 2015; 194: 21–27.
Stark GR, Darnell JE Jr . The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty. Immunity 2012; 36: 503–514.
Levine RL . JAK-mutant myeloproliferative neoplasms. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2012; 355: 119–133.
Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C, Fourouclas N, Swanton S et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet 2005; 365: 1054–1061.
James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, Staerk J, Delhommeau F, Lacout C et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature 2005; 434: 1144–1148.
Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 1779–1790.
Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, Ebert BL, Wernig G, Huntly BJ et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 387–397.
Zhao R, Xing S, Li Z, Fu X, Li Q, Krantz SB et al. Identification of an acquired JAK2 mutation in polycythemia vera. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 22788–22792.
Mullally A, Lane SW, Brumme K, Ebert BL . Myeloproliferative neoplasm animal models. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2012; 26: 1065–1081.
Scott LM, Tong W, Levine RL, Scott MA, Beer PA, Stratton MR et al. JAK2 exon 12 mutations in polycythemia vera and idiopathic erythrocytosis. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 459–468.
Grisouard J, Li S, Kubovcakova L, Rao TN, Meyer SC, Lundberg P et al. JAK2 exon 12 mutant mice display isolated erythrocytosis and changes in iron metabolism favoring increased erythropoiesis. Blood 2016; 128: 839–851.
Verstovsek S, Mesa RA, Gotlib J, Levy RS, Gupta V, DiPersio JF et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 799–807.
Harrison C, Kiladjian JJ, Al-Ali HK, Gisslinger H, Waltzman R, Stalbovskaya V et al. JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 787–798.
Lu X, Huang LJ, Lodish HF . Dimerization by a cytokine receptor is necessary for constitutive activation of JAK2V617F. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 5258–5266.
Lu X, Levine R, Tong W, Wernig G, Pikman Y, Zarnegar S et al. Expression of a homodimeric type I cytokine receptor is required for JAK2V617F-mediated transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 18962–18967.
Pradhan A, Lambert QT, Griner LN, Reuther GW . Activation of JAK2-V617F by components of heterodimeric cytokine receptors. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 16651–16663.
Staerk J, Kallin A, Demoulin JB, Vainchenker W, Constantinescu SN . JAK1 and Tyk2 activation by the homologous polycythemia vera JAK2 V617F mutation: cross-talk with IGF1 receptor. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 41893–41899.
Bercovich D, Ganmore I, Scott LM, Wainreb G, Birger Y, Elimelech A et al. Mutations of JAK2 in acute lymphoblastic leukaemias associated with Down's syndrome. Lancet 2008; 372: 1484–1492.
Malinge S, Ben-Abdelali R, Settegrana C, Radford-Weiss I, Debre M, Beldjord K et al. Novel activating JAK2 mutation in a patient with Down syndrome and B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2007; 109: 2202–2204.
Zhao L, Dong H, Zhang CC, Kinch L, Osawa M, Iacovino M et al. A JAK2 interdomain linker relays Epo receptor engagement signals to kinase activation. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 26988–26998.
Kiel MJ, Yilmaz OH, Iwashita T, Terhorst C, Morrison SJ . SLAM family receptors distinguish hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and reveal endothelial niches for stem cells. Cell 2005; 121: 1109–1121.
Akashi K, Traver D, Miyamoto T, Weissman IL . A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature 2000; 404: 193–197.
Liu Y, Pop R, Sadegh C, Brugnara C, Haase VH, Socolovsky M . Suppression of Fas-FasL coexpression by erythropoietin mediates erythroblast expansion during the erythropoietic stress response in vivo. Blood 2006; 108: 123–133.
Sulahian R, Cleaver O, Huang LJ . Ligand-induced EpoR internalization is mediated by JAK2 and p85 and is impaired by mutations responsible for primary familial and congenital polycythemia. Blood 2009; 113: 5287–5297.
Li J, Kent DG, Chen E, Green AR . Mouse models of myeloproliferative neoplasms: JAK of all grades. Dis Model Mech 2011; 4: 311–317.
Skoda RC . Less Jak2 makes more platelets. Blood 2014; 124: 2168–2169.
Koulnis M, Porpiglia E, Hidalgo D, Socolovsky M . Erythropoiesis: from molecular pathways to system properties. Adv Exp Med Biol 2014; 844: 37–58.
Koury MJ, Bondurant MC . Erythropoietin retards DNA breakdown and prevents programmed death in erythroid progenitor cells. Science 1990; 248: 378–381.
Panopoulos AD, Watowich SS . Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: molecular mechanisms of action during steady state and 'emergency' hematopoiesis. Cytokine 2008; 42: 277–288.
Richards MK, Liu F, Iwasaki H, Akashi K, Link DC . Pivotal role of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in the development of progenitors in the common myeloid pathway. Blood 2003; 102: 3562–3568.
Funakoshi-Tago M, Pelletier S, Matsuda T, Parganas E, Ihle JN . Receptor specific downregulation of cytokine signaling by autophosphorylation in the FERM domain of Jak2. EMBO J 2006; 25: 4763–4772.
Funakoshi-Tago M, Pelletier S, Moritake H, Parganas E, Ihle JN . Jak2 FERM domain interaction with the erythropoietin receptor regulates Jak2 kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 1792–1801.
Nelson EA, Sharma SV, Settleman J, Frank DA . A chemical biology approach to developing STAT inhibitors: molecular strategies for accelerating clinical translation. Oncotarget 2011; 2: 518–524.
Zhang J, Socolovsky M, Gross AW, Lodish HF . Role of Ras signaling in erythroid differentiation of mouse fetal liver cells: functional analysis by a flow cytometry-based novel culture system. Blood 2003; 102: 3938–3946.
Scott LM . The JAK2 exon 12 mutations: a comprehensive review. Am J Hematol 2011; 86: 668–676.
Scott LM, Scott MA, Campbell PJ, Green AR . Progenitors homozygous for the V617F mutation occur in most patients with polycythemia vera, but not essential thrombocythemia. Blood 2006; 108: 2435–2437.
Kilpivaara O, Levine RL . JAK2 and MPL mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms: discovery and science. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1813–1817.
Chen E, Beer PA, Godfrey AL, Ortmann CA, Li J, Costa-Pereira AP et al. Distinct clinical phenotypes associated with JAK2V617F reflect differential STAT1 signaling. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 524–535.
Walz C, Ahmed W, Lazarides K, Betancur M, Patel N, Hennighausen L et al. Essential role for Stat5a/b in myeloproliferative neoplasms induced by BCR-ABL1 and JAK2(V617F) in mice. Blood 2012; 119: 3550–3560.
Yan D, Hutchison RE, Mohi G . Critical requirement for Stat5 in a mouse model of polycythemia vera. Blood 2012; 119: 3539–3549.
Choong ML, Pecquet C, Pendharkar V, Diaconu CC, Yong JW, Tai SJ et al. Combination treatment for myeloproliferative neoplasms using JAK and pan-class I PI3K inhibitors. J Cell Mol Med 2013; 17: 1397–1409.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Emery Bresnick, Saghi Ghaffari, Peter Michaely, Sandy Schmid, Jim Palis, Kathleen McGrath, Jian Xu, Srdan Verstovsek, Yumin Shen, Siayareh Rambally and Cheryl Lewis for helpful discussions and input. This study was supported by funding from the National Institute of Health (HL089966), Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT, RP110090) and the Ladies Leukemia League to LJ-SH, from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81200379) to ZH and a post-doctoral training grant from CPRIT to HY.
Author contributions
HY, YM, ZH, LZ, M-CH and LJ-SH designed and performed research, and analyzed data. SAM analyzed data. HY and LJ-SH wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, H., Ma, Y., Hong, Z. et al. Activating JAK2 mutants reveal cytokine receptor coupling differences that impact outcomes in myeloproliferative neoplasm. Leukemia 31, 2122–2131 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.1
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Long-term follow-up of JAK2 exon 12 polycythemia vera: a French Intergroup of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (FIM) study
Leukemia (2021)
-
The role of driver mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms: insights from mouse models
International Journal of Hematology (2020)
-
Philadelphia-Negative Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Laboratory Workup in the Era of Next-Generation Sequencing
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2019)
-
A natural compound derivative P-13 inhibits STAT3 signaling by covalently inhibiting Janus kinase 2
Investigational New Drugs (2019)