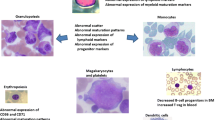
Abstract
Definite progress has been made in the exploration of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) by flow cytometry (FCM) since the publication of the World Health Organization 2008 classification of myeloid neoplasms. An international working party initiated within the European LeukemiaNet and extended to include members from Australia, Canada, Japan, Taiwan and the United States has, through several workshops, developed and subsequently published consensus recommendations. The latter deal with preanalytical precautions, and propose small and large panels, which allow evaluating immunophenotypic anomalies and calculating myelodysplasia scores. The current paper provides guidelines that strongly recommend the integration of FCM data with other diagnostic tools in the diagnostic work-up of MDS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kern W, Haferlach C, Schnittger S, Haferlach T . Clinical utility of multiparameter flow cytometry in the diagnosis of 1013 patients with suspected myelodysplastic syndrome: correlation to cytomorphology, cytogenetics, and clinical data. Cancer 2010; 116: 4549–4563.
van de Loosdrecht AA, Westers TM, Westra AH, Drager AM, van der Velden VH, Ossenkoppele GJ . Identification of distinct prognostic subgroups in low- and intermediate-1-risk myelodysplastic syndromes by flow cytometry. Blood 2008; 111: 1067–1077.
Oka S, Muroi K, Fujiwara S, Oh I, Matsuyama T, Ohmine K et al. Prediction of progression from refractory cytopenia with unilineage dysplasia by analysis of bone marrow blast cell composition. J Clin Exp Hematop 2012; 52: 63–66.
Della Porta MG, Lanza F, Del VL . Flow cytometry immunophenotyping for the evaluation of bone marrow dysplasia. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2011; 80: 201–211.
Chopra A, Pati H, Mahapatra M, Mishra P, Seth T, Kumar S et al. Flow cytometry in myelodysplastic syndrome: analysis of diagnostic utility using maturation pattern-based and quantitative approaches. Ann Hematol 2012; 91: 1351–1362.
Chung JW, Park CJ, Cha CH, Cho YU, Jang S, Chi HS et al. A combination of CD15/CD10, CD64/CD33, CD16/CD13 or CD11b flow cytometric granulocyte panels is sensitive and specific for diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome. Ann Clin Lab Sci 2012; 42: 271–280.
Matarraz S, Lopez A, Barrena S, Fernandez C, Jensen E, Flores-Montero J et al. Bone marrow cells from myelodysplastic syndromes show altered immunophenotypic profiles that may contribute to the diagnosis and prognostic stratification of the disease: a pilot study on a series of 56 patients. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2010; 78: 154–168.
Truong F, Smith BR, Stachurski D, Cerny J, Medeiros LJ, Woda BA et al. The utility of flow cytometric immunophenotyping in cytopenic patients with a non-diagnostic bone marrow: a prospective study. Leuk Res 2009; 33: 1039–1046.
Ogata K, Della Porta MG, Malcovati L, Picone C, Yokose N, Matsuda A et al. Diagnostic utility of flow cytometry in low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes: a prospective validation study. Haematologica 2009; 94: 1066–1074.
Westers TM, Alhan C, Chamuleau ME, van der Vorst MJ, Eeltink C, Ossenkoppele GJ et al. Aberrant immunophenotype of blasts in myelodysplastic syndromes is a clinically relevant biomarker in predicting response to growth factor treatment. Blood 2010; 115: 1779–1784.
Westers TM, van der Velden VH, Alhan C, Bekkema R, Bijkerk A, Brooimans RA et al. Implementation of flow cytometry in the diagnostic work-up of myelodysplastic syndromes in a multicenter approach: report from the Dutch Working Party on Flow Cytometry in MDS. Leuk Res 2012; 36: 422–430.
Falco P, Levis A, Stacchini A, Ciriello MM, Geuna M, Notari P et al. Prognostic relevance of cytometric quantitative assessment in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Eur J Haematol 2011; 87: 409–418.
Chu SC, Wang TF, Li CC, Kao RH, Li DK, Su YC et al. Flow cytometric scoring system as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res 2011; 35: 868–873.
Xu F, Guo J, Wu LY, He Q, Zhang Z, Chang CK et al. Diagnostic application and clinical significance of FCM progress scoring system based on immunophenotyping in CD34+ blasts in myelodysplastic syndromes. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2013; 84: 267–278.
Burbury KL, Westerman DA . Role of flow cytometry in myelodysplastic syndromes: diagnosis, classification, prognosis and response assessment. Leuk Lymphoma 2014; 55: 749–760.
van Dongen JJ, Lhermitte L, Bottcher S, Almeida J, van der Velden VH, Flores-Montero J et al. EuroFlow antibody panels for standardized n-dimensional flow cytometric immunophenotyping of normal, reactive and malignant leukocytes. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1908–1975.
Arenillas L, Mallo M, Ramos F, Guinta K, Barragan E, Lumbreras E et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism array karyotyping: a diagnostic and prognostic tool in myelodysplastic syndromes with unsuccessful conventional cytogenetic testing. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013; 52: 1167–1177.
Otrock ZK, Tiu RV, Maciejewski JP, Sekeres MA . The need for additional genetic markers for myelodysplastic syndrome stratification: what does the future hold for prognostication? Expert Rev Hematol 2013; 6: 59–68.
Haferlach T, Nagata Y, Grossmann V, Okuno Y, Bacher U, Nagae G et al. Landscape of genetic lesions in 944 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2014; 28: 241–247.
Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Malcovati L, Tauro S, Gundem G, Van LP et al. Clinical and biological implications of driver mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2013; 122: 3616–3627.
Bene MC . Immunophenotyping of myelodysplasia. Haematologica 2003; 88: 363.
Porwit A . Role of flow cytometry in diagnostics of myelodysplastic syndromes–beyond the WHO 2008 classification. Semin Diagn Pathol 2011; 28: 273–282.
van de Loosdrecht AA, Westers TM . Cutting edge: flow cytometry in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2013; 11: 892–902.
Valent P, Horny HP, Bennett JM, Fonatsch C, Germing U, Greenberg P et al. Definitions and standards in the diagnosis and treatment of the myelodysplastic syndromes: consensus statements and report from a working conference. Leuk Res 2007; 31: 727–736.
Brunning R, Orazi A, Germing U, Le Beau M, Porwit A, Baumann I et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes/neoplasms, overview. In: Swerdlow S, Campo E, Harris NL, affe E, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissue.. Lyon: WHI, 2008; pp 88–93.
Malcovati L, Hellstrom-Lindberg E, Bowen D, Ades L, Cermak J, del CC et al. Diagnosis and treatment of primary myelodysplastic syndromes in adults: recommendations from the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2013; 122: 2943–2964.
van de Loosdrecht AA, Alhan C, Bene MC, Della Porta MG, Drager AM, Feuillard J et al. Standardization of flow cytometry in myelodysplastic syndromes: report from the first European LeukemiaNet working conference on flow cytometry in myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 2009; 94: 1124–1134.
Westers TM, Ireland R, Kern W, Alhan C, Balleisen JS, Bettelheim P et al. Standardization of flow cytometry in myelodysplastic syndromes: a report from an international consortium and the European LeukemiaNet Working Group. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1730–1741.
Greenberg PL, Attar E, Bennett JM, Bloomfield CD, De Castro CM, Deeg HJ et al. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: myelodysplastic syndromes. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2011; 9: 30–56.
Greenberg PL, Attar E, Bennett JM, Bloomfield CD, Borate U, De Castro CM et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes: clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2013; 11: 838–874.
Garcia-Manero G . Myelodysplastic syndromes: 2014 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 2014; 89: 97–108.
van de Loosdrecht AA, Ireland R, Kern W, Della Porta MG, Alhan C, Balleisen JS et al. Rationale for the clinical application of flow cytometry in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes: position paper of an International Consortium and the European LeukemiaNet Working Group. Leuk Lymphoma 2013; 54: 472–475.
Della Porta MG, Picone C, Pascutto C, Malcovati L, Tamura H, Handa H et al. Multicenter validation of a reproducible flow cytometric score for the diagnosis of low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes: results of a European LeukemiaNET study. Haematologica 2012; 97: 1209–1217.
Wood B, Jevremovic D, Béné MC, Yan M, Jacobs P, Litwin V . ICSH/ICCS Working Group. Validation of cell-based fluorescence assays: practice guidelines from the ICSH and ICCS - part V - assay performance criteria. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2013; 84: 315–323.
Aalbers AM, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM, de H V, Te Marvelde JG, de Jong AX, van der Burg M et al. Applicability of a reproducible flow cytometry scoring system in the diagnosis of refractory cytopenia of childhood. Leukemia 2013; 27: 1923–1925.
Kussick SJ, Fromm JR, Rossini A, Li Y, Chang A, Norwood TH et al. Four-color flow cytometry shows strong concordance with bone marrow morphology and cytogenetics in the evaluation for myelodysplasia. Am J Clin Pathol 2005; 124: 170–181.
Kern W, Bacher U, Schnittger S, Alpermann T, Haferlach C, Haferlach T . Multiparameter flow cytometry reveals myelodysplasia-related aberrant antigen expression in myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2013; 84: 194–197.
Della Porta MG, Alessandrino EP, Bacigalupo A, van Lint MT, Malcovati L, Pascutto C et al. Predictive factors for the outcome of allogeneic transplantation in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome stratified according to the revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R). Blood 2014; 123: 2333–2342.
Wells DA, Benesch M, Loken MR, Vallejo C, Myerson D, Leisenring WM et al. Myeloid and monocytic dyspoiesis as determined by flow cytometric scoring in myelodysplastic syndrome correlates with the IPSS and with outcome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2003; 102: 394–403.
Xu F, Li X, Wu L, He Q, Zhang Z, Chang C . Flow cytometric scoring system (FCMSS) assisted diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and the biological significance of FCMSS-based immunophenotypes. Br J Haematol 2010; 149: 587–597.
Ogata K, Kishikawa Y, Satoh C, Tamura H, Dan K, Hayashi A . Diagnostic application of flow cytometric characteristics of CD34+ cells in low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2006; 108: 1037–1044.
Stetler-Stevenson M, Arthur DC, Jabbour N, Xie XY, Molldrem J, Barrett AJ et al. Diagnostic utility of flow cytometric immunophenotyping in myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2001; 98: 979–987.
Schanz J, Steidl C, Fonatsch C, Pfeilstocker M, Nosslinger T, Tuechler H et al. Coalesced multicentric analysis of 2,351 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes indicates an underestimation of poor-risk cytogenetics of myelodysplastic syndromes in the international prognostic scoring system. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 1963–1970.
Gupta R, Soupir CP, Johari V, Hasserjian RP . Myelodysplastic syndrome with isolated deletion of chromosome 20q: an indolent disease with minimal morphological dysplasia and frequent thrombocytopenic presentation. Br J Haematol 2007; 139: 265–268.
Rashidi HH, Xu X, Wang HY, Shafi NQ, Rameshkumar K, Messer K et al. Utility of peripheral blood flow cytometry in differentiating low grade versus high grade myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and in the evaluation of cytopenias. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2012; 5: 224–230.
Ogata K, Kakumoto K, Matsuda A, Tohyama K, Tamura H, Ueda Y et al. Differences in blast immunophenotypes among disease types in myelodysplastic syndromes: a multicenter validation study. Leuk Res 2012; 36: 1229–1236.
Sandes AF, Kerbauy DM, Matarraz S, Chauffaille ML, Lopez A, Orfao A et al. Combined flow cytometric assessment of CD45, HLA-DR, CD34, and CD117 expression is a useful approach for reliable quantification of blast cells in myelodysplastic syndromes. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2013; 84: 157–166.
Matarraz S, Lopez A, Barrena S, Fernandez C, Jensen E, Flores J et al. The immunophenotype of different immature, myeloid and B-cell lineage-committed CD34+ hematopoietic cells allows discrimination between normal/reactive and myelodysplastic syndrome precursors. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1175–1183.
De SD, Trullemans F, Jochmans K, Renmans W, Smet L, Heylen O et al. Diagnostic potential of CD34+ cell antigen expression in myelodysplastic syndromes. Am J Clin Pathol 2012; 138: 732–743.
Monreal MB, Pardo ML, Pavlovsky MA, Fernandez I, Corrado CS, Giere I et al. Increased immature hematopoietic progenitor cells CD34+/CD38dim in myelodysplasia. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2006; 70: 63–70.
Greenberg PL, Tuechler H, Schanz J, Sanz G, Garcia-Manero G, Sole F et al. Revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2012; 120: 2454–2465.
Sandes AF, Yamamoto M, Matarraz S, Chauffaille ML, Quijano S, Lopez A et al. Altered immunophenotypic features of peripheral blood platelets in myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 2012; 97: 895–902.
Xu F, Wu L, He Q, Zhang Z, Chang C, Li X . Immunophenotypic analysis of erythroid dysplasia and its diagnostic application in myelodysplastic syndromes. Intern Med J 2012; 42: 401–411.
Mathis S, Chapuis N, Debord C, Rouquette A, Radford-Weiss I, Park S et al. Flow cytometric detection of dyserythropoiesis: a sensitive and powerful diagnostic tool for myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2013; 27: 1981–1987.
Della Porta MG, Malcovati L, Invernizzi R, Travaglino E, Pascutto C, Maffioli M et al. Flow cytometry evaluation of erythroid dysplasia in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 2006; 20: 549–555.
Krasselt M, Baerwald C, Wagner U, Rossol M . CD56+ monocytes have a dysregulated cytokine response to lipopolysaccharide and accumulate in rheumatoid arthritis and immunosenescence. Arthritis Res Ther 2013; 15: R139.
Veltroni M, Sainati L, Zecca M, Fenu S, Tridello G, Testi AM et al. Advanced pediatric myelodysplastic syndromes: can immunophenotypic characterization of blast cells be a diagnostic and prognostic tool? Pediatr Blood Cancer 2009; 52: 357–363.
Niemeyer CM, Baumann I . Classification of childhood aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2011; 2011: 84–89.
Hellstrom-Lindberg E, van de Loosdrecht A . Erythropoiesis stimulating agents and other growth factors in low-risk MDS. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013; 26: 401–410.
Alhan C, Westers TM, van der Helm LH, Eeltink C, Huls G, Witte BI et al. Absence of aberrant myeloid progenitors by flow cytometry is associated with favorable response to azacitidine in higher risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2014; 86: 207–215.
Hrusak O, Porwit-MacDonald A . Antigen expression patterns reflecting genotype of acute leukemias. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1233–1258.
Arnoulet C, Béné MC, Durrieu F, Feuillard J, Fossat C, Husson B et al. Four- and five-color flow cytometry analysis of leukocyte differentiation pathways in normal bone marrow: a reference document based on a systematic approach by the GTLLF and GEIL. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2010; 78: 4–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porwit, A., van de Loosdrecht, A., Bettelheim, P. et al. Revisiting guidelines for integration of flow cytometry results in the WHO classification of myelodysplastic syndromes—proposal from the International/European LeukemiaNet Working Group for Flow Cytometry in MDS. Leukemia 28, 1793–1798 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.191
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.191
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Diagnostik bei unklaren Zytopenien – wie und wann suchen wir nach klonaler Hämatopoese?
Die Innere Medizin (2022)
-
Monitoring treatment with 5-Azacitidine by flow cytometry predicts duration of hematological response in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome
Annals of Hematology (2021)
-
Enumeration of CD34+ blasts by immunohistochemistry in bone marrow biopsies from MDS patients may have significant impact on final WHO classification
Journal of Hematopathology (2020)
-
A pilot study on the usefulness of peripheral blood flow cytometry for the diagnosis of lower risk myelodysplastic syndromes: the “MDS thermometer”
BMC Hematology (2018)
-
Diagnostic algorithm for lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes
Leukemia (2018)