Abstract
Background/Objective:
Puberty is a period defined by large changes in adipose tissue accumulation and distribution; however, longitudinal patterns of ectopic fat development have not been shown. We have previously shown significant declines in beta-cell function (BCF) across puberty and hypothesize that accumulation of ectopic fat deposition, particularly hepatic fat, will predict this fall.
Subject/Methods:
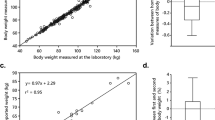
We conducted a longitudinal study and examined 2-year change in abdominal fat distribution and type 2 diabetes risk markers in 76 Hispanic children and young adults (16.1±0.5 years, 66% obese, 52% male, 51% post-pubertal). Subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue (SAAT), visceral adipose tissue (VAT), hepatic fat fraction (HFF) and pancreatic fat fraction (PFF) were measured by 3-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging, and markers of type 2 diabetes risk were collected at fasting and during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
Results:
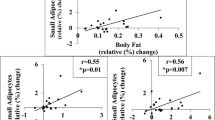
Baseline pubertal status significantly moderated the 2-year change in ectopic fat deposition, such that VAT, HFF and PFF increased in individuals during late and post-pubertal growth, whereas children earlier in their pubertal development decreased ectopic accumulation and had less VAT accumulation (VAT: pTanner*time=0.044, 0.31±0.08 l vs 0.03±0.10 l; HFF: pTanner*time=0.007, 1.34±0.87% vs −2.61±1.11%; PFF: pTanner*time<0.001, 1.61±0.39% vs −0.96±0.50%). Independent of pubertal status, the 2-year increase in HFF and VAT significantly associated with a decline in BCF (ß=−1.04, P=0.038; ß=−1.81, P=0.020) and metabolic function, while accumulation of SAAT significantly associated with BCF (ß=1.36, P=0.012) and metabolic improvement. HFF accumulation was the only depot to significantly predict clinical markers of type 2 diabetes risk, fasting glucose and HbA1c, and circulating free fatty acid levels (ß=1.00, P=0.034; ß=1.00, P=0.015; ß=01.01, P=0.024).
Conclusions:
The accumulation of SAAT defends against type 2 diabetes risk and potentially ectopic fat accumulation. Intra-abdominal VAT and HFF accumulation both associate with metabolic decline and BCF, while HFF predicts an even greater number of metabolic risk features.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knittle JL, Timmers K, Ginsberg-Fellner F, Brown RE, Katz DP . The growth of adipose tissue in children and adolescents. Cross-sectional and longitudinal studies of adipose cell number and size. J Clin Invest 1979; 63: 239–246.
Landgraf K, Rockstroh D, Wagner IV, Weise S, Tauscher R, Schwartze JT et al. Evidence of early alterations in adipose tissue biology and function and its association with obesity-related inflammation and insulin resistance in children. Diabetes 2015; 64: 1249–1261.
Taylor RW, Grant AM, Williams SM, Goulding A . Sex differences in regional body fat distribution from pre- to postpuberty. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2010; 18: 1410–1416.
Goulding A, Taylor RW, Gold E, Lewis-Barned NJ . Regional body fat distribution in relation to pubertal stage: a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry study of New Zealand girls and young women. Am J Clin Nutr 1996; 64: 546–551.
Roemmich JN, Rogol AD . Hormonal changes during puberty and their relationship to fat distribution. Am J Hum Biol 1999; 11: 209–224.
Huang TT, Johnson MS, Figueroa-Colon R, Dwyer JH, Goran MI . Growth of visceral fat, subcutaneous abdominal fat, and total body fat in children. Obes Res 2001; 9: 283–289.
Johnson MS, Figueroa-Colon R, Huang TT, Dwyer JH, Goran MI . Longitudinal changes in body fat in African American and Caucasian children: influence of fasting insulin and insulin sensitivity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 3182–3187.
Huang TT-K, Johnson MS, Gower BA, Goran MI . Effect of changes in fat distribution on the rates of change of insulin response in children. Obes Res 2002; 10: 978–984.
Ball GD, Huang TT, Gower BA, Cruz ML, Shaibi GQ, Weigensberg MJ et al. Longitudinal changes in insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion, and beta-cell function during puberty. J Pediatr 2006; 148: 16–22.
Goran MI, Shaibi GQ, Weigensberg MJ, Davis JN, Cruz ML . Deterioration of insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in overweight Hispanic children during pubertal transition: a longitudinal assessment. Int J Pediatr Obes 2006; 1: 139–145.
Goran MI, Lane C, Toledo-Corral C, Weigensberg MJ . Persistence of pre-diabetes in overweight and obese Hispanic children: association with progressive insulin resistance, poor beta-cell function, and increasing visceral fat. Diabetes 2008; 57: 3007–3012.
Toledo-Corral CM, Alderete TL, Hu HH, Nayak K, Esplana S, Liu T et al. Ectopic fat deposition in prediabetic overweight and obese minority adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013; 98: 1115–1121.
Pratley RE, Weyer C . The role of impaired early insulin secretion in the pathogenesis of Type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2001; 44: 929–945.
Kelly LA, Lane CJ, Weigensberg MJ, Toledo-Corral CM, Goran MI . Pubertal changes of insulin sensitivity, acute insulin response, and β-cell function in overweight Latino youth. The Journal of Pediatrics 2011; 158: 442–446.
Ravussin E, Smith SR . Increased fat intake, impaired fat oxidation, and failure of fat cell proliferation result in ectopic fat storage, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2002; 967: 363–378.
McQuaid SE, Hodson L, Neville MJ, Dennis AL, Cheeseman J, Humphreys SM et al. Downregulation of adipose tissue fatty acid trafficking in obesity: a driver for ectopic fat deposition? Diabetes 2011; 60: 47–55.
Alderete TL, Toledo-Corral CM, Desai P, Weigensberg MJ, Goran MI . Liver fat has a stronger association with risk factors for type 2 diabetes in African-American compared with Hispanic adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013; 98: 3748–3754.
Fabbrini E, Magkos F, Mohammed BS, Pietka T, Abumrad NA, Patterson BW et al. Intrahepatic fat, not visceral fat, is linked with metabolic complications of obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 15430–15435.
D'Adamo E, Cali AM, Weiss R, Santoro N, Pierpont B, Northrup V et al. Central role of fatty liver in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in obese adolescents. Diabetes Care 2010; 33: 1817–1822.
Kim JS, Lê K-A, Mahurkar S, Davis JN, Goran MI . Influence of elevated liver fat on circulating adipocytokines and insulin resistance in obese Hispanic adolescents. Pediatr Obes 2012; 7: 158–164.
Wicklow BA, Wittmeier KD, MacIntosh AC, Sellers EA, Ryner L, Serrai H et al. Metabolic consequences of hepatic steatosis in overweight and obese adolescents. Diabetes Care 2012; 35: 905–910.
Toledo-Corral CM, Vargas LG, Goran MI, Weigensberg MJ . Hemoglobin A1c above threshold level is associated with decreased β-cell function in overweight Latino youth. J Pediatr 2012; 160: 751–756.
Toledo-Corral CM, Alderete TL, Richey J, Sequeira P, Goran MI, Weigensberg MJ . Fasting, post-OGTT challenge, and nocturnal free fatty acids in prediabetic versus normal glucose tolerant overweight and obese Latino adolescents. Acta Diabetol 2015; 52: 277–284.
Hu HH, Nayak KS, Goran MI . Assessment of abdominal adipose tissue and organ fat content by magnetic resonance imaging. Obes Rev 2011; 12: e504–e515.
Hu HH, Kim H-W, Nayak KS, Goran MI . Comparison of fat-water MRI and single-voxel MRS in the assessment of hepatic and pancreatic fat fractions in humans. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2010; 18: 841–847.
Alabousi A, Al-Attar S, Joy TR, Hegele RA, McKenzie CA . Evaluation of adipose tissue volume quantification with IDEAL fat-water separation. J Magn Reson Imaging 2011; 34: 474–479.
Reeder SB, Cruite I, Hamilton G, Sirlin CB . Quantitative assessment of liver fat with magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. J Magn Reson Imaging 2011; 34: 729–749.
Marshal WA, Tanner JM . Variations in the pattern of pubertal changes in boys. Arch Dis Child 1970; 45: 13–23.
Matsuda M, DeFronzo RA . Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 1999; 22: 1462–1470.
DeFronzo RA, Matsuda M . Reduced time points to calculate the composite index. Diabetes Care 2010; 33: e93.
Diggle P, Heagerty P, Liang K-Y, Zeger S . Analysis of Longitudinal Data. Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002.
Martin AD, Daniel MZ, Drinkwater DT, Clarys JP . Adipose tissue density, estimated adipose lipid fraction and whole body adiposity in male cadavers. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1994; 18: 79–83.
Rosenbaum M, Presta E, Hirsch J, Leibel RL . Regional differences in adrenoreceptor status of adipose tissue in adults and prepubertal children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1991; 73: 341–347.
Khan T, Muise ES, Iyengar P, Wang ZV, Chandalia M, Abate N et al. Metabolic dysregulation and adipose tissue fibrosis: role of collagen VI. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 1575–1591.
Perseghin G . Viewpoints on the way to a consensus session: where does insulin resistance start? The liver. Diabetes Care 2009; 32 (Suppl 2): S164–S167.
Boden G, Shulman GI . Free fatty acids in obesity and type 2 diabetes: defining their role in the development of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction. Eur J Clin Invest 2002; 32 (Suppl 3): 14–23.
Kantartzis K, Machann J, Schick F, Fritsche A, Häring H-U, Stefan N . The impact of liver fat vs visceral fat in determining categories of prediabetes. Diabetologia 2010; 53: 882–889.
Kahn SE . Clinical review 135: The importance of beta-cell failure in the development and progression of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 4047–4058.
Virtue S, Vidal-Puig A . Adipose tissue expandability, lipotoxicity and the Metabolic Syndrome—an allostatic perspective. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1801: 338–349.
Fabbrini E, Tamboli RA, Magkos F, Marks-Shulman PA, Eckhauser AW, Richards WO et al. Surgical removal of omental fat does not improve insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular risk factors in obese adults. Gastroenterology 2010; 139: 448–455.
Stefan N, Häring HU . The role of hepatokines in metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2013; 9: 144–152.
Stefan N, Sun Q, Fritsche A, Machann J, Schick F, Gerst F et al. Impact of the adipokine adiponectin and the hepatokine fetuin-A on the development of type 2 diabetes: prospective cohort- and cross-sectional phenotyping studies. PLoS One 2014; 9: e92238.
Linder K, Springer F, Machann J, Schick F, Fritsche A, Häring HU et al. Relationships of body composition and liver fat content with insulin resistance in obesity-matched adolescents and adults. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2014; 22: 1325–1331.
Acknowledgements
The project described was supported by Grant Number R01DK059211 from the National Institute of Diabetes And Digestive And Kidney Diseases. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute of Diabetes And Digestive And Kidney Diseases or the National Institutes of Health. We would like to thank all the Childhood Obesity Research Core (CORC) research team, as well as the nursing staff at the CTU. In addition, we are grateful for our study participants and their families for their involvement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gyllenhammer, L., Alderete, T., Toledo-Corral, C. et al. Saturation of subcutaneous adipose tissue expansion and accumulation of ectopic fat associated with metabolic dysfunction during late and post-pubertal growth. Int J Obes 40, 601–606 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.207
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.207
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Visceral adiposity and respiratory outcomes in children and adults: a systematic review
International Journal of Obesity (2022)
-
Pediatric obesity-related non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: waist-to-height ratio best anthropometrical predictor
Pediatric Research (2021)
-
Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and primary hypertension
Pediatric Nephrology (2021)
-
Performance of anthropometric indicators as predictors of metabolic syndrome in Brazilian adolescents
BMC Pediatrics (2018)
-
Liver volume and hepatic adiposity in childhood: relations to body growth and visceral fat
International Journal of Obesity (2018)