Abstract
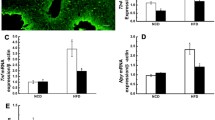
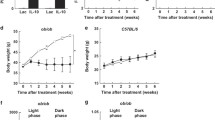
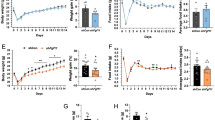
Leptin targets specific receptors (OB-R) expressed in the hypothalamus to regulate energy balance. Leptin decreases food intake in normal weight individuals, but this effect is blunted in obese subjects who are characterized by a state of leptin resistance. The prevention of leptin resistance is one of the major goals of obesity research. Recently, we identified endospanin 1 as a negative regulator of OB-R, which by interacting with OB-R retains the receptor inside the cell. We show here that in obese mice endospanin 1 is upregulated in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (ARC), the major brain structure involved in body weight regulation, suggesting that endospanin 1 is implicated in obesity development and/or the installation of leptin resistance. In contrast, silencing of endospanin 1 with lentiviral vectors in the ARC of obese mice fully restores leptin responsiveness when combined with a switch to ad libitum fed chow diet. The recovery of central leptin sensitivity is accompanied by sustained body weight loss and amelioration of blood lipid parameters and steatosis. Collectively, our results define endospanin 1 as a novel therapeutic target against obesity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bates SH, Stearns WH, Dundon TA, Schubert M, Tso AW, Wang Y et al. STAT3 signalling is required for leptin regulation of energy balance but not reproduction. Nature 2003; 421: 856–859.
Buettner C, Pocai A, Muse ED, Etgen AM, Myers MG Jr, Rossetti L . Critical role of STAT3 in leptin's metabolic actions. Cell Metab 2006; 4: 49–60.
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM . Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994; 372: 425–432.
Tartaglia LA, Dembski M, Weng X, Deng N, Culpepper J, Devos R et al. Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell 1995; 83: 1263–1271.
Myers MG, Cowley MA, Munzberg H . Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 2008; 70: 537–556.
Bjorbaek C . Central leptin receptor action and resistance in obesity. J Invest Med 2009; 57: 789–794.
St-Pierre J, Tremblay ML . Modulation of leptin resistance by protein tyrosine phosphatases. Cell Metab 2012; 15: 292–297.
Ozcan L, Ergin AS, Lu A, Chung J, Sarkar S, Nie D et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays a central role in development of leptin resistance. Cell Metab 2009; 9: 35–51.
Hosoi T, Yamaguchi R, Noji K, Matsuo S, Baba S, Toyoda K et al. Flurbiprofen ameliorated obesity by attenuating leptin resistance induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. EMBO Mol Med 2014; 6: 335–346.
Adam CL, Findlay PA . Decreased blood-brain leptin transfer in an ovine model of obesity and weight loss: resolving the cause of leptin resistance. Int J Obes 2010; 34: 980–988.
Balland E, Dam J, Langlet F, Caron E, Steculorum S, Messina A et al. Hypothalamic tanycytes are an ERK-gated conduit for leptin into the brain. Cell Metab 2014; 19: 293–301.
Diano S, Kalra SP, Horvath TL . Leptin receptor immunoreactivity is associated with the Golgi apparatus of hypothalamic neurons and glial cells. J Neuroendocrinol 1998; 10: 647–650.
Belouzard S, Delcroix D, Rouille Y . Low levels of expression of leptin receptor at the cell surface result from constitutive endocytosis and intracellular retention in the biosynthetic pathway. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 28499–28508.
Seron K, Couturier C, Belouzard S, Bacart J, Monte D, Corset L et al. Endospanins regulate a postinternalization step of the leptin receptor endocytic pathway. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 17968–17981.
Couturier C, Sarkis C, Seron K, Belouzard S, Chen P, Lenain A et al. Silencing of OB-RGRP in mouse hypothalamic arcuate nucleus increases leptin receptor signaling and prevents diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acadb Sci USA 2007; 104: 19476–19481.
Bailleul B, Akerblom I, Strosberg AD . The leptin receptor promoter controls expression of a second distinct protein. Nucleic Acids Res 1997; 25: 2752–2758.
Vauthier V, Jaillard S, Journel H, Dubourg C, Jockers R, Dam J . Homozygous deletion of an 80 kb region comprising part of DNAJC6 and LEPR genes on chromosome 1P31.3 is associated with early onset obesity, mental retardation and epilepsy. Mol Genet Metab 2012; 106: 345–350.
Tung YC, Ma M, Piper S, Coll A, O'Rahilly S, Yeo GS . Novel leptin-regulated genes revealed by transcriptional profiling of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 12419–12426.
Shi H, Akunuru S, Bierman JC, Hodge KM, Mitchell MC, Foster MT et al. Diet-induced obese mice are leptin insufficient after weight reduction. Obesity 2009; 17: 1702–1709.
Munzberg H, Flier JS, Bjorbaek C . Region-specific leptin resistance within the hypothalamus of diet-induced obese mice. Endocrinology 2004; 145: 4880–4889.
Guo J, Jou W, Gavrilova O, Hall KD . Persistent diet-induced obesity in male C57BL/6 mice resulting from temporary obesigenic diets. PLoS One 2009; 4: e5370.
Enriori PJ, Evans AE, Sinnayah P, Jobst EE, Tonelli-Lemos L, Billes SK et al. Diet-induced obesity causes severe but reversible leptin resistance in arcuate melanocortin neurons. Cell Metab 2007; 5: 181–194.
Wadden TA, Sternberg JA, Letizia KA, Stunkard AJ, Foster GD . Treatment of obesity by very low calorie diet, behavior therapy, and their combination: a five-year perspective. Int J Obes 1989; 13: 39–46.
Safer DJ . Diet, behavior modification, and exercise: a review of obesity treatments from a long-term perspective. South Med J 1991; 84: 1470–1474.
Rosenbaum M, Sy M, Pavlovich K, Leibel RL, Hirsch J . Leptin reverses weight loss-induced changes in regional neural activity responses to visual food stimuli. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 2583–2591.
Levin BE, Dunn-Meynell AA . Defense of body weight against chronic caloric restriction in obesity-prone and -resistant rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Compar Physiol 2000; 278: R231–R237.
Guyenet SJ, Schwartz MW . Clinical review: Regulation of food intake, energy balance, and body fat mass: implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012; 97: 745–755.
Bouret SG, Gorski JN, Patterson CM, Chen S, Levin BE, Simerly RB . Hypothalamic neural projections are permanently disrupted in diet-induced obese rats. Cell Metab 2008; 7: 179–185.
Adams TD, Gress RE, Smith SC, Halverson RC, Simper SC, Rosamond WD et al. Long-term mortality after gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 753–761.
Sjostrom L, Narbro K, Sjostrom CD, Karason K, Larsson B, Wedel H et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 741–752.
Flum DR, Salem L, Elrod JA, Dellinger EP, Cheadle A, Chan L . Early mortality among Medicare beneficiaries undergoing bariatric surgical procedures. JAMA 2005; 294: 1903–1908.
Zingmond DS, McGory ML, Ko CY . Hospitalization before and after gastric bypass surgery. JAMA 2005; 294: 1918–1924.
Stroh C, Birk D, Flade-Kuthe R, Frenken M, Herbig B, Hohne S et al. A nationwide survey on bariatric surgery in Germany—results 2005-2007. Obesity Surg 2009; 19: 105–112.
Rucker D, Padwal R, Li SK, Curioni C, Lau DC . Long term pharmacotherapy for obesity and overweight: updated meta-analysis. BMJ 2007; 335: 1194–1199.
Christensen R, Kristensen PK, Bartels EM, Bliddal H, Astrup A . Efficacy and safety of the weight-loss drug rimonabant: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2007; 370: 1706–1713.
Griffen L, Anchors M . Asymptomatic mitral and aortic valve disease is seen in half of the patients taking 'phen-fen'. Arch Intern Med 1998; 158: 102.
Field BC, Wren AM, Peters V, Baynes KC, Martin NM, Patterson M et al. PYY3-36 and oxyntomodulin can be additive in their effect on food intake in overweight and obese humans. Diabetes 2010; 59: 1635–1639.
Hainer V, Hainerova IA . Do we need anti-obesity drugs? Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28: 8–20.
Reed AS, Unger EK, Olofsson LE, Piper ML, Myers MG Jr, Xu AW . Functional role of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 upregulation in hypothalamic leptin resistance and long-term energy homeostasis. Diabetes 2010; 59: 894–906.
Clemmensen C, Chabenne J, Finan B, Sullivan L, Fischer K, Kuchler D et al. GLP-1/glucagon co-agonism restores leptin responsiveness in obese mice chronically maintained on an obesogenic diet. Diabetes 2013; 63: 1422–1427.
Roth JD, Roland BL, Cole RL, Trevaskis JL, Weyer C, Koda JE et al. Leptin responsiveness restored by amylin agonism in diet-induced obesity: evidence from nonclinical and clinical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 7257–7262.
Aiuti A, Biasco L, Scaramuzza S, Ferrua F, Cicalese MP, Baricordi C et al. Lentiviral hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy in patients with Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome. Science 2013; 341: 1233151.
Biffi A, Montini E, Lorioli L, Cesani M, Fumagalli F, Plati T et al. Lentiviral hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy benefits metachromatic leukodystrophy. Science 2013; 341: 1233158.
Kim TH, Choi DH, Vauthier V, Dam J, Li X, Nam YJ et al. Anti-obesity phenotypic screening looking to increase OBR cell surface expression. J Biomol Scr 2013; 19: 88–99.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement no. 241592 (to RJ), the Agence Nationale de la Recherche ANR-12-JSV1-0011 (to JD), Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), a research fellowship of the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (to VV), a PhD fellowship from the Region Ile de France (CODDIM) (to MP) and a PhD fellowship from the University Paris-Sud (to CR). We thank the Cochin Institute's Morphology and Histology facility for technical assistance.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
JD and RJ wrote the manuscript; JD and RJ managed the project; VV, PC, TDS, MP, CR, JD, CS performed research and analyzed data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Gene Therapy website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vauthier, V., Swartz, T., Chen, P. et al. Endospanin 1 silencing in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus contributes to sustained weight loss of high fat diet obese mice. Gene Ther 21, 638–644 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2014.36
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2014.36
- Springer Nature Limited