Abstract
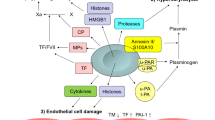
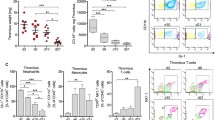
Recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin (rTM), a potent anticoagulant, has been used for the treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation in Japan since 2008. Interestingly, rTM possesses anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective functions. This study examined whether rTM alleviates GVHD in a murine hematopoietic SCT (HSCT) model. Use of rTM significantly improved the survival of mice on day 28 of transplantation (survival rate 70% in rTM - treated mice vs 35% in control, P<0.05) in association with a significant decrease in plasma levels of IL-6, IFN-γ and high-mobility group B1 DNA-binding protein on day 7 of HSCT. Intriguingly, the proportion of regulatory T cells in the spleen was significantly increased in rTM-treated mice on day 7 of transplantation compared with control diluent-treated mice. In addition, elevated plasma levels of TM and fibrin/fibrinogen degradation product were noted in HSCT-recipient mice, suggesting coagulopathy caused by endothelial cell damage in this GVHD model. The use of rTM potently decreased these levels. Importantly, rTM did not hamper the anti-GVL and engraftment of hematopoietic cells. Taken together, the use of rTM may prevent GVHD and serve as a potential therapeutic strategy to improve clinical outcomes in individuals who receive HSCT.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maruyama I . Recombinant thrombomodulin and activated protein C in the treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost 1999; 82: 718–721.
Saito H, Maruyama I, Shimazaki S, Yamamoto Y, Aikawa N, Ohno R et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin (ART-123) in disseminated intravascular coagulation: results of a phase III, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. J Thromb Haemost 2007; 5: 31–41.
Ikezoe T . Pathogenesis of disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia, and its treatment using recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin. Int J Hematol 2014; 100: 27–37.
Abeyama K, Stern DM, Ito Y, Kawahara K, Yoshimoto Y, Tanaka M et al. The N-terminal domain of thrombomodulin sequesters high-mobility group-B1 protein, a novel antiinflammatory mechanism. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1267–1274.
Conway EM, Van de Wouwer M, Pollefeyt S, Jurk K, Van Aken H, De Vriese A et al. The lectin-like domain of thrombomodulin confers protection from neutrophil-mediated tissue damage by suppressing adhesion molecule expression via nuclear factor kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Exp Med 2002; 196: 565–577.
Ikezoe T, Yang J, Nishioka C, Honda G, Furihata M, Yokoyama A . Thrombomodulin protects endothelial cells from a calcineurin inhibitor-induced cytotoxicity by upregulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase/myeloid leukemia cell-1 signaling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2012; 32: 2259–2270.
Ikezoe T, Togitani K, Komatsu N, Isaka M, Yokoyama A . Successful treatment of sinusoidal obstructive syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin. Bone Marrow Transplant 2010; 45: 783–785.
Sakai M, Ikezoe T, Bandobashi K, Togitani K, Yokoyama A . Successful treatment of transplantation-associated thrombotic microangiopathy with recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin. Bone Marrow Transplant 2010; 45: 803–805.
Ikezoe T, Takeuchi A, Taniguchi A, Togitani K, Yokoyama A . Recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin counteracts capillary leakage associated with engraftment syndrome. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 616–618.
Ikezoe T, Takeuchi A, Chi S, Takaoka M, Anabuki K, Kim T et al. Effect of recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin on clinical outcomes of patients with coagulopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur J Haematol 2013; 91: 442–447.
Luft T, Dietrich S, Falk C, Conzelmann M, Hess M, Benner A et al. Steroid-refractory GVHD: T-cell attack within a vulnerable endothelial system. Blood 2011; 118: 1685–1692.
Dietrich S, Okun JG, Schmidt K, Falk CS, Wagner AH, Karamustafa S et al. High pre-transplant serum nitrate levels predict risk of acute steroid-refractory graft-versus-host disease in the absence of statin therapy. Haematologica 2014; 99: 541–547.
Dietrich S, Falk CS, Benner A, Karamustafa S, Hahn E, Andrulis M et al. Endothelial vulnerability and endothelial damage are associated with risk of graft-versus-host disease and response to steroid treatment. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 22–27.
Nagato M, Okamoto K, Abe Y, Higure A, Yamaguchi K . Recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin decreases the plasma high-mobility group box-1 protein levels, whereas improving the acute liver injury and survival rates in experimental endotoxemia. Crit Care Med 2009; 37: 2181–2186.
Pearson T, Shultz LD, Miller D, King M, Laning J, Fodor W et al. Non-obese diabetic-recombination activating gene-1 (NODRag1 null) interleukin (IL)-2 receptor common gamma chain (IL2r gamma null) null mice: a radioresistant model for human lymphohaematopoietic engraftment. Clin Exp Immunol 2008; 154: 270–284.
Ikezoe T, Yang Y, Heber D, Taguchi H, Koeffler HP . PC-SPES: a potent inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappa B rescues mice from lipopolysaccharide-induced septic shock. Mol Pharmacol 2003; 64: 1521–1529.
Gallez-Hawkins GM, Thao L, Palmer J, Dagis A, Li X, Franck AE et al. Increased programmed death-1 molecule expression in cytomegalovirus disease and acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 872–880.
Hoffmann P, Ermann J, Edinger M, Fathman CG, Strober S . Donor-type CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells suppress lethal acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Exp Med 2002; 196: 389–399.
Matzinger P . The JAM test. A simple assay for DNA fragmentation and cell death. J Immunol Methods 1991; 145: 185–192.
Nomura S, Ozasa R, Nakanishi T, Fujita S, Miyaji M, Mori S et al. Can recombinant thrombomodulin play a preventive role for veno-occlusive disease after haematopoietic stem cell transplantation?. Thromb Haemost 2011; 105: 1118–1120.
Van de Wouwer M, Plaisance S, De Vriese A, Waelkens E, Collen D, Persson J et al. The lectin-like domain of thrombomodulin interferes with complement activation and protects against arthritis. J Thromb Haemost 2006; 4: 1813–1824.
Yamakawa K, Ogura H, Fujimi S, Morikawa M, Ogawa Y, Mohri T et al. Recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin in sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation: a multicenter propensity score analysis. Intensive Care Med 2013; 39: 644–652.
Kudo D, Toyama M, Aoyagi T, Akahori Y, Yamamoto H, Ishii K et al. Involvement of high mobility group box 1 and the therapeutic effect of recombinant thrombomodulin in a mouse model of severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol 2013; 173: 276–287.
Ishii H, Majerus PW . Thrombomodulin is present in human plasma and urine. J Clin Invest 1985; 76: 2178–2181.
Gando S, Kameue T, Matsuda N, Hayakawa M, Hoshino H, Kato H . Serial changes in neutrophil-endothelial activation markers during the course of sepsis associated with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Res 2005; 116: 91–100.
Carreras E, Diaz-Ricart M . The role of the endothelium in the short-term complications of hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 1495–1502.
Geiger H, Pawar SA, Kerschen EJ, Nattamai KJ, Hernandez I, Liang HP et al. Pharmacological targeting of the thrombomodulin-activated protein C pathway mitigates radiation toxicity. Nat Med 2012; 18: 1123–1129.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported, in part, by JSPS KAKENHI grant number 23591421 and 26461406, Research for Promoting Technological Seeds, The Uehara Memorial Foundation and The Senshin Medical Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikezoe, T., Yang, J., Nishioka, C. et al. Thrombomodulin alleviates murine GVHD in association with an increase in the proportion of regulatory T cells in the spleen. Bone Marrow Transplant 50, 113–120 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.208
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.208
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
High incidence of thromboembolism in patients with chronic GVHD: association with severity of GVHD and donor-recipient ABO blood group
Blood Cancer Journal (2021)
-
Graft protective effect and induction of CD4+Foxp3+ cell by Thrombomodulin on allograft arteriosclerosis in mice
Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery (2018)
-
G-protein coupled receptor 15 mediates angiogenesis and cytoprotective function of thrombomodulin
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: opening Pandora’s box
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)
-
The fifth epidermal growth factor-like region of thrombomodulin exerts cytoprotective function and prevents SOS in a murine model
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)