Abstract
Background:
Vaginal brachytherapy (VBT) in high–intermediate-risk endometrial cancer (EC) provides a significant reduction in the risk of local cancer recurrence, but without survival benefit and with increased mucosal atrophy. Five-year local control is estimated to be similar for VBT and a watchful waiting policy (WWP), in which patients receive VBT combined with external radiation in case of a recurrence. Our aim was to assess treatment preferences of EC patients and clinicians regarding VBT and WWP, and to evaluate their preferred and perceived involvement in treatment decision making.
Methods:
Interviews were held with 95 treated EC patients. The treatment trade-off method was used to assess the minimally desired benefit from VBT in local control. Patients’ preferred and perceived involvement in decision making were assessed using a questionnaire. Seventy-seven clinicians completed a questionnaire assessing their minimally desired benefit and preferred involvement in decision making.
Results:
Minimally desired benefit of VBT was significantly lower for patients than for clinicians (median=0 vs 8%, P<0.001), for irradiated than for non-irradiated patients (median=0 vs 6.5%, P<0.001), and for radiation oncologists than for gynaecologists (median=4 vs 13%, P<0.001). Substantial variation existed within the groups of patients and clinicians. Participants preferred the patient and clinician to share in the decision about VBT. However, irradiated patients indicated low perceived involvement in actual treatment decision making.
Conclusions:
We found variations between and within patients and clinicians in minimally desired benefit from VBT. However, the recurrence risk at which patients preferred VBT was low. Our results showed that patients consider active participation in decision making essential.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Endometrial cancer (EC) is the most common gynaecological malignancy in Western countries, with an incidence of 15–25 per 100 000 women per year (Bray et al, 2005). In most cases, primary treatment consists of total hysterectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy. Several randomised trials have established the role of radiotherapy in high–intermediate-risk EC (Creutzberg et al, 2000; Keys et al, 2004; Blake et al, 2009). Vaginal brachytherapy (VBT) provides a highly significant reduction in the risk of vaginal cancer recurrence (with freedom from local cancer recurrence, from now on termed ‘local control’), but without survival benefit (Nout et al, 2010). However, VBT is associated with side effects such as mucosal atrophy (Nout et al, 2010; Nout et al, 2012). An alternative to standard postoperative VBT could be a watchful waiting policy (WWP), in which patients are treated with radiotherapy only if they develop a vaginal relapse. The ultimate 5-year local control including treatment for relapse is estimated to be similar for VBT and WWP (Thomas, 2010). However, treatment of a vaginal relapse is more intensive, as it consists of both external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) and VBT. With WWP, ∼86% of EC patients will remain disease free and will not require radiotherapy at all (Thomas, 2010). Therefore, the question remains if upfront treatment with VBT for all EC patients with high-intermediate risk factors or WWP should be preferred. This question is the rationale of the fourth Post-Operative Radiation Therapy in Endometrial Carcinoma (PORTEC-4) trial, in which a WWP is randomly compared to VBT (Creutzberg and Nout, 2012).
No studies have been done on preferences of EC patients’ and clinicians’ preferences with regard to treatment strategies and treatment outcomes, despite the potential benefits of VBT not necessarily outweighing its potential side effects. At the same time, WWP can be perceived as ‘doing nothing’. Research has shown that cancer patients feel that ‘doing nothing’ is no choice, and experience considerable pressure, also from family members and doctors, to seek active treatment (Charles et al, 1998; Chapple et al, 2002; Jansen et al, 2004). Most studies on preferences in other cancer settings have reported on situations where the benefit of active treatment is larger than foregoing treatment. In the present case though, the ultimate 5-year local control is estimated to be very high and similar for both treatment strategies.
We expect individual patients to value treatment strategies and outcomes very differently, and thus, the treatment decision seems highly suitable for involving patients (Muller-Engelmann et al, 2011; Wong and Szumacher, 2012). Involving patients in decision making facilitates incorporating their preferences in treatment decisions (Pieterse et al, 2007). This is especially relevant since preferences are difficult to predict based on socio-demographic factors or disease characteristics (Wright et al, 1994; Pieterse et al, 2011), and patients and clinicians repeatedly have been shown to value treatment outcomes differently (Montgomery and Fahey, 2001; Pieterse et al, 2007; Stalmeier et al, 2007). Research has shown that patients are willing to accept a higher chance of local recurrence to improve functional outcomes of treatments (Cassileth et al, 1980; Jenkins et al, 2001; van Tol-Geerdink et al, 2006; Kennedy et al, 2011). Clinicians tend to underestimate patients’ preference for less toxic treatments, as well as their preferred involvement in decision making (van Tol-Geerdink et al, 2006; Stalmeier et al, 2007).
The aim of this study was to assess the minimally desired benefit from VBT, in terms of local control and compared to WWP, of EC patients and treating clinicians (radiation oncologists and gynaecologists). Also, patients’ preferred and perceived roles in treatment decision making were examined, as well as clinicians’ decisional role preferences.
Materials and methods
Study population—patients and clinicians
Participants were EC patients, randomly selected from hospital databases and approached via their treating clinician. Selection criteria were: having undergone surgery with or without VBT between 2007 and 2013, aged <90 years, and having no history of other malignancies. We aimed to include 100 EC patients, half of whom had been treated with surgery alone (low-risk EC), and half with surgery followed by VBT (high–intermediate-risk EC).
For the clinician study, we approached all 198 clinicians of the Dutch Gynecologic Oncology Group via email. After 2 weeks, clinicians received a reminder.
Study procedures
Individual face-to-face interviews were held with each patient to assess the minimally desired benefit from VBT. Five interviewers were trained and adhered to a strict interview script. Socio-demographic details, medical history, and preferred and perceived involvement in decision making were assessed by self-report questionnaire in the weeks before the interview.
Clinicians were asked to fill out a web-based questionnaire in which their treatment preferences, socio-demographic factors and work-related details and attitudes towards treatment decision making were assessed.
The Medical Ethics Committee of Leiden University Medical Center approved the study.
Measures
Patients’ minimally desired absolute benefit from VBT, in terms of 5-year local control and compared to WWP, was assessed face to face using the treatment trade-off method (TTM; Llewellyn-Thomas, 1997). Patients were asked to imagine that they had recently been diagnosed with EC and that their clinician offered them two treatment strategies. We made explicit that the situation was hypothetical and did not refer to their situation. After sequentially offering the information on the TTM board (Figure 1), we started with presenting a 14% risk of cancer recurrence at 5 years for treatment A (surgery alone) and a 2% risk of cancer recurrence for treatment B (surgery and VBT). We then asked patients to weigh recurrence rate, side effects and burden of treatments and to indicate which treatment strategy they preferred at this 12% benefit of treatment B. Next, the probability of local recurrence after surgery alone was varied systematically and patients were asked each time which treatment they preferred. Patients’ minimally desired benefit (recurrence rate with WWP minus the 2% recurrence rate after VBT) was searched by bracketing the recurrence rate either within the range of 2–14 out of 100 (if their initial preference was treatment B: surgery and VBT, indicating that they required a benefit of 12% or less) or within the range of 15–100 out of 100 (if their initial preference was treatment A: surgery alone, indicating that they required more than 12% benefit). For example, when a patient indicated that she preferred treatment B at a 12% benefit, we then presented a probability of local recurrence after surgery alone of 2% (no benefit of treatment) and asked which treatment she would prefer. If she indicated to prefer treatment A, we then presented a probability of local recurrence after surgery alone of 8% (6% benefit of treatment) and again asked which treatment she would prefer. The probability of local recurrence after surgery alone was varied until patients’ minimally desired benefit was reached. We built in a check for understanding in patients preferring VBT for no additional benefit by lowering the recurrence rate after surgery alone to 0% (a 2% disadvantage of VBT).
Information presented in the TTM on treatment options. The numbers in the margin represent the order in which the board was built up. The initially offered figures for surgery only were 86 out of 100 women having no recurrence, 14 having recurrence, thus implying a 12% benefit of VBT compared to WWP. The light grey boxes represent potential side effects of VBT, and dark grey boxes represent potential side effects of EBRT.
We pilot tested a self-administered format of the TTM in 10 treated EC patients. Patients evaluated this format to be too difficult because of the high amount of (new) medical information. We therefore decided to use the traditional face-to-face format for the TTM in patients. Clinicians were offered the TTM as part of an online questionnaire. Instead of sequentially offering the information, all information was given to them at once. Clinicians were asked at which minimally desired absolute benefit of VBT they would prefer VBT, and recurrence rate was not systematically varied.
We assessed patients’ and clinicians’ preferred decisional role using a modified version of the Control Preferences Scale (CPS), in which participants were asked to select one of five statements on roles in treatment decision making (Degner et al, 1997; Salkeld et al, 2004). The roles ranged from (A) the patient makes the decision about VBT alone, through (B) the patient makes the decision after considering the doctor's opinion, (C) the patient makes the decision together with the clinician, (D) the clinician makes the decision after considering the patient's opinion, to (E) the clinician makes the decision on VBT alone.
Irradiated patients had actually faced the decision whether or not to undergo radiation. We explored to what extent they felt they had been involved in this decision by asking them: To what extent did you have space to (1) think about benefits and harms of VBT, (2) give your opinion on the benefits and harms of VBT, and (3) participate in decision making to your preferred extent. They could respond to each question using a score between 1 (not at all) and 7 (a lot). Finally, we asked: Do you feel you had a choice in the decision about whether or not to undergo VBT? Responses could be negative, affirmative or ‘I don’t know’.
Both patients’ and clinicians’ questionnaire contained additional questions regarding socio-demographic details, medical history (patients) and work-related details (clinicians).
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to describe participant characteristics and minimally desired benefit from VBT (TTM). Preferred benefit scores were not normally distributed, so we present medians and compared between groups with Mann-Whitney U tests. Using χ2-tests, patients and clinicians were compared on decisional role preferences (CPS) and perceived involvement, after subdivision into two categories by merging response categories 1–3 and 5–7. Significance testing was done two sided at α=0.05.
Results
Participants
In total, 140 eligible patients, treated between 2007 and 2013, were approached. Of these patients, 95 (68%) were interviewed and completed the questionnaire.
Of the 198 clinicians approached, 77 (39%; 52 gynaecologists, response rate 32%; 25 radiation oncologists, response rate 69%) completed the online questionnaire including the TTM.
In Table 1 participant demographic characteristics, and treatment (patients) and work-related (clinicians) characteristics are listed.
Treatment preference and minimally desired benefit from VBT
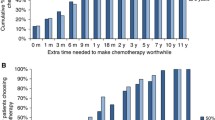
In Table 2 minimally desired benefit from VBT in terms of local control and compared to WWP is listed. Figure 2 shows the cumulative proportion of participants preferring VBT according to minimum benefit. Overall, minimally desired benefit was significantly lower for patients than for clinicians (median=0 vs 8%, U=1709, z=−5.8; P<0.001). Irradiated patients required a significantly lower benefit than non-irradiated patients (median=0 vs 6.5%, U=509, z=−5.08; P<0.001). There was no significant association between minimally desired benefit from VBT and patients’ age, educational level, having a partner or children, or comorbidity. Minimally desired benefit was significantly lower for radiation oncologists than for gynaecologists (median=4 vs 13%, U=293, z=−3.2; P=0.001). There was no significant association between minimally desired benefit from VBT and clinicians’ age, gender, institution (academic/non-academic), years since specialisation or number of EC patients treated per year.
Preferred involvement
Figure 3 depicts the patients’ and clinicians’ preferences regarding their role in the decision about VBT in the treatment of EC. No significant associations were found between decisional role preferences and patients’ treatment, age, educational level, having a partner or children, or comorbidity. Clinicians who had specialised more recently had a stronger preference for a more active clinician’s role in deciding about VBT (χ2=6.87, P<0.05). No significant associations were found between decisional role preferences and clinicians’ age, gender, specialisation, institution (academic/non-academic), or number of EC patients treated per year.
Perceived actual involvement in decision making about VBT
A majority of irradiated patients indicated that they had lacked space to think about benefits and harms of VBT (42%), give their opinion on these benefits and harms (43%) or participate in decision making to their preferred extent (45%), with a high within-subject overlap between the responses to the three questions. Older patients (⩾68) more often indicated not to have been involved in the decision to their preferred extent (χ2=7.37, P<0.05). Otherwise, there were no significant associations between perceived involvement and patients’ time since diagnosis, educational level, having a partner or children, or comorbidity.
A total of 44% of irradiated patients indicated they felt they had had no choice regarding VBT. There were no significant associations between whether patients felt they had had a choice and patients’ age, educational level, having a partner or children, or comorbidity.
Discussion
This study had a dual objective. First, to assess patients’ and clinicians’ minimally desired benefit from VBT, in terms of local control (defined as freedom from local cancer recurrence at 5 years) and compared to WWP. Second, to assess patients’ and clinicians’ preferred involvement in this decision, as well as perceived actual involvement in this decision of irradiated EC patients.
Our study showed considerable variation between, as well as within, patients and clinicians in their minimally desired benefit from VBT compared to WWP. Patients preferred VBT at a lower minimal benefit than clinicians. Furthermore, irradiated patients and radiation oncologists preferred VBT at a lower minimal benefit than, respectively, non-irradiated patients and gynaecologists. The variation within groups could not be explained by socio-demographic factors or work-related characteristics. The difference in minimally desired benefit between clinicians from different specialties has also been shown in earlier research, with clinicians generally requiring less benefit from the treatment of their specialty (Stiggelbout et al, 2000; Fowler et al, 2000). Since patients highly value clinicians’ recommendations, these can lead patients to make or agree with decisions that go against what they would otherwise prefer (Gurmankin et al, 2002; Stiggelbout et al, 2007). The importance of clinicians’ recommendations and the substantial variance in both patients’ and clinicians’ treatment preferences highlight the need for involving EC patients in decisions about VBT.
Overall, most patients preferred VBT at a low benefit in local control, although the ultimate 5-year local control is estimated to be similar for both treatment strategies. Choosing VBT despite no benefit in 5-year local control is possibly explained by patients preferring to seek active treatment (Chapple et al, 2002), and seeking to be assured of being disease free sooner. Another explanation could be that patients want to make sure they have done everything possible, as opposed to ‘doing nothing’ (Charles et al, 1998). Furthermore, patients might consider possible side effects of VBT as relatively mild, compared to possible side effects of EBRT.
Two clinicians (8%) and 56 patients (59% of total; 79% of irradiated patients) indicated to choose VBT at no additional benefit. We assumed their answers implied a strong preference for VBT or ‘active treatment’ rather than as an indication of misunderstanding. Since deleting them would bias the minimally desired benefit upwards, we decided against removing them from the analysis. This preference of treatment despite no benefit is a seemingly non-rational answer and has been found in earlier studies, especially among irradiated patients (Jansen et al, 2001; Pieterse et al, 2007). It is possibly caused by anticipated regret and a wish to have done everything one could. Another possible explanation is positive experiences with VBT and post hoc justification. The latter implies that patients may have a desire to justify the prior decision as being the correct one (Jansen et al, 2001). In particular, none of these included patients had experienced a relapse and they could have assumed that this was a result of VBT.
The large majority of patients and clinicians preferred both the patient and clinician to share the decision about VBT. However, individual differences occur in the interpretation of sharing decisions, which may range from receiving information or assent to a treatment recommendation to actively deciding on treatment (Moumjid et al, 2007; Moreau et al, 2012). Clinicians should be aware of patients’ wish to participate in treatment decisions and involve them as much as possible to the patient’s preferred extent.
A possible limitation of this study is the different methods used in assessing the minimally desired benefit in the patient vs clinician group. We intended to measure the minimally desired benefit in a direct way through an online questionnaire in both groups. However, after pilot testing the self-report questionnaire, we concluded that this method was not feasible for participants unfamiliar with the complicated medical information. Patients as well as clinicians evaluated the methods used as clear (data not shown). Another possible limitation is that patients in our study had already started or finished their treatment. Owing to logistical reasons, we were unable to include patients at the moment they were actually facing this treatment decision.
In the PORTEC-4 trial, a postoperative WWP is compared with standard VBT in a randomised clinical trial (Creutzberg and Nout, 2012). This study will provide data on overall side effects and quality of life of treated EC patients. Furthermore, results will show whether the exact relapse rate after WWP is indeed ∼14%, and whether the 5-year local control, including treatment for relapse, is indeed similar for both treatment strategies. Our study shows that for a benefit of 12%, over 90% of radiation oncologists, but <50% of gynaecologists would recommend VBT, while most of the patients would prefer VBT. Clinicians should be aware of this variation and be transparent to their colleagues and patients on their considerations to recommend one or the other treatment strategy.
In conclusion, our results showed a considerable variation between, as well as within, patients and clinicians in how they value local control, harms and burden of treatment. We recommend that clinicians inform patients on the benefits and harms of treatment strategies, elicit patients’ preferences and consider these preferences in their treatment recommendation.
References
Blake P, Swart AM, Orton J, Kitchener H, Whelan T, Lukka H, Eisenhauer E, Bacon M, Tu D, Parmar MK, Amos C, Murray C, Qian W (2009) Adjuvant external beam radiotherapy in the treatment of endometrial cancer (MRC ASTEC and NCIC CTG EN.5 randomised trials): pooled trial results, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Lancet 373 (9658): 137–146.
Bray F, Loos AH, Oostindier M, Weiderpass E (2005) Geographic and temporal variations in cancer of the corpus uteri: incidence and mortality in pre- and postmenopausal women in Europe. Int J Cancer 117 (1): 123–131.
Cassileth BR, Zupkis RV, Sutton-Smith K, March V (1980) Information and participation preferences among cancer patients. Ann Intern Med 92 (6): 832–836.
Chapple A, Ziebland S, Herxheimer A, McPherson A, Shepperd S, Miller R (2002) Is ‘watchful waiting’ a real choice for men with prostate cancer? A qualitative study. BJU Int 90 (3): 257–264.
Charles C, Redko C, Whelan T, Gafni A, Reyno L (1998) Doing nothing is no choice: lay constructions of treatment decision-making among women with early-stage breast cancer. Sociol Health Illn 20 (1): 71–95.
Creutzberg CL, Nout RA (2012) [The PORTEC-4 trial: phase III randomised trial investigating the role and dose of vaginal brachytherapy for endometrial carcinoma]. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Oncologie 9 (4): 183–187.
Creutzberg CL, van Putten WL, Koper PC, Lybeert ML, Jobsen JJ, Warlam-Rodenhuis CC, De Winter KA, Lutgens LC, van den Bergh AC, Steen-Banasik E, Beerman H, van Lent M (2000) Surgery and postoperative radiotherapy versus surgery alone for patients with stage-1 endometrial carcinoma: multicentre randomised trial. PORTEC Study Group. Post Operative Radiation Therapy in Endometrial Carcinoma. Lancet 355 (9213): 1404–1411.
Degner LF, Sloan JA, Venkatesh P (1997) The Control Preferences Scale. Can J Nurs Res 29 (3): 21–43.
Fowler FJ Jr, McNaughton CM, Albertsen PC, Zietman A, Elliott DB, Barry MJ (2000) Comparison of recommendations by urologists and radiation oncologists for treatment of clinically localized prostate cancer. JAMA 283 (24): 3217–3222.
Gurmankin AD, Baron J, Hershey JC, Ubel PA (2002) The role of physicians’ recommendations in medical treatment decisions. Med Decis Making 22 (3): 262–271.
Jansen SJ, Kievit J, Nooij MA, de Haes JC, Overpelt IM, van SH, Maartense E, Stiggelbout AM (2001) Patients’ preferences for adjuvant chemotherapy in early-stage breast cancer: is treatment worthwhile? Br J Cancer 84 (12): 1577–1585.
Jansen SJ, Otten W, Stiggelbout AM (2004) Review of determinants of patients’ preferences for adjuvant therapy in cancer. J Clin Oncol 22 (15): 3181–3190.
Jenkins V, Fallowfield L, Saul J (2001) Information needs of patients with cancer: results from a large study in UK cancer centres. Br J Cancer 84 (1): 48–51.
Kennedy ED, Schmocker S, Victor C, Baxter NN, Kim J, Brierley J, McLeod RS (2011) Do patients consider preoperative chemoradiation for primary rectal cancer worthwhile? Cancer 117 (13): 2853–2862.
Keys HM, Roberts JA, Brunetto VL, Zaino RJ, Spirtos NM, Bloss JD, Pearlman A, Maiman MA, Bell JG (2004) A phase III trial of surgery with or without adjunctive external pelvic radiation therapy in intermediate risk endometrial adenocarcinoma: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol 92 (3): 744–751.
Llewellyn-Thomas HA (1997) Investigating patients’ preferences for different treatment options. Can J Nurs Res 29 (3): 45–64.
Montgomery AA, Fahey T (2001) How do patients’ treatment preferences compare with those of clinicians? Qual Health Care 10 (Suppl 1): i39–i43.
Moreau A, Carol L, Dedianne MC, Dupraz C, Perdrix C, Laine X, Souweine G (2012) What perceptions do patients have of decision making (DM)? Toward an integrative patient-centered care model. A qualitative study using focus-group interviews. Patient Educ Couns 87 (2): 206–211.
Moumjid N, Gafni A, Bremond A, Carrere MO (2007) Shared decision making in the medical encounter: are we all talking about the same thing? Med Decis Making 27 (5): 539–546.
Muller-Engelmann M, Keller H, Donner-Banzhoff N, Krones T (2011) Shared decision making in medicine: the influence of situational treatment factors. Patient Educ Couns 82 (2): 240–246.
Nout RA, Putter H, Jurgenliemk-Schulz IM, Jobsen JJ, Lutgens LC, van der Steen-Banasik EM, Mens JW, Slot A, Stenfert Kroese MC, Nijman HW, van de Poll-Franse LV, Creutzberg CL (2012) Five-year quality of life of endometrial cancer patients treated in the randomised Post Operative Radiation Therapy in Endometrial Cancer (PORTEC-2) trial and comparison with norm data. Eur J Cancer 48 (11): 1638–1648.
Nout RA, Smit VT, Putter H, Jurgenliemk-Schulz IM, Jobsen JJ, Lutgens LC, van der Steen-Banasik EM, Mens JW, Slot A, Kroese MC, van Bunningen BN, Ansink AC, van Putten WL, Creutzberg CL (2010) Vaginal brachytherapy versus pelvic external beam radiotherapy for patients with endometrial cancer of high-intermediate risk (PORTEC-2): an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet 375 (9717): 816–823.
Pieterse AH, Stalmeier PF, Kroep JR, Stiggelbout AM (2011) [Adjuvant cancer treatment: what benefit does the patient consider worthwhile?]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 155 (45): A3905.
Pieterse AH, Stiggelbout AM, Baas-Thijssen MC, van de Velde CJ, Marijnen CA (2007) Benefit from preoperative radiotherapy in rectal cancer treatment: disease-free patients’ and oncologists' preferences. Br J Cancer 97 (6): 717–724.
Salkeld G, Solomon M, Short L, Butow PN (2004) A matter of trust—patient’s views on decision-making in colorectal cancer. Health Expect 7 (2): 104–114.
Stalmeier PF, van Tol-Geerdink JJ, van Lin EN, Schimmel E, Huizenga H, van Daal WA, Leer JW (2007) Doctors’ and patients’ preferences for participation and treatment in curative prostate cancer radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 25 (21): 3096–3100.
Stiggelbout AM, de Haes JC, van de Velde CJ (2000) Adjuvant chemotherapy in node negative breast cancer: patterns of use and oncologists’ preferences. Ann Oncol 11 (5): 631–633.
Stiggelbout AM, Jansen SJ, Otten W, Baas-Thijssen MC, van SH, van de Velde CJ (2007) How important is the opinion of significant others to cancer patients' adjuvant chemotherapy decision-making? Support Care Cancer 15 (3): 319–325.
Thomas GM (2010) A role for adjuvant radiation in clinically early carcinoma of the endometrium? Int J Gynecol Cancer 20 (11 Suppl 2): S64–S66.
van Tol-Geerdink JJ, Stalmeier PF, van Lin EN, Schimmel EC, Huizenga H, van Daal WA, Leer JW (2006) Do patients with localized prostate cancer treatment really want more aggressive treatment? J Clin Oncol 24 (28): 4581–4586.
Wong J, Szumacher E (2012) Patients’ decision-making in radiation oncology. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res 12 (1): 95–104.
Wright J, Jones G, Whelan T, Lukka H (1994) Patient preference for high or low dose rate brachytherapy in carcinoma of the cervix. Radiother Oncol 33 (3): 187–194.
Acknowledgements
We thank all participating patients and clinicians for their efforts. We also thank Nanny van Duijn-Bakker and Monique Baas-Thijssen for their contribution in interviewing patients. Furthermore, we thank the referring gynaecologists for their participation in this study: Reinier de Graaf Group, Delft (Astrid Baalbergen, MD); Atrium Medical Center, Heerlen (Mirjam Engelen, MD, PhD). We thank the Dutch Cancer Society for their support (UL2011-5336 and UL2009-4431).
Disclaimer
The study sponsors had no involvement on the study design, in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Kunneman, M., Pieterse, A., Stiggelbout, A. et al. Treatment preferences and involvement in treatment decision making of patients with endometrial cancer and clinicians. Br J Cancer 111, 674–679 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.322
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.322
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Differences between physician and patient preferences for cancer treatments: a systematic review
BMC Cancer (2023)
-
Adjuvant immunotherapy recommendations for stage III melanoma: physician and nurse interviews
BMC Cancer (2021)
-
Representativeness of personality and involvement preferences in a web-based survey on healthcare decision-making
BMC Health Services Research (2020)
-
Using the Threshold Technique to Elicit Patient Preferences: An Introduction to the Method and an Overview of Existing Empirical Applications
Applied Health Economics and Health Policy (2020)