Abstract
Urban air pollution has emerged as an acute problem in recent years because of its detrimental effects on health and living conditions. The research presented here aims at attaining a better understanding of phenomena associated with atmospheric pollution, and in particular with aerosol particles. The specific goal was to develop a form of air quality modelling which can forecast urban air quality for the next day using airborne pollutant, meteorological and timing variables.
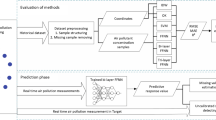
Hourly airborne pollutant and meteorological averages collected during the years 1995–1997 were analysed in order to identify air quality episodes having typical and the most probable combinations of air pollutant and meteorological variables. This modelling was done using the Self-Organising Map (SOM) algorithm, Sammon's mapping and fuzzy distance metrics. The clusters of data that were found were characterised by statistics. Several overlapping Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) models were then applied to the clustered data, each of which represented one pollution episode. The actual levels for individual pollutants could then be calculated using a combination of the MLP models which were appropriate in that situation.
The analysis phase of the modelling gave clear and intuitive results regarding air quality in the area where the data had been collected. The resulting forecast showed that the modelling of gaseous pollutants is more reliable than that of the particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comrie A. C.: 1997, Comparing neural networks and regression models for ozone forecasting, Journal of Air and Waste Management Assiciation 47, 653–663
Gardner M. W., Dorling S. R.: 1998, Artificial neural networks (the multi-layer perceptron)-a review of applications in the atmospheric sciences, Atmospheric Environment 32, 2627–2636
Gardner M. W., Dorling S. R.: 1999, Neural network modelling and prediction of hourly NOx and NO2 concentrations in urban air in London, Atmospheric Environment 33, 709–719
Haykin S.: 1994, Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Hecht-Nielsen R.: 1991, Neurocomputing, Reprinted with corrections, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc.
Kohonen T.: 1995, Self-Organizing Maps, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Germany Koikkalainen P.: 1994, Progress with the tree-structured self-organizing map, ECAI'94. Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Aug 1994, Editor Cohn, A., Wiley &; Sons, 211-215.
Poole D., Macworth A., Goebel R.: 1998, Computational Intelligence, A Logical Approach, Oxford University Press
Sammon Jr J. W.: 1969, A nonlinear mapping for data structure analysis, IEEE Transactions on Computers, C-18(5), 401–409
Willmott C.: 1982, Some comments on the evaluation of the model performance, Bulletin American Meteorological Society 63, 1309–1313
Yi J., Prybutok V. R.: 1996, A neural network model forecasting for prediction of daily maximum ozone concentration in an industrialized urban area, Environmental Pollution 92, 349–357
Zimmermann H.-J.: 1991, Fuzzy set theory and its applications, Second Edition, Kluwer Academic Publishers
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolehmainen, M., Martikainen, H., Hiltunen, T. et al. Forecasting Air Quality Parameters Using Hybrid Neural Network Modelling. Environ Monit Assess 65, 277–286 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006498914708
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006498914708