Abstract
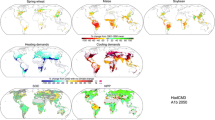
This study uses empirical agricultural impact models to compare the U.S. climate change predictions of 16 General Circulation Models (GCMs). The impact analysis provides a policy-relevant index by which to judge complex climate predictions. National aggregate impacts vary widely across the 16 GCMs because of varying regional and seasonal patterns of predicted climate change. Examining the predicted impacts from the full set of GCMs reveals that the seasonal detail in the GCM predictions is so noisy that it is not significantly different from a constant annual change. However, a consistent regional pattern does emerge across the set of models. Nonetheless, aggregating climate change across seasons and regions within the United States, using a national-annual climate change provides a reasonable and efficient approximation to the expected impact predicted by the 16 GCM models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boer, G. J., McFarlane, N. A., and Lazare, M.: 1992, ‘Greenhouse Gas Induced Climate Change Simulated with the Canadian Climate Centre Second Generation General Circulation Model’, J. Clim. 5, 1045–1077.
Carter, T. R., Parry, M. L., Harasawa, H., and Nishioka, S.: 1994, IPCC Technical Guidelines for Assessing Climate Change Impacts and Adaptations, University College London and Center for Global Environmental Research, London, United Kingdom and Tsukuba, Japan. pp. 52–53.
Cohen, S. J., Boer, G. J., McFarlane, N., Blanchet, J. P., Lazare, M., Sargent, N. E., Majaess, F. G., Phillips, D. P., Webb, M., and Cutler, T.: 1990, Application of the Canadian Climate Centre General Circulation Model Output for Regional Climate Impact Studies, Canadian Climate Centre, Downsview, Ontario, Canada, pp. 1–18.
Cubasch, U., Meehl, G., and Zhao, Z. C.: 1994, IPCC WGI Initiative: Evaluation of Regional Climate Simulations, reprinted by EPRI, Palo Alto, pp. 1–17.
Efron, B.: 1987, ‘Better Bootstrap Confidence Intervals’, J. Amer. Stat. Assoc. 82, 171–200.
Efron, B. and Tibshirani, R.: 1986, ‘Bootstrap Measures for Standard Errors, Confidence Intervals, and Other Measures of Statistical Accuracy’, Stat. Sci. 1, 54–77.
Grotch, S. L. and MacCracken, M. C.: 1991, ‘The Use of General Circulation Models to Predict Regional Climate Change’, J. Clim. 4, 286–303.
Hansen, J., Russell, G., Rind, D., Stone, P., Lacis, A., Lebedeff, S., Reudy, R., and Travis, L.: 1983, ‘Efficient Three-Dimensional Models for Climate Studies: Models I and II’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 111, 609–662.
Hansen, J., Lacis, A. Rind, D., Russell, L., Stone, P., Fung, I., Ruedy, R., and Lerner, J.: 1984, ‘Climate Sensitivity Analysis of Feedback Mechanisms’, in Hansen, J. and Takahashi, T. (eds.), Climate Processes and Climate Sensitivity, AGU, Washington, Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 29, 130–163.
Hansen, J., Fung, I., Lacis, A., Rind, D., Lebedeff, S., Ruedy, R., Russel, G., and Stone, P.: 1988, ‘Global Climate Changes as Forecast by Goddard Institute for Space Studies Three-Dimensional Model’, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 9341–9364.
Hart, T. L., Bourke, W. McAvaney, B. J., Forgan, B. W., and McGregor, J. L.: 1990, ‘Atmospheric General Circulation Simulations with the BMRC Global Spectral Model: The Impact of Revised Physical Parameterizations’, J. Clim. 3, 436–459.
Henderson-Sellers, A., Dickinson, R. E., Durbidge, T. B., Kennedy, P. J., McGuffie, K., and Pitman, A. J.: 1993, ‘Tropical Deforestation: Modelling Local to Regional-Scale Climate Change’, J. Geophys. Res. 98(D4), 7289–7315.
Ibbotson, R. and Brinson, G.: 1987, Investment Markets, McGraw-Hill, New York, pp. 57–62.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: 1990, Climate Change: The IPCC Scientific Assessment, Houghton, J. T., Jenkins, G. J., and Ephraums, J. J. (eds.), Cambridge University Press, New York, pp. xi–xxxiii.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: 1992, Climate Change 1992: The Supplementary Report to the IPCC Scientific Assessment, Houghton, J. T., Callander, B. A., and Varney, S. K. (eds.), Cambridge University Press, New York, pp. 5–20.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: 1994, Climate Change 1994: Radiative Forcing of Climate Change and An Evaluation of the IPCC IS92 Emission Scenarios, Houghton, J. T., Meira Filho, L. G., Bruce, J., Lee, Hoesung, Callander, B. A., Haites, E., Harris, N., and Maskell, K. (eds.), Cambridge University Press, New York, pp. 11–34.
Leemans, R. and Cramer, W. P.: 1991, The IIASA Database for Mean Monthly Values of Temperature, Precipitation, and Cloudiness on a Global Terrestrial Grid, Raster Data on a 30 minute Geographic (lat/long) 360 × 720 grid, IIASA, Laxenburg, Austria, pp. A03–A09.
Legates, D. R. and Willmott, C. J.: 1989, Monthly Average Surface Air Temperature and Precipitation, Digital Raster Data on a 30 minute Geographic (lat/long) 360× 721 grid (centroid-registered on.5 degree meridians), National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, pp. A04–A12.
Legates, D. R. and Willmott, C. J.: 1990, ‘Mean Seasonal and Spatial Variability in Global Surface Air Temperature’, Theor. Appl. Climatol. 41, 11–21.
Legates, D. R. and Willmott, C. J.: 1990, ‘Mean Seasonal and Spatial Variability in Gauge-Corrected Global Precipitation’, Int. J. Clim. 10, 111–127.
McFarlane, N. A., Boer, N. A., Blanchet, J. P., and Lazare, M.: 1992, ‘The Canadian Climate Centre Second Generation General Circulation Model and its Equilibrium Climate’, J. Clim. 5, 1013–1044.
McGregor, J. L., Gordon, I. G., Watterson, I. G., Dix, M. R., and Rotstayn, L. D.: 1993, The CSIRO 9-level Atmospheric General Circulation Model, CSIRO Division of Atmospheric Research Tech. Paper No. 26, Mordialloc, Australia, p. 89.
Mendelsohn, R., Nordhaus, W., and Shaw, D.: 1994, ‘The Impact of Global Warming on Agriculture: A Ricardian Analysis’, American Economic Review, 753–771.
Mendelsohn, R., Nordhaus, W., and Shaw, D.: 1996, The Impact of Climate Variation on Agriculture, manuscript, Yale School of Forestry and Environmental Studies, New Haven, CT, pp. 1–36.
Morgan, M. G. and Henrion, M.: 1990, Uncertainty: A Guide to Dealing with Uncertainty in Quantitative Risk and Policy Analysis, Cambridge University Press, New York, pp. 47–71.
Oerlemans, J.: 1989, ‘A Projection of Future Sea Level’, Climatic Change 15, 151–174.
Oglesby, R. and Saltzman, B.: 1992, ‘Equilibrium Climate Statistics of a GCM as a Function of Atmospheric CO2’, J. Clim. 5(1), 66–92.
Phillips, T. J.: 1994, A Summary Documentation of the AMIP Models, Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison, UCRL-ID-116384, University of California, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, pp. 1–22.
Schlesinger, M. E. and Verbitsky, M. Ya.: 1996, ‘Simulation of Glacial Onset with a Coupled Atmospheric General Circulation/Mixed-Layer Ocean-Ice-Sheet/Asthenosphere Model’, Paleaoclimates-Data and Modelling, 2, 179–201.
Schlesinger, M. E. and Zhao, Z.-C.: 1989, ‘Seasonal Climate Changes Induced by Doubled CO2 as Simulated by the OSU Atmospheric GCM/Mixed-Layer Ocean Model’, J. Clim. 2, 459–495.
Shlyakhter, A. I. and Kammen, D. M.: 1992, ‘Sea Level Rise or Fall?’, Nature 357, 25.
Stone, P. H.: 1992, ‘Forecast Cloudy: The Limits of Global Warming Models’, Technology Review 95, 32–40.
Thompson, S. L. and Pollard, D.: 1995, ‘A Global Climate Model (GENESIS) with a Land Surface Transfer Scheme (LSX) Part 1: Present Climate Simulation’, J. Clim. 8, 732–761.
Viner, D. and Hulme, M.: 1994, The Climate Impacts LINK Project, CRU of University of East Anglia, Norwich, U. K., pp. 10–17.
Wang, W-C., Dudek, M. P., and Liang, X.: 1992, ‘Inadequacy of Effective CO2 as a Proxy to Assess the Greenhouse Effect of Other Radiative Gases’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 19, 1375–1378.
Washington, W. and Meehl, G.: 1992, ‘Greenhouse Sensitivity Experiments with Penetrative Cumulus Convection and Tropical Cirrus Albedo Effects’, Clim. Dyn. 8, 211–233.
Watterson, I. G., Dix, M. R., Gordon, H. B., and McGregor, J. L.: 1995, ‘The CSIRO Nine-Level Atmospheric General Circulation Model and its Equilibrium Present and Doubled CO2 Climates’, Australian Meteorological Magazine 44(2), 111–125.
Wetherald, R. T. and Jenne, R.: 1989, mimeo, NCAR, Boulder, CO, pp. 1–4.
Wetherald, R. T. and Manabe, S.: 1986, ‘An Investigation of Cloud Cover Change in Response to Thermal Forcing’, Climatic Change 8, 5–23.
Wetherald, R. T. and Manabe, S.: 1988, ‘Cloud Feedback Processes in a General Circulation Model’, J. Atmos. Sci. 45, 1397–1415.
Willmott, C. J. and Legates, D. R.: 1993, ‘A Comparison of GCM-Simulated and Observed Mean January and July Surface Air Temperature’, J. Clim. 6, 274–291.
Wilson, C. A. and Mitchel, J. F. B.: 1987, ‘A Doubled CO2 Climate Sensitivity Experiment With a Global Climate Model Including a Simple Ocean’, J. Geophys. Res., 92, 13315–13343.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, L.J., Shaw, D. & Mendelsohn, R. Evaluating GCM Output with Impact Models. Climatic Change 39, 111–133 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005369006034
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005369006034