Abstract
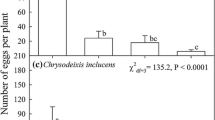
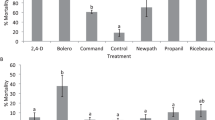
Herbivory by insects and mites on physic nut (Jatropha curcas L.) seedlings was investigated and compared with irrigation in the semi-arid Sahelian Niger, utilizing a randomized complete block design experiment. Three water treatment protocols were applied and the types of damage were recorded. Less than 5% of the seedlings died during the 10-month trial period with sap suckers causing the most damage on the surviving plants. Plants with high production of biomass and leaf cover (foliage) were most strongly positively correlated with irrigation and were also the plants that endured the highest degree of herbivory. The low dieback may indicate that defence mechanisms counteract seedling herbivory and that drought-stressed plants invest more in their defence mechanism system than vital plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addinsoft (2013) XLSTAT Version 2013.5.03.https://doi.org/www.xlstat.com.
Anitha K. and Varaprasad K. S. (2012) Jatropha pests and diseases: an overview, pp. 175–217. In Jatropha, Challenges for a New Energy Crop: Volume 1: Farming, Economics and Biofuel (edited by N. Carels, M. Sujatha and B. Bahadur). Springer-Verlag, New York. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-4806-8_10.
Biondi M., Urbani F. and D’Alessandro P. (2013) Revision of the Aphthona cookei species group in Sub-Saharan Africa: pests of Jatropha curcas L. in biodiesel plantations (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae, Galerucinae, Alticini). Entomologia 1: e7. doi: https://doi.org/10.4081/entomologia.2013.e7.
Contran N., Chessa L., Lubino M., Bellavite D., Roggero P. P. and Enne G. (2013) State-of-the-art of the Jatropha curcas productive chain: from sowing to biodiesel and by-products. Industrial Crops and Products 42, 202–215. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.05.037.
Datinon B. D., Glitho A. I., Tamo M., Amevoin K., Goergen G. and Douro Kpindou O. K. (2013) Inventory of major insects of Jatropha curcas L. (Euphorbiaceae) and their natural enemies in southern Benin. ARPN Journal of Agricultural and Biological Science 8, 711–718.
Djimmy W. Y. and Nacro S. (2015a) Estimation of yield loss of Jatropha curcas L. due to Calidea spp. (Heteroptera: Scutelleridae), in the sub-Sudanian zone of Burkina Faso. International Journal of Agriculture Innovations and Research 3, 1522–1526.
Djimmy W. Y. and Nacro S. (2015b) Study on the biology of Calidea spp. (Heteroptera: Scutelleridae), an insect pest of Jatropha curcas in South-Sudanian zone of Burkina Faso. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 1–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/sav120.
Evaristo A. B., Venzon M., Matos F. S., de Freitas R.G., Kuki K. N. and dos Santos Dias L. A. (2013) Susceptibility and physiological responses of Jatropha curcas accessions to broad mite infestation. Experimental and Applied Acarology 60, 485–496. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-013-9666-x.
Goutai L. (2002) The photosynthesis and water use efficiency of eight garden tree species. Forest Research 15, 291–296.
Habou Z. A., Adam T., Haubruge E., Mergeai G. and Verheggen F. J. (2014) Insects associated with Jatropha curcas Linn. (Euphorbiaceae) in West Niger. Journal of Insect Science 14, 1–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/ieu117.
Habou Z. A., Haubruge É., Adam T. and Verheggen F. J. (2013) Insectes ravageurs et propriétés biocides de Jatropha curcas L. (Euphorbiaceae): synthèse bibliographique. Biotechnology, Agronomy, Society and Environment 17, 604–612.
Heller J. (1996) Physic Nut, Jatropha curcas L. Promoting the Conservation and Use of Underutilized and Neglected Crops. 1. Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research, Gatersleben/ International Plant Genetic Resources Institute, Rome. ISBN 92-9043-278-0.
IFAD-FAO (2010) Jatropha: a smallholder bioenergy crop-the potential for pro-poor development. Integrated Crop Management 8, 114.
Islam A. K. M. A., Yaakob Z. and Anuar N. (2011) Jatropha: a multipurpose plant with considerable potential for the tropics. Scientific Research and Essays 6, 2597–2605. doi: https://doi.org/10.5897/SRE10.611.
Jactel H., Petit J., Desprez-Loustau M.-L., Delzon S., Piou D., Battisti A. and Koricheva J. (2012) Drought effects on damage by forest insects and pathogens: a meta-analysis. Global Change Biology 18, 267–276. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02512.x.
Jongman R. H. G., Ter Braak C. J. F. and van Tongeren O. F. R. (eds) (1995) Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology. Cambridge University Press, New York, USA. 299 pp.
Kumar S. and Kaushik N. (2013) Endophytic fungi isolated from oil-seed crop Jatropha curcas produces oil and exhibit antifungal activity. PLoS ONE 8, e56202. doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056202.
Lama A. D., Vuorisalo T. and Niemelä P. (2014) Global patterns of arthropod herbivory on an invasive plant, the physic nut (Jatropha curcas L.). Journal of Applied Entomology 139, 1–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jen.12161.
Maes W. H., Trabucco A., Achten W. M. J. and Muys B. (2009) Climatic growing conditions of Jatropha curcas L. Biomass and Bioenergy 33, 1481–1485. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2009.06.001.
Makkar H. P. S., Becker K. and Schmook B. (1998) Edible provenances of Jatropha curcas from Quintana Roo state of Mexico and effect of roasting on antinutrient and toxic factors in seeds. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition 52, 31–36.
Maxmen A. (2013) Crop pests: under attack. Nature 501, S15–S17. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/501S15a.
Minengu J. D., Mobambo P. and Mergeai G. (2014) Influence de l’environnement et des pratiques culturales sur la productivité de Jatropha curcas L. en Afrique subsaharienne (synthèse bibliographique). Biotechnology, Agronomy, Society and Environment 18, 290–300.
Minengu J. D., Verheggen F. and Mergeai G. (2015) Dynamic and impact of major insect pests on Jatropha curcas L. in two cropping systems with contrasting characteristics in the province of Kinshasa (DRC). Tropicultura 33, 163–175.
Qin X., Zheng X., Huang X., Lii Y., Shao C., Xu Y. and Chen F. (2014) A novel transcription factor JcNAC1 response to stress in new model woody plant Jatropha curcas. Planta 239, 511–520. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1993-y.
Ratnadass A. and Wink M. (2012) The phorbol ester fraction from Jatropha curcas seed oil: potential and limits for crop protection against insect pests. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, 16157–16171. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131216157.
Sapeta H., Costa J. M., Lourenço T., Maroco J. and van der Linde P. (2013) Drought stress response in Jatropha curcas: growth and physiology. Environmental and Experimental Botany 85, 76–84. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.08.012.
Sawadogo A., Nagolo E., Nacro S., Rouamba M. and Kenis M. (2015) Population dynamics of Aphthona whitfieldi (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), pest of Jatropha curcas, and environmental factors favoring its abundance in Burkina Faso. Journal of Insect Science 15, 108. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/iev084.
Singh M., Ranjan S., Verma K. K., Pathre U. V. and Shirke P. A. (2013) Photosynthetic characteristics of red and green leaves in growing seedlings of Jatropha curcas. Turkish Journal of Biology 38, 457–468. doi: https://doi.org/10.3906/biy-1312-98.
Singh K., Singh B., Verma S. K. and Patra D. D. (2014) Jatropha curcas: a ten year story from hope to despair. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 35, 356–360. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.04.033.
Sop T. K., Kagambèga F. W., Bellefontaine R., Schmiedel U. and Thiombiano A. (2012) Effects of organic amendment on early growth performance of Jatropha curcas L. on a severely degraded site in the Sub-Sahel of Burkina Faso. Agroforestry Systems 86, 387–399. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-011-9421-4.
Ter Braak C. J. F. and Šmilauer P. (2009) Canoco for Windows V 4.56. Biometris-quantitative methods in the life and earth sciences. Plant Research International. Wageningen University and Research Centre, the Netherlands.
Terren M., Mignon J., De Clerck C., Jijakli H., Savery S., de Haveskercke P. J., Winandy S. and Mergeai G. (2012) Principal disease and insect pests of Jatropha curcas L. in the lower valley of the Senegal river. Tropicultura 30, 222–229.
Thomas R., Sah N. K. and Sharma P. B. (2008) Therapeutic biology of Jatropha curcas: a mini review. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 9, 315–324.
Traore M., Bismarck Nacro H., Tabo R., Nikiema A. and Ousmane H. (2012) Potential for agronomical enhancement of millet yield via Jatropha curcas oilcake fertilizer amendment using placed application technique. International Journal of Biological and Chemical Sciences 6, 808–819. doi: https://doi.org/10.4314/ijbcs.v6i2.23.
West L. T., Wilding L. P., Landeck J. K. and Calhoun J. G. (1984) Soil Survey of the ICRISAT Sahelian Center, Niger, West Africa. Soil and Crop Sciences Department/TropSoils, Texas A&M University System, College Station, Texas/International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT). 82 pp.
Zhang C., Zhang L., Zhang S., Zhu S., Wu P., Chen Y., Li M., Jiang H. and Wu G. (2015) Global analysis of gene expression profiles in physic nut (Jatropha curcas L.) seedlings exposed to drought stress. BMC Plant Biology 15, 17. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0397-x.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thunes, K.H., Ratnadass, A., Nikiema, A. et al. Pest damage on Jatropha curcas (Euphorbiaceae): the effect of seedling irrigation in Sahelian Niger. Int J Trop Insect Sci 36, 140–145 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758416000084
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758416000084