Abstract
Background
Liver fibrosis is a chronic lesion which ultimately results in cirrhosis and possible death. Although the high incidence and lethality, few therapies are effective for liver fibrosis. Fraxetin (7,8-dihydroxy-6-methoxy coumarin), a natural product extracted from cortex fraxini, has exhibited a significant hepatoprotective and anti-fibrotic properties. However, the underlying mechanism of the anti-hepatic fibrotic property remains unknown.
Methods
48 Male Sprague Dawley rats were divided into four groups at random which were named as normal group, model group, fraxetin 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg group. The experimental model of liver fibrosis was founded by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) rats which were simultaneously treated with fraxetin (25 mg/kg or 50 mg/kg). Normal groups received equal volumes of saline and peanut oil.
Results
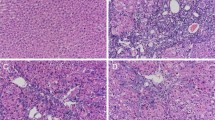
Results showed that fraxetin ameliorated CCl4 induced liver damage and fibrosis. Furthermore, histopathology examinations revealed that fraxetin improved the morphology and alleviated collagen deposition in fibrotic liver. Fraxetin inhibited inflammation and hepatocytes apoptosis by modulating the NF-κB/IκBα, MAPKs and Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathways.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that fraxetin is effective in preventing liver fibrosis through inhibiting inflammation and hepatocytes apoptosis which is associated with regulating NF-κB/IκBα, MAPKs and Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathways in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman SL. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J Biol Chem 2000;275(4):2247–50.
Eng FJ, Friedman SL, Fibrogenesis I. New insights into hepatic stellate cell activation: the simple becomes complex. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2000;279(1):G7–G11.
Liu M, Xu Y, Han X, Yin L, Xu L, Qi Y, et al. Dioscin alleviates alcoholic liver fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Sci Rep 2015;5:18038.
Yang J, Liu Q, Cao S, Xu T, Li X, Zhou D, et al. MicroRNA-145 increases the apoptosis of activated hepatic stellate cells induced by TRAIL through NF-κB signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 2017;8:980.
Li X, Jin Q, Yao Q, Xu B, Li L, Zhang S, et al. The flavonoid quercetin ameliorates liver inflammation and fibrosis by regulating hepatic macrophages activation and polarization in mice. Front Pharmacol 2018;9:72.
Wang Y, Wang R, Wang Y, Peng R, Wu Y, Yuan Y. Ginkgo biloba extract mitigates liver fibrosis and apoptosis by regulating p38 MAPK, NF-κB/IκBα, and Bcl-2/Bax signaling. Drug Des Devel Ther 2015;9:6303–17.
Peng R, Wang S, Wang R, Wang Y, Wu Y, Yuan Y. Antifibrotic effects of tanshinol in experimental hepatic fibrosis by targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K1 signaling pathways. Discov Med 2017;23(125):81.
Ge MX, He HW, Shao RG, Liu H. Recent progression in the utilization of autophagy-regulating nature compound as anti-liver fibrosis agents. J Asian Nat Prod Res 2017;19(2):109–13.
Fernandez-Puntero B, Barroso I, Iglesias I, Benedí J, Villar A. Antioxidant activity of Fraxetin: in vivo and ex vivo parameters in normal situation versus induced stress. Biol Pharm Bull 2001;24(7):777–84.
Witaicenis A, Seito LN, da Silveira Chagas A, de Almeida [107_TD$DIFF]Jr LD, et al. Antioxidant and intestinal anti-inflammatory effects of plant-derived coumarin derivatives. Phytomedicine 2014;21(3):240–6.
Martín-Aragón S, Benedí JM, Villar AM. Modifications on antioxidant capacity and lipid peroxidation in mice under fraxetin treatment. J Pharm Pharmacol 1997;49(1):49–52.
Molina-Jiménez MF, Sánchez-Reus MI, Andres D, Cascales M, Benedi J. Neuroprotective effect of fraxetin and myricetin against rotenone-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res 2004;1009(1):9–16.
Liu G, Liu Z, Yan Y, Wang H. Effect of fraxetin on proliferation and apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Oncol Lett 2017;14(6):7374–8.
Sánchez-Reus MI, Peinado II, Molina-Jiménez MF, Benedí J. Fraxetin prevents rotenone-induced apoptosis by induction of endogenous glutathione in human neuroblastoma cells. Neurosci Res 2005;53(1):48–56.
Chen X, Ying X, Sun W, Zhu H, Jiang X, Chen B. The therapeutic effect of fraxetin on ethanol-induced hepatic fibrosis by enhancing ethanol metabolism, inhibiting oxidative stress and modulating inflammatory mediators in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 2018;56:98–104.
Chen X, Ying X, Zhang W, Chen Y, Shi C, Hou Y, et al. The hepatoprotective effect of fraxetin on carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic fibrosis by antioxidative activities in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 2013;17(3):543–7.
Jiang M, Wu YL, Li X, Zhang Y, Xia KL, Cui BW, et al. Oligomeric proanthocyanidin derived from grape seeds inhibited NF-κB signaling in activated HSC: involvement of JNK/ERK MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Biomed Pharmacother 2017;93:674–80.
Luedde T, Schwabe RF. NF-κB in the liver-linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;8(2):108–18.
Oakley F, Meso M, Iredale JP, Green K, Marek CJ, Zhou X, et al. Inhibition of inhibitor of kappaB kinases stimulates hepatic stellate cell apoptosis and accelerated recovery from rat liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2005;128(1):108–20.
Chávez E, Reyes-Gordillo K, Segovia J, Shibayama M, Tsutsumi V, Vergara P, et al. Resveratrol prevents fibrosis, NF-κB activation and TGF-β increases induced by chronic CCl4 treatment in rats. J Appl Toxicol 2008;28(1):35–43.
Muriel P. NF-kappaB in liver diseases: a target for drug therapy. J Appl Toxicol 2010;29(2):91–100.
Zhang LB, Man ZT, Li W, Zhang W, Wang XQ, Sun S. Calcitonin protects chondrocytes from lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response through MAPK/Wnt/NF-κB pathways. Mol Immunol 2017;87:249–57.
Talavera MM, Kralik N, Jin Y, Chen B, Liu Y, Nelin LD. Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis in immature rat intestinal epithelial cells. Pediatr Res 2015;78(2):128–36.
Wang Y, Li B, Zhu J, Zhang Q, Zhang X, Li L, et al. Lonicera caerulea berry extract suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via Toll-like receptor and oxidative stress-associated mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Food Funct 2016;7(10):4267–77.
Cho H, Park JH, Ahn EK, Oh JS. Kobophenol A isolated from roots of Caragana sinica (Buc’hoz) Rehder exhibits anti-inflammatory activity by regulating NF-κB nuclear translocation in J774A.1 cells. Toxicol Rep 2018;5:647–53.
Schindler JF, Monahan JB, Smith WG. p38 pathway kinases as anti-inflammatory drug targets. J Dent Res 2007;86(9):800–11.
Kumar S, Boehm J, Lee JC. p38 MAP kinases: key signalling molecules as therapeutic targets for inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2003;2(9):717–26.
Chen XJ, Tang ZZ, Zhu GG, Cheng Q, Zhang WK, Li HM, et al. JNK signaling is required for the MIP-1α-associated regulation of Kupffer cells in the heat stroke response. Mol Med Rep 2017;16(3):2389–96.
Guo Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Guo X, Zhang H, Zheng G, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 (IGFBPrP1) contributes to liver inflammation and fibrosis via activation of the ERK1/2 pathway. Hepatol Int 2015;9(1):130–41.
Clichici S, Olteanu D, Filip A, Nagy AL, Oros A, Mircea PA. Beneficial effects of silymarin after the discontinuation of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. J Med Food 2016;19(8):789–97.
Shu M, Huang DD, Hung ZA, Hu XR, Zhang S. Inhibition of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways alleviate carbon tetrachloride (CC14)-induced liver fibrosis in Toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) deficiency mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016;471(1):233–9.
Canbay A, Feldstein A, Baskin-Bey E, Bronk SF, Gores GJ. The caspase inhibitor IDN-6556 attenuates hepatic injury and fibrosis in the bile duct ligated mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2004;308(3):1191–6.
Wang R, Zhang H, Wang Y, Song F, Yuan Y. Inhibitory effects of quercetin on the progression of liver fibrosis through the regulation of NF-κB /IκBα, p38 MAPK, and Bcl-2/Bax signaling. Int Immunopharmacol 2017;47:126–33.
Li C, Luo J, Li L, Cheng M, Huang N, Liu J, et al. The collagenolytic effects of the traditional Chinese medicine preparation, Han-Dan-Gan-Le, contribute to reversal of chemical-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Life Sci 2003;72(14):1563–71.
Bunting K, Rao S, Hardy K, Woltring D, Denyer GS, Wang J, et al. Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in T cells to identify targets of the NF-kappa B transcription factor c-Rel. J Immunol 2007;178(11):7097–109.
Wang S, Hibberd ML, Pettersson S, Lee YK. Enterococcus faecalis from healthy infants modulates inflammation through MAPK signaling pathways. PLoS One 2014;9(5)e97523.
Karunakaran S, Ravindranath V. Activation of p38 MAPK in the substantia nigra leads to nuclear translocation of NF-κB in MPTP-treated mice: implication in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 2009;109(6):1791–9.
Lee SM, Kim EJ, Suk K, Lee WH. Stimulation of Fas (CD95) induces production of pro-inflammatory mediators through ERK/JNK-dependent activation of NF-κB in THP-1 cells. Cell Immunol 2011;271(1):157–62.
Wasmuth HE, Weiskirchen R. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: modulation of stellate cells by chemokines. Z Gastroenterol 2010;48(1):38–45.
Kitano M, Bloomston PM. Hepatic stellate cells and microRNAs in pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. J Clin Med 2016;5(3):38.
Taylor RC, Cullen SP, Martin SJ. Apoptosis: controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008;9(3):231–41.
Jin S, Dai CL. Attenuation of reperfusion-induced hepatocyte apoptosis is associated with reversed bcl-2/bax ratio in hemi-hepatic artery-preserved portal occlusion. J Surg Res 2012;174(2):298–304.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, B., Wang, R., Li, S. et al. Antifibrotic effects of Fraxetin on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis by targeting NF-κB/IκBα, MAPKs and Bcl-2/Bax pathways. Pharmacol. Rep 71, 409–416 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2019.01.008
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2019.01.008