Abstract
Background
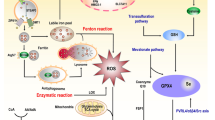
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a redox-sensitive transcription factor regulating the expression of various cytoprotective genes. Constitutive Nrf2 activation in many cancers enhances cell survival and resistance to anti-cancer drugs. Our previous studies have shown that FTY720 induced autophagy-related apoptosis and necroptosis and inhibited invasion and migration in human glioblastoma cells. However, whether FTY720 regulated Nrf2 in glioblastoma cells remained unclear.
Methods
Cell viability assay, western blot, migration and invasion assay, short hairpin RNA (shRNA) were used.
Results
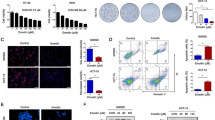
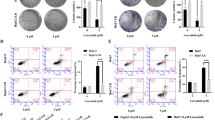
We found that FTY720 suppressed the protein and mRNA levels of Nrf2 in human U251MG and U87MG glioblastoma cells lines. In addition, the protein and mRNA levels of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and NADPH:quinine oxidoreductase-1 (NQO-1), two representative target factors of Nrf2, also decreased upon FTY720 treatment. Knockdown of Nrf2 further promoted the anti-cancer effects of FTY720, while activation of Nrf2 exist the opposite effects. In addition, FTY720 significantly sensitized glioblastoma cells to temozolomide (TMZ). However, activation of Nrf2 essentially abolished the induced sensitivity by FTY720.
Conclusion
Our results indicated the potential application of FTY720 in treatment of glioblastoma and demonstrated that inhibition of Nrf2 can enhance the sensitivity of cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Germano IM, Emdad L, Qadeer ZA, Binello E, Uzzaman M. Embryonic stem cell (ESC)-mediated transgene delivery induces growth suppression, apoptosis and radiosensitization, and overcomes temozolomide resistance in malignant gliomas. Cancer Gene Ther 2010;17(9):664–74.
Zhang L, Wang H, Zhu J, Ding K, Xu J. FTY720 reduces migration and invasion of human glioblastoma cell lines via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway. Tumour Biol 2014;35(11):10707–14.
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY, Olson JJ. Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin 2010;60(3):166–93.
Moi P, Chan K, Asunis I, Cao A, Kan YW. Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994;91(21):9926–30.
Villeneuve NF, Lau A, Zhang DD. Regulation of the Nrf2-Keap1 antioxidant response by the ubiquitin proteasome system: an insight into cullin-ring ubiquitin ligases. Antioxid Redox Signal 2010;13(11):1699–712.
Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M, Zenke Y, Chiba T, et al. Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol 2004;24(16):7130–9.
de Vries HE, Witte M, Hondius D, Rozemuller AJ, Drukarch B, Hoozemans J, et al. Nrf2-induced antioxidant protection: a promising target to counteract ROS-mediated damage in neurodegenerative disease? Free Radic Biol Med 2008;45(10):1375–83.
Chen CY, Jang JH, Li MH, Surh YJ. Resveratrol upregulates heme oxygenase-1 expression via activation of NF-E2-related factor 2 in PC12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005;331(4):993–1000.
Higgins LG, Cavin C, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Hayes JD. Induction of cancer chemopreventive enzymes by coffee is mediated by transcription factor Nrf2. Evidence that the coffee-specific diterpenes cafestol and kahweol confer protection against acrolein. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2008;226(3):328–37.
Kensler TW, Curphey TJ, Maxiutenko Y, Roebuck BD. Chemoprotection by organosulfur inducers of phase 2 enzymes: dithiolethiones and dithiins. Drug Metabol Drug Interact 2000;17(1–4):3–22.
Balogun E, Hoque M, Gong P, Killeen E, Green CJ, Foresti R, et al. Curcumin activates the haem oxygenase-1 gene via regulation of Nrf2 and the antioxidant-responsive element. Biochem J 2003;371(Pt 3):887–95.
Satoh T, Kosaka K, Itoh K, Kobayashi A, Yamamoto M, Shimojo Y, et al. Carnosic acid, a catechol-type electrophilic compound, protects neurons both in vitro and in vivo through activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway via S-alkylation of targeted cysteines on Keap1. J Neurochem 2008;104(4):1116–31.
Ben-Dor A, Steiner M, Gheber L, Danilenko M, Dubi N, Linnewiel K, et al. Carotenoids activate the antioxidant response element transcription system. Mol Cancer Ther 2005;4(1):177–86.
Becks L, Prince M, Burson H, Christophe C, Broadway M, Itoh K, et al. Aggressive mammary carcinoma progression in Nrf2 knockout mice treated with 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene. BMC Cancer 2010;10:540.
Khor TO, Huang MT, Prawan A, Liu Y, Hao X, Yu S, et al. Increased susceptibility of Nrf2 knockout mice to colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2008;1(3):187–91.
Zhang C, Wang HJ, Bao QC, Wang L, Guo TK, Chen WL, et al. NRF2 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by increasing RhoA/ROCK pathway signal transduction. Oncotarget 2016;7(45):73593–606.
Chio II, Jafarnejad SM, Ponz-Sarvise M, Park Y, Rivera K, Palm W, et al. NRF2 promotes tumor maintenance by modulating mRNA translation in pancreatic cancer. Cell 2016;166(4):963–76.
Tian Y, Wu K, Liu Q, Han N, Zhang L, Chu Q, et al. Modification of platinum sensitivity by KEAP1/NRF2 signals in non-small cell lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol 2016;9(1):83.
Khalil HS, Langdon SP, Goltsov A, Soininen T, Harrison DJ, Bown J, et al. A novel mechanism of action of HER2 targeted immunotherapy is explained by inhibition of NRF2 function in ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016;7(46):75874–901.
Menegon S, Columbano A, Giordano S. The dual roles of NRF2 in cancer. Trends Mol Med 2016;22(7):578–93.
Hayes JD, McMahon M. NRF2 and KEAP1 mutations: permanent activation of an adaptive response in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci 2009;34(4):176–88.
Hayes JD, McMahon M. The double-edged sword of Nrf2: subversion of redox homeostasis during the evolution of cancer. Mol Cell 2006;21(6):732–4.
Pan H, Wang H, Zhu L, Mao L, Qiao L, Su X. The role of Nrf2 in migration and invasion of human glioma cell U251. World Neurosurg 2013;80(3–4):363–70.
Pan H, Wang H, Zhu L, Wang X, Cong Z, Sun K, et al. The involvement of Nrf2-ARE pathway in regulation of apoptosis in human glioblastoma cell U251. Neurol Res 2013;35(1):71–8.
Shen Y, Cai M, Xia W, Liu J, Zhang Q, Xie H, et al. FTY720, a synthetic compound from Isaria sinclairii, inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett 2007;254(2):288–97.
Zhang L, Wang HD, Ji XJ, Cong ZX, Zhu JH, Zhou Y. FTY720 for cancer therapy (review). Oncol Rep 2013;30(6):2571–8.
Pitman MR, Woodcock JM, Lopez AF, Pitson SM. Molecular targets of FTY720 (fingolimod). Curr Mol Med 2012;12(10):1207–19.
Brinkmann V, Davis MD, Heise CE, Albert R, Cottens S, Hof R, et al. The immune modulator FTY720 targets sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. J Biol Chem 2002;277(24):21453–7.
Mehling M, Johnson TA, Antel J, Kappos L, Bar-Or A. Clinical immunology of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator fingolimod (FTY720) in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2011;76(8 Suppl. 3):S20–7.
Chiba K, Matsuyuki H, Maeda Y, Sugahara K. Role of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor type 1 in lymphocyte egress from secondary lymphoid tissues and thymus. Cell Mol Immunol 2006;3(1):11–9.
Sonoda Y, Yamamoto D, Sakurai S, Hasegawa M, Aizu-Yokota E, Momoi T, et al. FTY720, a novel immunosuppressive agent, induces apoptosis in human glioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001;281(2):282–8.
Azuma H, Takahara S, Ichimaru N, Wang JD, Itoh Y, Otsuki Y, et al. Marked prevention of tumor growth and metastasis by a novel immunosuppressive agent, FTY720, in mouse breast cancer models. Cancer Res 2002;62(5):1410–9.
Chua CW, Lee DT, Ling MT, Zhou C, Man K, Ho J, et al. FTY720, a fungus metabolite, inhibits in vivo growth of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 2005;117(6):1039–48.
Lee TK, Man K, Ho JW, Sun CK, Ng KT, Wang XH, et al. FTY720 induces apoptosis of human hepatoma cell lines through PI3-K-mediated Akt dephosphorylation. Carcinogenesis 2004;25(12):2397–405.
Zhang L, Wang H, Ding K, Xu J. FTY720 induces autophagy-related apoptosis and necroptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Toxicol Lett 2015;236(1):43–59.
Sukumari-Ramesh S, Prasad N, Alleyne CH, Vender JR, Dhandapani KM. Overexpression of Nrf2 attenuates Carmustine-induced cytotoxicity in U87MG human glioma cells. BMC Cancer 2015;15:118.
Zhou Y, Wang HD, Zhu L, Cong ZX, Li N, Ji XJ, et al. Knockdown of Nrf2 enhances autophagy induced by temozolomide in U251 human glioma cell line. Oncol Rep 2013;29(1):394–400.
Zhang L, Wang H, Xu J, Zhu J, Ding K. Inhibition of cathepsin S induces autophagy and apoptosis in human glioblastoma cell lines through ROS-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and JNK signaling pathways. Toxicol Lett 2014;228(3):248–59.
Liu Q, Alinari L, Chen CS, Yan F, Dalton JT, Lapalombella R, et al. FTY720 shows promising in vitro and in vivo preclinical activity by downmodulating Cyclin D1 and phospho-Akt in mantle cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2010;16(12):3182–92.
Zhou S, Ye W, Shao Q, Zhang M, Liang J. Nrf2 is a potential therapeutic target in radioresistance in human cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2013;88(3):706–15.
Mendichovszky I, Jackson A. Imaging hypoxia in gliomas. Br J Radiol 2011;84(2):S145–58.
Noda NN, Kumeta H, Nakatogawa H, Satoo K, Adachi W, Ishii J, et al. Structural basis of target recognition by Atg8/LC3 during selective autophagy. Genes Cells 2008;13(12):1211–8.
Larsen KB, Lamark T, Overvatn A, Harneshaug I, Johansen T, Bjorkoy G. A reporter cell system to monitor autophagy based on p62/SQSTM1. Autophagy 2010;6(6):784–93.
Puissant A, Fenouille N, Auberger P. When autophagy meets cancer through p62/SQSTM1. Am J Cancer Res 2012;2(4):397–413.
Fan W, Tang Z, Chen D, Moughon D, Ding X, Chen S, et al. Keap1 facilitates p62-mediated ubiquitin aggregate clearance via autophagy. Autophagy 2010;6(5):614–21.
White C, Alshaker H, Cooper C, Winkler M, Pchejetski D. The emerging role of FTY720 (Fingolimod) in cancer treatment. Oncotarget 2016;7(17):23106–27.
Davis ME. Glioblastoma: overview of disease and treatment. Clin J Oncol Nurs 2016;20(5):S2–8.
Estrada-Bernal A, Palanichamy K, Ray Chaudhury A, Van Brocklyn JR. Induction of brain tumor stem cell apoptosis by FTY720: a potential therapeutic agent for glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 2012;14(4):405–15.
Homma S, Ishii Y, Morishima Y, Yamadori T, Matsuno Y, Haraguchi N, et al. Nrf2 enhances cell proliferation and resistance to anticancer drugs in human lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2009;15(10):3423–32.
Wang XJ, Sun Z, Villeneuve NF, Zhang S, Zhao F, Li Y, et al. Nrf2 enhances resistance of cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs, the dark side of Nrf2. Carcinogenesis 2008;29(6):1235–43.
Shibata T, Kokubu A, Gotoh M, Ojima H, Ohta T, Yamamoto M, et al. Genetic alteration of Keap1 confers constitutive Nrf2 activation and resistance to chemotherapy in gallbladder cancer. Gastroenterology 2008;135(4)1358–68 68, e1–e4.
Zhang P, Singh A, Yegnasubramanian S, Esopi D, Kombairaju P, Bodas M, et al. Loss of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 function in prostate cancer cells causes chemoresistance and radioresistance and promotes tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther 2010;9(2):336–46.
Rocha CR, Kajitani GS, Quinet A, Fortunato RS, Menck CF. NRF2 and glutathione are key resistance mediators to temozolomide in glioma and melanoma cells. Oncotarget 2016;7(30):48081–92.
Cong ZX, Wang HD, Zhou Y, Wang JW, Pan H, Zhang DD, et al. Temozolomide and irradiation combined treatment-induced Nrf2 activation increases chemoradiation sensitivity in human glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol 2014;116(1):41–8.
Ma L, Liu J, Zhang X, Qi J, Yu W, Gu Y. p38 MAPK-dependent Nrf2 induction enhances the resistance of glioma cells against TMZ. Med Oncol 2015;32(3):69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Wang, H. FTY720 inhibits the Nrf2/ARE pathway in human glioblastoma cell lines and sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide. Pharmacol. Rep 69, 1186–1193 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.07.003
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.07.003