Abstract
Background
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most malignant and invasive human brain tumor and it is characterized by a poor prognosis and short survival time. The PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway plays a crucial role in GBM development and it is connected with the regulation of apoptosis and autophagy. Akt is involved in various aspects of cancer cell biology such as cell survival, in addition to both apoptosis and autophagy.
The current study was undertaken to examine the effect of the siRNAs that target AKT3 and PI3KCA genes on the apoptosis and autophagy of T98G cells.
Methods
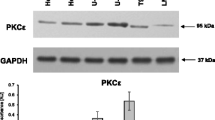
T98G cells were transfected with AKT3 and/or PI3KCA siRNAs. Alterations in the mRNA expression of apoptosis- and autophagy-related genes were analyzed using QRT-PCR. LC3IIA protein-positive cells were identified using flow cytometry with specific antibodies.
Results
Our findings demonstrate for the first time that the siRNAs that target AKT3 and PI3KCA change the expression of the genes that are related to apoptosis and autophagy and change the expression of the LC3IIA protein in T98G cells.
Conclusions
Thus, there is a high probability that the knockdown of these genes induces apoptosis and autophagy in T98G cells, but further studies are necessary in order to clarify and check whether autophagy induction is a positive phenomenon for the treatment of GBM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mrugala MM. Advances and challenges in the treatment of glioblastoma: a clinician’s perspective. Discov Med 2013;15:221–30.
Burris HA. Overcoming acquired resistance to anticancer therapy: focus on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2013;71:829–42.
Sami A, Karsy M. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in glioblastoma: novel therapeutic agents and advances in understanding. Tumour Biol 2013;34:1991–2.
Mure H, Matsuzaki K, Kitazato KT, Mizobuchi Y, Kuwayama K, Kageji T, et al. Akt2 and Akt3 play a pivotal role in malignant gliomas. Neuro-oncol 2010;12:221–32.
Hafsi S, Pezzino FM, Candido S, Ligresti G, Spandidos DA, Soua Z, et al. Gene alterations in the PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathway as a mechanism of drug-resistance. Int J Oncol 2012;40:639–44 [Review].
Tanaka S, Louis DN, Curry WT, Batchelor TT, Dietrich J. Diagnostic and therapeutic avenues for glioblastoma: no longer a dead end? Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2013;10:14–26.
Weber GL, Parat M-O, Binder ZA, Gallia GL, Riggins GJ. Abrogation of PI3KCA or PIK3R1 reduces proliferation, migration and invasion in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Oncotarget 2011;2:833–49.
Zhou X-K, Tang S-S, Yi G, Hou M, Chen J-H, Yang B, et al. RNAi knockdown of PI3KCA preferentially inhibits invasion of mutant PI3KCA cells. World J Gastroenterol 2011;17:3700–8.
Mitsutoshi N, Daisuke K, Takuya W, Yutaka H, Lei T, Ilya VP. Aberrant signaling pathways in glioma. Cancers 2011;3(3):3242–78.
Knobbe CB, Reifenberger G. Genetic alterations and aberrant expression of genes related to the phosphatidyl-inositol-3′-kinase/protein kinase B (Akt) signal transduction pathway in glioblastomas. Brain Pathol 2003;13:507–18.
Mendoza MC, Blenis J. PHLPPing it off: phosphatases get in the Akt. Mol Cell 2007;25:798–800.
Duronio V. The life of a cell: apoptosis regulation by the PI3K/PKB pathway. Biochem J 2008;415:333–44.
Parcellier A, Tintignac LA, Zhuravleva E, Hemmings BA. PKB and the mitochondria: AKTing on apoptosis. Cell Signal 2008;20:21–30.
Fulda S. Modulation of mitochondrial apoptosis by PI3K inhibitors. Mitochondrion 2013;13:195–8.
Fan Q-W, Weiss WA. Targeting the RTK-PI3K-mTOR axis in malignant glioma: overcoming resistance. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2010;347:279–96.
Laplante M, Sabatini DM. Regulation of mTORC1 and its impact on gene expression at a glance. J Cell Sci 2013;126:1713–9.
Stein GH. T98G: an anchorage-independent human tumor cell line that exhibits stationary phase G1 arrest in vitro. J Cell Physiol 1979;99:43–54.
Paul-Samojedny M, Suchanek R, Borkowska P, Pudełko A, Owczarek A, Kowalczyk M, et al. Knockdown of AKT3 (PKBγ) and PI3KCA suppresses cell viability and proliferation and induces the apoptosis of glioblastoma multiforme T98G cells. Biomed Res Int 2014;2014:1–12 [ID 768181].
Tanida I, Ueno T, Kominami E. LC3 conjugation system in mammalian autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2004;36:2503–18.
He H, Dang Y, Dai F, Guo Z, Wu J, She X, et al. Post-translational modifications of three members of the human MAP1LC3 family and detection of a novel type of modification for MAP1LC3B. J Biol Chem 2003;278(31):29278–87.
Sukhdeo K, Paramban RI, Vidal JG, Elia J, Martin J, Rivera M, et al. Multiplex flow cytometry barcoding and antibody arrays identify surface antigen profiles of primary and metastatic colon cancer cell lines. PLOS ONE 2013;8(1):e53015.
Ziegler DS, Kung AL, Kieran MW. Anti-apoptosis mechanisms in malignant gliomas. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:493–500.
Lefranc F, Facchini V, Kiss R. Proautophagic drugs: a novel means to combat apoptosis-resistant cancers, with a special emphasis on glioblastomas. Oncologist 2007;12:1395–403.
Gozuacik D, Kimchi A. Autophagy as a cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism. Oncogene 2004;23:2891–6.
Ren Y, Huang F, Liu Y, Yang Y, Jiang Q, Xu C. Autophagy inhibition through PI3K/Akt increases apoptosis by sodium selenite in NB4 cells. BMB Rep 2009;42:599–604.
Klionsky DJ, Meijer AJ, Codogno P. Autophagy and p70S6 kinase. Autophagy 2005;1:59–60.
Degenhardt K, Mathew R, Beaudoin B, Bray K, Anderson D, Chen G, et al. Autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and restricts necrosis, inflammation and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2006;10:51–64.
Degtyarev M, De Mazière A, Klumperman J, Bray K, Anderson D, Chen G, et al. Autophagy, an achilles’ heel AKTing against cancer? Autophagy 2009;5:415–8.
González-Polo R-A, Boya P, Pauleau A-L, Jalil A, Larochette N, Souquère S, et al. The apoptosis/autophagy paradox: autophagic vacuolization before apoptotic death. J Cell Sci 2005;118:3091–102.
Janku F, McConkey DJ, Hong DS, Kurzrock R. Autophagy as a target for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2011;8:528–39.
Amaravadi RK, Yu D, Lum JJ, Bui T, Christophorou MA, Evan GI, et al. Autophagy inhibition enhances therapy-induced apoptosis in a Myc-induced model of lymphoma. J Clin Investig 2007;117:326–36.
Lemasters JJ, Nieminen AL, Qian T, Trost LC, Elmore SP, Nishimura Y, et al. The mitochondrial permeability transition in cell death: a common mechanism in necrosis, apoptosis and autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998;1366:177–96.
Zhu Y, Zhao L, Liu L, Gao P, Tian W, Wang X, et al. Beclin 1 cleavage by caspase-3 inactivates autophagy and promotes apoptosis. Protein Cell 2010;1:468–77.
Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S, Gao P, Tian W, Wang X, et al. Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy: cross talk, shortcuts and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol 2012;32:2–11.
Chan EY, Tooze SA. Evolution of Atg1 function and regulation. Autophagy 2009;5:758–65.
Hara T, Mizushima N. Role of ULK-FIP200 complex in mammalian autophagy: FIP200, a counterpart of yeast Atg17? Autophagy 2009;5:85–7.
Sinha S, Levine B. The autophagy effector Beclin 1: a novel BH3-only protein. Oncogene 2008;27(Suppl. 1):S137–48.
Strappazzon F, Vietri-Rudan M, Campello S, Nazio F, Florenzano F, Fimia GM. Mitochondrial BCL-2 inhibits AMBRA1-induced autophagy. EMBO J 2011;30: 1195–208.
Fimia GM, Stoykova A, Romagnoli A, Giunta L, Di Bartolomeo S, Nardacci R, et al. Ambra1 regulates autophagy and development of the nervous system. Nature 2007;447:1121–5.
Fimia GM, Corazzari M, Antonioli M, Piacentini M. Ambra1 at the crossroad between autophagy and cell death. Oncogene 2013;32:3311–8.
Rubinfeld B, Albert I, Porfiri E, Fiol C, Munemitsu S, Polakis P. Binding of GSK3beta to the APC-beta-catenin complex and regulation of complex assembly. Science 1996;272:1023–6.
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT, Tang D. The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 2011;18:571–80.
Oberstein A, Jeffrey PD, Shi Y. Crystal structure of the Bcl-XL-Beclin 1 peptide complex: Beclin 1 is a novel BH3-only protein. J Biol Chem 2007;282: 13123–32.
Pattingre S, Levine B. Bcl-2 inhibition of autophagy: a new route to cancer? Cancer Res 2006;66:2885–8.
Miracco C, Cosci E, Oliveri G, Luzi P, Pacenti L, Monciatti I, et al. Protein and mRNA expression of autophagy gene Beclin 1 in human brain tumours. Int J Oncol 2007;30:429–36.
Sun Q, Fan W, Zhong Q. Regulation of Beclin 1 in autophagy. Autophagy 2009;5:713–6.
Zhao Z, Ni D, Ghozalli I, Pirooz SD, Ma B, Liang C. UVRAG: at the crossroad of autophagy and genomic stability. Autophagy 2012;8:1392–3.
Yin X, Cao L, Peng Y, Tan Y, Xie M, Kang R, et al. A critical role for UVRAG in apoptosis. Autophagy 2011;7:1242–4.
Kanzawa T, Zhang L, Xiao L, Germano IM, Kondo Y, Kondo S. Arsenic trioxide induces autophagic cell death in malignant glioma cells by upregulation of mitochondrial cell death protein BNIP3. Oncogene 2005;24:980–91.
Burton TR, Eisenstat DD, Gibson SB. BNIP3 (Bcl-2 19 kDa interacting protein) acts as transcriptional repressor of apoptosis-inducing factor expression preventing cell death in human malignant gliomas. J Neurosci 2009;29:4189–99.
Seglen PO, Gordon PB. 3-Methyladenine: specific inhibitor of autophagic/lysosomal protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1982;79:1889–92.
Yamamoto A, Tagawa Y, Yoshimori T, Moriyama Y, Masaki R, Tashiro Y. Bafilomycin A1 prevents maturation of autophagic vacuoles by inhibiting fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes in rat hepatoma cell line, H-4-II-E cells. Cell Struct Funct 1998;23:33–42.
Kanzawa T, Germano IM, Komata T, Ito H, Kondo Y, Kondo S. Role of autophagy in temozolomide-induced cytotoxicity for malignant glioma cells. Cell Death Differ 2004;11:448–57.
Fimia GM, Piacentini M. Regulation of autophagy in mammals and its interplay with apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2010;201(67):1581–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul-Samojedny, M., Pudełko, A., Kowalczyk, M. et al. Knockdown of AKT3 and PI3KCA by RNA interference changes the expression of the genes that are related to apoptosis and autophagy in T98G glioblastoma multiforme cells. Pharmacol. Rep 67, 1115–1123 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2015.04.012
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2015.04.012