Abstract
Background
Modulation of the endocannabinoid (eCB) transmission is a promising approach to treating epilepsy. Animal models can be used to investigate this approach. Krushinsky-Molodkina (KM) rats have, genetically, audiogenic epilepsy. Moreover, in these animals, repeated induction of audiogenic seizures results in a progressive prolongation of the seizures, known as audiogenic kindling.
Methods
The present study evaluated, in these KM rats, acute and long-term effects of a single dose of 4 mg/kg of the cannabinoid-receptor agonist WIN55,212-2.
Results
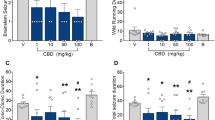
Administration of the single dose of WIN55,212-2 one hour before the 4th seizure delayed the kindling process by two weeks, without any acute effect on the audiogenic seizures.
Conclusions
This result suggests that short-term potentiation of the eCB system might modify the epileptogenic disease process in patients with a progressive course of epilepsy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hofmann ME, Frazier CJ. Marijuana endocannabinoids, and epilepsy: potential and challenges for improved therapeutic intervention. Exp Neurol 2013;244:43–50.
Alger BE. Endocannabinoids at the synapse a decade after the dies mirabilis (29 March 2001): what we still do not know. J Physiol 2012;590(Pt 10): 2203–12.
Katona I, Freund TF. Multiple functions of endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 2012;35:529–58.
Wallace MJ, Blair RE, Falenski KW, Martin BR, DeLorenzo RJ. The endogenous cannabinoid system regulates seizure frequency and duration in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003;307(1):129–37.
Chen K, Neu A, Howard AL, Foldy C, Echegoyen J, Hilgenberg L, et al. Prevention of plasticity of endocannabinoid signaling inhibits persistent limbic hyperexcitability caused by developmental seizures. J Neurosci 2007;27(1):46–58.
Echegoyen J, Armstrong C, Morgan RJ, Soltesz I. Single application of a CB1 receptor antagonist rapidly following head injury prevents long-term hyperexcitability in a rat model. Epilepsy Res 2009;85(1):123–7.
Mechoulam R, Lichtman AH. Neuroscience. Stout guards of the central nervous system. Science 2003;302(5642):65–7.
van Rijn CM, Perescis MF, Vinogradova L, van Luijtelaar G. Endocannabinoid system protects against cryptogenic seizures. Pharmacol Rep 2011;63(1):165–8.
Wendt H, Soerensen J, Wotjak CT, Potschka H. Targeting the endocannabinoid system in the amygdala kindling model of temporal lobe epilepsy in mice. Epilepsia 2011;52(7):e62–5.
Romanova LG, Zorina ZA, Korochkin LI. A genetic, physiological, and biochemical investigation of audiogenic seizures in rats. Behav Genet 1993;23(5):483–9.
Faingold CL. Emergent properties of CNS neuronal networks as targets for pharmacology: application to anticonvulsant drug action. Prog Neurobiol 2004;72(1):55–85.
Vinogradova LV, van Rijn CM. Anticonvulsive and antiepileptogenic effects of levetiracetam in the audiogenic kindling model. Epilepsia 2008;49(7):1160–8.
Jobe PC, Picchioni AL, Chin L. Role of brain norepinephrine in audiogenic seizure in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1973;184(1):1–10.
Hirsch E, Danober L, Simler S, Pereira de Vasconcelos A, Maton B, Nehlig A, et al. The amygdala is critical for seizure propagation from brainstem to forebrain. Neuroscience 1997;77(4):975–84.
Tupal S, Faingold CL. Precipitous induction of audiogenic kindling by activation of adenylyl cyclase in the amygdala. Epilepsia 2010;51(3):354–61.
Vinogradova LV, Shatskova AB, van Rijn CM. Pro-epileptic effects of the cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR141716 in a model of audiogenic epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 2011;96(3):250–6.
Ramikie TS, Patel S. Endocannabinoid signaling in the amygdala: anatomy, synaptic signaling, behavior, and adaptations to stress. Neuroscience 2012;204:38–52 [Review].
Tsou K, Brown S, Sanudo-Pena MC, Mackie K, Walker JM. Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 1998;83(2):393–411.
Gaffuri AL, Ladarre D, Lenkei Z. Type-1 cannabinoid receptor signaling in neuronal development. Pharmacology 2012;90(1–2):19–39 [Review].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinogradova, L.V., van Rijn, C.M. Long-term disease-modifying effect of the endocannabinoid agonist WIN55,212-2 in a rat model of audiogenic epilepsy. Pharmacol. Rep 67, 501–503 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.12.002
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.12.002