Abstract
Background
A preliminary evaluation of antinociceptive activity of a new cyclic dermorphin/deltorphin tetrapeptide analog restricted via a urea bridge and containing C-terminal ureidoethylamid {[H-Tyr-d-Lys(&1)-Phe-Dab(&2)-CH2CH2NHCONH2][&1CO&2]} (cUP-1) revealed a significant and long-lasting increase of pain threshold to thermal stimulation after systemic application. The current studies were aimed at further evaluation of cUP-1 activity in animal models of somatic and visceral pain. The influence of cUP-1 on motor functions was also investigated.
Methods
The influence of cUP-1 (0.5–2 mg kg−1, iv) on nociceptive threshold to mechanical pressure and analgesic efficacy in formalin and acetic acid-induced writhing tests were estimated. The antinociceptive effect of cUP-1 was compared to that of morphine (MF). The influence of cUP-1 (1, 4 and 8 mg kg−1, iv) on locomotor activity, motor coordination and muscle strength was estimated using open field and rota-rod tests and a grip strength measurement.
Results
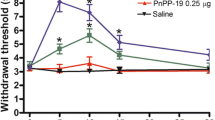
Administration of cUP-1 in doses of 1 and 2 mg kg−1 elicited a significant increase of nociceptive threshold to mechanical pressure. MF applied in the same doses induced an antinociceptive effect only at the higher dose (2 mg kg−1). There were no marked differences between the effect of cUP-1 and MF at each dose, at relative time points. In the writhing test and both phases of the formalin test, cUP-1 showed a significant, dose-dependent antinociceptive effect which did not markedly differ from that of MF. cUP-1 did not significantly affect motor functions of mice.
Conclusions
Systemic application of cUP-1 elicited a dose-dependent antinociceptive effect. The analgesic efficacy of cUP-1 on mechanical nociception, visceral and formalin-induced pain was comparable to that of MF. cUP-1 did not impair motor functions of mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cherny N, Ripamonti C, Pereira J, Davis C, Fallon M, McQuay H, et al. Strategies to manage the adverse effects of oral morphine: an evidence-based report. J Clin Oncol 2001;19(9):2542–54.
Wilson PR. Complications of opiate pharmacotherapy. Semin Pain Med 2004;2(4):228–32.
Kreil G, Barra D, Simmaco M, Erspamer V, Erspamer GF, Negri L, et al. Deltorphin, a novel amphibian skin peptide with high selectivity and affinity for delta opioid receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 1989;162(1):123–8.
Montecucchi PC, de Castiglione R, Piani S, Gozzini L, Erspamer V. Amino acid composition and sequence of dermorphin, a novel opiate-like peptide from the skin of Phyllomedusa sauvagei. Int J Pept Protein Res 1981;17(3):275–83.
Erspamer V, Melchiorri P, Falconieri-Erspamer G, Negri L, Corsi R, Severini C, et al. Deltorphins: a family of naturally occurring peptides with high affinity and selectivity for delta opioid binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989;86:5188–92.
Melchiorri P, Negri L, Falconieri-Erspamer G, Severini C, Corsi R, Soaje M, et al. Structure–activity relationship of the d-opioid-selective agonists, deltorphins. Eur J Pharmacol 1991;195:201–7.
Broccardo M, Erspamer V, Falconieri-Erspamer G, Improta G, Linari G, Melchiorri P, et al. Pharmacological data on dermorphins, a new class of potent opioid peptides from amphibian skin. Br J Pharmacol 1981;73(3):625–31.
Kisara K, Sakurada S, Sakurada T, Sasaki Y, Sato T, Suzuki K, et al. Dermorphin analogues containing d-kyotorphin: structure–antinociceptive relationships in mice. Br J Pharmacol 1986;87(1):183–9.
Negri L, Lattanzi R, Melchiorri P. Production of antinociception by peripheral administration of [Lys7]dermorphin, a naturally occurring peptide with high affinity for mu-opioid receptors. Br J Pharmacol 1995;114(1):57–66.
Lazarus LH, Bryant SD, Cooper PS, Salvadori S. What peptides these deltorphins be. Prog Neurobiol 1999;57(4):377–420.
Negri L, Melchiorri P, Lattanzi R. Pharmacology of amphibian opiate peptides. Peptides 2000;21:1639–47.
Cheng PY, Wu D, Decena J, Soong Y, McCabe S, Szeto HH. Opioid-induced stimulation of fetal respiratory activity by [d-Ala2]deltorphin I. Eur J Pharmacol 1993;230(1):85–8.
Porreca F, Mosberg HI, Hurst R, Hruby VJ, Burks TF. Roles of mu, delta and kappa opioid receptors in spinal and supraspinal mediation of gastrointestinal transit effects and hot-plate analgesia in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1984;230(2):341–8.
Sheldon RJ, Rivière PJ, Malarchik ME, Moseberg HI, Burks TF, Porreca F. Opioid regulation of mucosal ion transport in the mouse isolated jejunum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1990;253(1):144–51.
Cowan A, Zhu XZ, Mosberg HI, Omnaas JR, Porreca F. Direct dependence studies in rats with agents selective for different types of opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1988;246(3):950–5.
Fiori A, Cardelli P, Negri L, Savi MR, Strom R, Erspamer V. Deltorphin transport across the blood–brain barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997;94(17):9469–74.
Negri L, Improta G. Distribution and metabolism of dermorphin in rats. Pharmacol Res Commun 1984;16:1183–94.
Chaki K, Kawamura S, Kisara K, Sakurada S, Sakurada T, Sasaki Y, et al. Antinociception and physical dependence produced by [d-Arg2] dermorphin tetrapeptide analogues and morphine in rats. Br J Pharmacol 1988;95(1):15–22.
Aldrich JV, McLaughlin JP. Opioid peptides: potential for drug development. Drug Discov Today Technol 2012;9(1):e23–31.
Mizoguchi H, Bagetta G, Sakurada T, Sakurada S. Dermorphin tetrapeptide analogs as potent and long-lasting analgesics with pharmacological profiles distinct from morphine. Peptides 2001;1(32):421–7.
Berezowska I, Chung NN, Lemieux C, Wilkes BC, Schiller PW. Cyclic dermorphin tetrapeptide analogues obtained via ring-closing metathesis. Acta Biochim Pol 2006;53(1):73–6.
Ciarkowski J, Zieleniak A, Rodziewicz-Motowidło S, Rusak Ł, Chung NN, Czaplewski C, et al. Deltorphin analogs restricted via a urea bridge: structure and opioid activity. Adv Exp Med Biol 2009;611:491–2.
Filip K, Oleszczuk M, Pawlak D, Wójcik J, Chung NN, Schiller PW, et al. Potent side-chain to side-chain cyclized dermorphin analogues containing a carbonyl bridge. J Pept Sci 2003;9:649–57.
Filip K, Oleszczuk M, Wójcik J, Chung NN, Schiller PW, Pawlak D, et al. Cyclic enkephalin and dermorphin analogues containing a carbonyl bridge. J Pept Sci 2005;11:347–52.
Pawlak D, Chung NN, Schiller PW, Izdebski J. Synthesis of a novel side-chain to side-chain cyclized enkephalin analogue containing a carbonyl bridge. J Pept Sci 1997;3:277–81.
Pawlak D, Oleszczuk M, Wójcik J, Pachulska M, Chung NN, Schiller PW, et al. Highly potent side-chain to side-chain cyclized enkephalin analogues containing a carbonyl bridge: synthesis, biology and conformation. J Pept Sci 2001; 7:128–40.
Perlikowska R, do-Rego JC, Cravezic A, Fichna J, Wyrebska A, Toth G, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of cyclic endomorphin-2 analogs. Peptides 2010;31(2):339–45.
Ro S, Zhu Q, Lee CW, Goodman M, Darlak K, Spatola AF, et al. Highly potent side chain-main chain cyclized dermorphin–deltorphin analogues: an integrated approach including synthesis, bioassays, NMR spectroscopy and molecular modeling. J Pept Sci 1995;3:157–74.
Rodziewicz-Motowidło S, Czaplewski C, Luczak S, Ciarkowski J. Conformation– activity relationships of cyclo-constrained µ/δ opioid agonists derived from the N-terminal tetrapeptide segment of dermorphin/deltorphin. J Pept Sci 2008;14(8):898–902.
Said-Nejad OE, Felder ER, Mierke DF, Yamazaki T, Schiller PW, Goodman M. 14-membered cyclic opioids related to dermorphin and their partially retroinverso modified analogues. I. Synthesis and biological activity. Int J Pept Protein Res 1992;39:145–60.
Schiller PW, Weltrowska G, Nguyen TM, Wilkes BC, Chung NN, Lemieux C. Conformationally restricted deltorphin analogues. J Med Chem 1992;35(21): 3956–61.
Witkowska E, Nowakowski M, Oleszczuk M, Filip K, Ciszewska M, Chung NN, et al. Ureido group containing cyclic dermorphin(1–7) analogues: synthesis, biology and conformation. J Pept Sci 2007;13:519–28.
Zieleniak A, Rodziewicz-Motowidło S, Rusak L, Chung NN, Czaplewski C, Witkowska E, et al. Deltorphin analogs restricted via a urea bridge: structure and opioid activity. J Pept Sci 2008;14(7):830–7.
Kotlinska J, Bochenski M, Lagowska-Lenard M, Gibula-Bruzda E, Witkowska E, Izdebski J. Enkephalin derivative, cyclo[Nepsilon, Nbeta-carbonyl-d-Lys2, Dap5] enkephalinamide (cUENK6), induces a highly potent antinociception in rats. Neuropeptides 2009;43:221–8.
Kotlinska JH, Gibula-Bruzda E, Witkowska E, Chung NN, Schiller PW, Izdebski J. Antinociceptive effects of two deltorphins analogs in the tail-immersion test in rats. Peptides 2013;39:103–10.
Bańkowski K, Witkowska E, Michalak OM, Sidoryk K, Szymanek E, Antkowiak B, et al. Synthesis, biological activity and resistance to proteolytic digestion of new cyclic dermorphin/deltorphin analogues. Eur J Med Chem 2013;63C:457–67.
Ciszewska M, Kwasiborska M, Nowakowski M, Oleszczuk M, Wójcik J, Chung NN, et al. N-(ureidoethyl)amides of cyclic enkephalin analogs. J Pept Sci 2009;15(4):312–8.
Anseloni VC, Ennis M, Lidow MS. Optimization of the mechanical nociceptive threshold testing with the Randall–Selitto assay. J Neurosci Methods 2003;131(1–2):93–7.
Randall LO, Selitto JJ. A method for measurement of analgesic activity of inflammed tissue. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 1957;111:409–15.
Wheeler-Aceto H, Porreca F, Cowan A. The rat paw formalin test: comparison of noxious agents. Pain 1990;40:229–38.
Koster R, Anderson M, DeBeer EJ. Acetic acid for analgesic screening. Fed Proc 1959;18:412.
Tallarida RJ, Murray RB. Manual of pharmacologic calculations with computer programs. 2nd ed. New York: Springer Verlag; 1986.
Royce JR. On the construct validity of open-field measures. Psychol Bull 1977;84(6):1098–106.
Dunham NW, Miya TS. A note on a simple apparatus for detecting neurological deficit in rats and mice. J Am Pharm Assoc 1957;46:208–9.
Usenko AB, Emel’yanova TG, Myasoedov NF. Dermorphins are natural opioids with unique primary structure that determines their biological specificity. Biol Bull 2002;29:154–64.
Ambo A, Niizuma H, Sasaki A, Kohara H, Sasaki Y. Dermorphin tetrapeptide analogues with 2′,6′-dimethylphenylalanine (Dmp) substituted for aromatic amino acids have high mu opioid receptor binding and biological activities. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2003;13(7):1269–72.
Chaki K, Sakurada S, Sakurada T, Sato T, Kawamura S, Kisara K, et al. Comparison of the antinociceptive effects of new [d-Arg2]-dermorphin tetrapeptide analogs and morphine in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1988;31: 439–44.
Chiba T, Murase H, Ambo A, Sasaki Y. Antinociceptive activity of deltorphin analogs in the formalin test. Life Sci 1996;59(20):1717–22.
Hammond DL, Wang H, Nakashima N, Basbaum AI. Differential effects of intrathecally administered delta and mu opioid receptor agonists on formalinevoked nociception and on the expression of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1998;284(1):378–87.
Holdridge SV, Cahill CM. Spinal administration of a delta opioid receptor agonist attenuates hyperalgesia and allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pain 2007;11:685–93.
Łabuz D, Chocyk A, Wędzony K, Toth G, Przewłocka B. Endomorphin-2, deltorphin II and their analogs suppress formalin-induced nociception and c-Fos expression in the rat spinal cord. Life Sci 2003;73(4):403–12.
Łabuz D, Toth G, Machelska H, Przewłocka B, Borsodi A, Przewłocki R. Antinociceptive effects of isoleucine derivatives of deltorphin I and deltorphin II in rat spinal cord: a search for selectivity of delta receptor subtypes. Neuropeptides 1998;32(6):511–7.
Mika J, Przewłocki R, Przewłocka B. The role of delta-opioid receptor subtypes in neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 2001;415(1):31–7.
Otis V, Sarret P, Gendron L. Spinal activation of delta opioid receptors alleviates cancer-related bone pain. Neuroscience 2011;183:221–9.
Piekielna J, Perlikowska R, Gach K, Janecka A. Cyclization in opioid peptides. Curr Drug Targets 2013;14(7):798–816.
Ciszewska M, Ruszczyńska K, Oleszczuk M, Chung NN, Witkowska E, Schiller PW, et al. Cyclic enkephalin-deltorphin hybrids containing a carbonyl bridge: structure and opioid activity. Acta Biochim Pol 2011;58(2):225–30.
Fontani G, Vergnani L, Salvadori S, Voglino N, Aloisi AM, Portaluppi F, et al. Effect of dermorphin on behavior and hippocampal electrical activity in rabbits. Life Sci 1993;52(3):323–8.
Puglisi-Allegra S, Castellano C, Filibeck U, Oliverio A, Melchiorri P. Behavioural data on dermorphins in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 1982;82(3–4):223–7.
Usenko AB, Uranova MG, Emel’yanova TG, Andreeva LA, Alfeeva LYu, Kamenskii AA, et al. Effects of dermorphin and its analogues on spontaneous behavior in white rats. Dokl Biol Sci 2000;370:36–9.
Meyer ME, McLaurin BI, Meyer ME. DALDA (H-Tyr-d-Arg-Phe-Lys-NH2), a potent mu-opioid peptide agonist, affects various patterns of locomotor activities. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1995;51(1):149–51.
Yang YR, Lee EH, Chiu TH. Electrophysiological and behavioral effects of Tyr-d-Arg-Phe-Sar on locus coeruleus neurons of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 1998; 351(1):23–30.
Longoni R, Spina L, Mulas A, Carboni E, Garau L, Melchiorri P, et al. (d-Ala2)-deltorphin II: D1-dependent stereotypies and stimulation of dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 1991;11(6):1565–76.
Negri L, Noviello V, Angelucci F. Behavioural effects of deltorphins in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 1991;209(3):163–8.
Fontani G, Vergnani L, Salvadori S, Voglino N, Aloisi AM, Portaluppi F, et al. Effect of deltorphin on behavior and hippocampal electrical activity in rabbits. Physiol Behav 1993;53:285–90.
Negri L, Noviello L, Noviello V. Antinociceptive and behavioral effects of synthetic deltorphin analogs. Eur J Pharmacol 1996;296(1):9–16.
Beaudry H, Proteau-Gagné A, Li S, Dory Y, Chavkin C, Gendron L. Differential noxious and motor tolerance of chronic delta opioid receptor agonists in rodents. Neuroscience 2009;161(2):381–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antkowiak, B., Paluch, M., Ciechanowska, M. et al. Antinociceptive effect of d-Lys2, Dab4 N-(ureidoethyl)amide, a new cyclic 1-4 dermorphin/deltorphin analog. Pharmacol. Rep 66, 600–605 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.01.007
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.01.007