Abstract
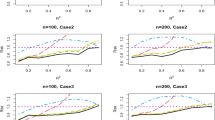
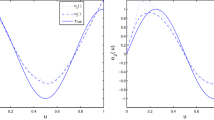
This paper is concerned with model averaging procedure for varying-coefficient partially linear models with missing responses. The profile least-squares estimation process and inverse probability weighted method are employed to estimate regression coefficients of the partially restricted models, in which the propensity score is estimated by the covariate balancing propensity score method. The estimators of the linear parameters are shown to be asymptotically normal. Then we develop the focused information criterion, formulate the frequentist model averaging estimators and construct the corresponding confidence intervals. Some simulation studies are conducted toexamine the finite sample performance of the proposed methods. We find that the covariate balancing propensity score improves the performance of the inverse probability weighted estimator. We also demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model averaging estimators over those of existing strategies in terms of mean squared error and coverage probability. Finally, our approach is further applied to a real data example.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, I., Leelahanon, S., & Li, Q. (2005). Efficient estimation of a semiparametric partially linear varying coefficient model. The Annals of Statistics, 33, 258–283.
Akaike, H. (1973). Maximum likelihood identification of Gaussian autoregressive moving average models. Biometrika, 60, 255–265.
Bravo, F. (2013). Partially linear varying coefficient models with missing at random responses. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 65, 721–762.
Buckland, S. T., Burnham, K. P., & Augustin, N. H. (1997). Model selection: an integral part of inference. Bioemtrics, 53, 603–618.
Burnham, K. P., & Anderson, D. R. (2002). Model selection and multimodel inference: A practical information theoretic approach (second ed.). New York: Springer.
Cai, Z., Fan, J., & Li, R. (2000). Efficient estimation and inferences for varying-coefficient models. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 95, 888–902.
Claeskens, G., & Hjort, N. L. (2003). The focused information criterion (with discussion). Journal of the American Statistical Association, 98, 900–916.
Claeskens, G., & Hjort, N. L. (2008). Model selection and model averaging. New York: Cambridge University Press, (Chapter 6).
Fan, J., & Huang, T. (2005). Profile likelihood inferences on semiparametric varying-coefficient partially linear models. Bernoulli, 11, 1031–1057.
Fan, J., & Li, R. (2004). New estimation and model selection procedures for semiparametric modeling in longitudinal data analysis. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 99, 710–723.
Fan, J., & Zhang, J. (2000). Two-step estimation of functional linear models with applications to longitudinal data. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B., 62, 303–322.
Guo, D., Xue, L., & Hu, Y. (2017). Covariate-balancing-propensity-score-based inference for linear models with missing responses. Statistics & Probability Letters, 123, 139–145.
Hansen, L. P. (1982). Large sample properties of generalized method of moments estimators. Econometrica, 50, 1029–1054.
Hansen, B. E. (2007). Least squares model averaging. Econometrica, 75, 1175–1189.
Hansen, B. E., & Racine, J. (2012). Jackknife model averaging. Journal of Econometrics, 167, 38–46.
Hjort, N. L., & Claeskens, G. (2003). Frequentist model average estimators. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 98, 879–899.
Hjort, N. L., & Claeskens, G. (2006). Focussed information criteria and model averaging for Cox’s hazard regression model. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 101, 1449–1464.
Hoeting, J. A., Madigan, D., Raftery, A. E., & Volinsky, C. T. (1999). Bayesian model averaging: a tutorial. Statistical Science, 14, 382–417.
Huang, J. Z., Wu, C. O., & Zhou, L. (2002). Varying-coefficient models and basis function approximations for the analysis of repeated measurements. Biometrika, 89, 111–128.
Imai, K., & Ratkovic, M. (2014). Covariate balancing propensity score. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B., 76, 243–263.
Kang, J. D., & Schafer, J.L. (2007). Demystifying double robustness:A comparison of alternative strategies for estimating a population mean from incomplete data (with discussion). Statistical Science, 22, 523–539.
Liang, H., Zou, G., Wan, A. T. K., & Zhang, X. (2011). Optimal weight choice for frequentist model average estimators. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 106, 1053–1066.
Mallows, C. L. (1973). Some comments on Cp. Technometrics, 15, 661–675.
Newey, W., & McFadden, D. (1994). Large sample estimation and hypothesis testing. In R. F. Engle, & D. L. McFadden (Eds.), Handbook of econometrics (pp. 2111–2245). Amsterdam: North-Holland.
Peter, B., Gerda, C., & Holger, D. (2014). Focussed model selection in quantile regression. Statistica Sinica, 24, 601–624.
Raftery, A., Madigan, D., & Hoeting, J. (1997). Bayesian model averaging for linear regression models. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 92, 179–191.
Schwarz, G. (1978). Estimating the dimension of a model. The Annals of Statistics, 6, 461–464.
Sun, Z., Su, Z., & Ma, J. (2014). Focused vector information criterion model selection and model averaging regression with missing response. Metrika, 77, 415–432.
Wan, A. T. K., Zhang, X., & Wang, S. (2014). Frequentist model averaging for multinomial and ordered logit models. International Journal of Forecasting, 30, 118–128.
Wan, A. T. K., Zhang, X., & Zou, G. (2010). Least squares model averaging by Mallows criterion. Journal of Econometrics, 122, 277–283.
Wang, Q., Lindon, O. B., & Härdle, W. (2004). Semiparametric regression analysis with missing response at random. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 99, 334–345.
Wang, Q., & Sun, Z. (2007). Estimation in partially linear models with missing responses at random. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 98, 1470–1493.
Wang, H., Zou, G., & Wan, A. T. K. (2012). Model averaging for varying-coefficient partially linear measurement error models. Electronic Journal of Statistics, 2012, 1017–1039.
Xia, Y., Zhang, W., & Tong, H. (2004). Efficient estimation for semivarying-coefficient models. Biometrika, 91, 661–681.
Xue, L., & Zhu, L. (2007). Empirical likelihood for a varying coefficient model with longitudinal data. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 102, 642–654.
You, J., & Chen, G. (2006). Estimation of a semiparametric varying-coefficient partially linear errors-in-variables model. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 97, 324–341.
Zhang, W., Lee, S. Y., & Song, X. (2002). Local polynomial fitting in semiparametric coefficient model. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 82, 166–188.
Zhang, X., & Liang, H. (2011). Focused information criterion and model averaging for generalized additive partial linear models. The Annals of Statistics, 39, 174–200.
Zhang, X., Wan, A. T. K., & Zhou, S. (2012). Focused information criteria, model selection, and model averaging in a Tobit Model with a nonzero threshold. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics, 30, 132–142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, J., Cheng, W., Hu, G. et al. Model averaging procedure for varying-coefficient partially linear models with missing responses. J. Korean Stat. Soc. 47, 379–394 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jkss.2018.04.004
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jkss.2018.04.004