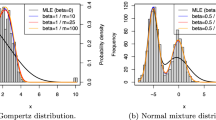
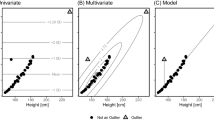
Abstract
Model based regression analysis always requires a certain choice of models which typically specifies the behavior of regression errors. The normal distribution is the most common choice for this purpose, but the estimator under normality is known to be too sensitive to outliers. As an alternative, heavy tailed distributions such as t distributions have been suggested. Though this choice can reduce the sensitivity to outliers, it also requires the choice of distributions and tuning parameters for practical use. In this paper, we propose a class of continuous Gaussian scale mixtures for the error distribution that contains most symmetric unimodal probability distributions including normal, t, Laplace, and stable distributions. With this quite flexible class of error distributions, we provide the asymptotic property and robust property of the proposed method, and show its successes along with numerical examples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, D. F., & Mallows, C. L. (1974). Scale mixtures of normal distributions. Journal of Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 36, 99–102.
Bartolucci, F., & Scaccia, L. (2005). The use of mixtures for dealing with non-normal regression errors. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 48, 821–834.
Beaton, A. E., & Tukey, J. W. (1974). The fitting of power series, meaning polynomials, illustrated on band-spectroscopic data. Technometrics, 16, 147–185.
Bellio, R., & Ventura, L. (2005). An introduction to robust estimaton with Rfuctions. In Proceedings of the 1st international workshop on robust statistics and R. Treviso: Department of Statistics, Ca’Foscari University (Venezia).
Bickel, P. J., Klaassen, C. A. J., Ritov, Y., & Wellner, J. A. (1993). Johns Hopkins series in the mathematical sciences, Efficient and adaptive estimation for semiparametric models. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Brownlee, K. A. (1960). Statistical theory and methodology in science and engineering. New York: John Wiley.
Croux, C., Rousseeuw, P. J., & Hössjer, O. (1994). Generalized s-estimators. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 89, 1271–1281.
Efron, B., & Olshen, R. A. (1978). How broad is the class of normal scale mixtures? Annals of Statistics, 6, 1159–1164.
Ghosal, S., & van der Vaart, A. W. (2001). Entropies and rates of convergence for maximum likelihood and Bayes estimation for mixtures of normal densities. The Annals of Statistics, 29, 1233–1263.
Hathaway, R. J. (1985). A constrained formulation of maximum-likelihood estimation for normal mixture distributions. Annals of Statistics, 13, 795–800.
Holzmann, H., Munk, A., & Gneiting, T. (2006). Identifiability of finite mixtures of elliptical distributions. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 33, 753–763.
Huber, P. J. (1964). Robust estimation of a location parameter. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 35, 73–101.
Huber, P.J. (1973). Robust regreesion: asymptotics, conjectures and monte carlo. Annals of Statistics, 1, 799–821.
Kelker, D. (1971). Infinite divisibility and variance mixtures of the normal distribution. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 42, 802–808.
Kiefer, J., & Wolfowitz, J. (1956). Consistency of the maximum likelihood estimator in the presence of infinitely many incidental parameters. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 27, 886–906.
Krasker, W. S., & Welsch, R. E. (1982). Efficient bounded-influence regression estimation. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 77, 595–607.
Lange, K. L, Little, R. J. A., & Taylor, J. M. G. (1989). Robust statistical modeling using the t distribution. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 84, 881–896.
Lange, K., & Sinsheimer, J. S. (1993). Normal/independent distributions and their applications in robust regression. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2, 175–198.
Lesperance, M. L, & Kalbfleisch, J. D. (1992). An algorithm for computing the nonparametric MLE of a mixing distribution. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 87, 120–126.
Lindsay, B. G. (1995). NSF-CBMS regional conference series in probability and statistics: vol 5. Mixture models: theory, geometry, and applications. US: IMS.
Maronna, R. A., & Yohai, V. J. (1981). Asymtotic behavior of general m-estimates for regression and scale with random carries. Zeitschrift für Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie und verwandte Gebiete, 58, 7–20.
Neyman, J., & Scott, E. L. (1948). Consistent estimation from partially consistent observations. Econometrica, 16, 1–32.
Rousseeuw, P. J., & Leroy, A. M. (1987). Robust regression and outlier detection. New York: Wiley.
Ruppert, D., Cressie, N., & Carroll, R. J. (1989). A transformation/weighting model for estimating michaelis-menten parameters. Biometrics, 45, 637–656.
Soffritti, G., & Galimberti, G. (2011). Multivariate linear regression with non-normal errors: a solution based on mixture models. Statistics and Computing, 21, 523–536.
Stromberg, A. J. (1993). Computation of high breakdown nonlinear regression parameters. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 88, 237–244.
Van der Vaart, A. W. (1988). Estimating a real parameter in a class of semiparametric models. Annnals of Statistics, 16(4), 1450–1474.
Van der Vaart, A. W. (1996). Efficient maximum likelihood estimation in semiparametric mixture models. Annals of Statistics, 24, 862–878.
Van der Vaart, A. W., & Wellner, J. A. (1996). Springer series in statistics, Weak convergence and empirical processes. New York: Springer-Verlag, With applications to statistics.
Wang, Y. (2007). On fast computation of the non-parametric maximum likelihood estimate of a mixing distribution. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 185–198.
West, M. (1984). Outlier models and prior distributions in bayesian liner regression. Journal of Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 46, 431–439.
West, M. (1987). On scale mixtures of normal distributions. Biometrika, 74, 646–648.
Yohai, V.J., & Zamar, R. H. (1988). High breakdown point estimates of regression by means of the minimization of an efficient scale. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 83, 406–413.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, B., Noh, J., Lee, T. et al. Adaptive robust regression with continuous Gaussian scale mixture errors. J. Korean Stat. Soc. 46, 113–125 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jkss.2016.08.002
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jkss.2016.08.002