Abstract
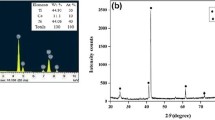
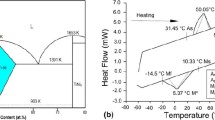
Ni55.8Ti shape memory alloys (SMAs) find applications in different fields of medical and engineering. In every field, surface integrity greatly affects the functional performance of shape memory alloy parts. In the present work, wire spark erosion machining of Ni55.8Ti shape memory alloys has been conducted and surface integrity parameters of the machined specimens have been evaluated. Experiments are designed using Taguchi L16 robust design of experiment technique. Effect of important process parameters, i.e. voltage, pulse-on time and pulse-off time on maximum surface roughness has been studied. Deterioration in surface integrity at various combinations of pulse-on and pulse-of time which produced high discharge energy has been observed. Scanned electron microscopic investigation, energy dispersive spectroscopy and XRD analyses, roughness measurement, and micro-hardness testing results are presented, analyzed and discussed. Optimization of process parameters resulted in surface integrity enhancement with low roughness (Rt - 7.78 μm and Ra - 1.45 μm) and very thin recast layer (4–6 μm) along with minimum subsurface defects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Grzesik, Advanced Machining Processes of Metallic Materials, Elsevier, Netherland, 2016.
J.P. Davim, Machining of Hard Materials, Springer, UK, 2011.
N. Sharma, K.K. Jangra, T. Raj, Fabrications of NiTi alloy: a review, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J. Mater. Des. Appl. 232 (3) (2018) 250–269.
J.M. Jani, M. Leary, A. Subic, M.A. Gibson, A review of shape memory alloy research, applications and opportunities, Mater. Des. 56 (4) (2014) 1078–1113.
K. Mehta, K. Gupta, Fabrication and Processing of Shape Memory Alloys, Springer, Switzerland, 2018.
L. Petrini, F. Migliavacca, Biomedical applications of shape memory alloys, J. Metall. (2011) 15, https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/501483.
M.H. Elahinia, M. Hashemi, M. Tabesh, S.B. Bhaduri, Manufacturing and processing of NiTi implants: a review, Prog. Mater. Sci. 57 (2012) 911–946.
C. Velmurugan, V. Senthilkumar, S. Dinesh, D. Arulkirubakaran, Machining of NiTi shape memory alloys a review, Mach. Sci. Technol. 22 (3) (2018) 355–401.
V. D’Anto, R. Rongo, G. Ametrano, G. Spagnuolo, P. Manzo, R. Martina, S. Paduano, R. Valletta, Evaluation of surface roughness of orthodontic wires by means of atomic force microscopy, Angle Orthodont. 82 (5) (2012), https://doi.org/10.2319/100211-620.1.
Y. Guo, A. Klink, C. Fu, J. Snyder, Machinability and surface integrity of Nitinol shape memory alloy, CIRP Ann. 62 (1) (2013) 83–86.
Y. Sun, Y. Gong, Y. Liu, Q. Li, Y. Zhou, Experimental study on surface characteristics and improvement of microelectrode machined by low speed wire electrical discharge turning, Arch. Civil Mech. Eng. 17 (4) (2017) 964–977.
J.A. McGeough, Advanced Methods of Machining, Chapman and Hall, London, UK, 1988.
K. Mouralova, R. Matousek, J. Kovar, J. Mach, L. Klakurkova, J. Bednar, Analyzing the surface layer after WEDM depending on the parameters of a machine for the 16MnCr5 steel, Measurement 94 (1) (2016) 771–779.
K. Mouralova, L. Klakurkova, R. Matousek, T. Prokes, R. Hrdy, V. Kana, Influence of the cut direction through the semifinished product on the occurrence of cracks for X210Cr12 steel using WEDM, Arch. Civil Mech. Eng. 18 (4) (2018) 1318–1331.
K. Mouralova, J. Kovar, L. Klakurkova, P. Blazik, M. Kalivoda, P. Kousal, Analysis of surface and subsurface layers after WEDM for Ti–6Al–4V with heat treatment, Measurement 116 (1) (2018) 556–564.
M. Mallaiah, R.F. Laubscher, S. Narendranath, S. Basavarajappa, V.N. Gaitonde, Evaluation of wire electro discharge machining characteristics of Ti50Ni50–xCux shape memory alloys, J. Mater. Res. 31 (12) (2016) 1801–1808.
M. Mallaiah, S. Narendranath, S. Basavarajappa, V.N. Gaitonde, Investigation on material removal rate, surface and subsurface characteristics in wire electro discharge machining of Ti50Ni50–xCux shape memory alloy, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L: J. Mater. Des. Appl. 232 (2) (2018) 164–177.
A. Roy, S. Narendranath, Impact of variation in wire electro discharge machining responses of homologous TiNiCu alloys for smart applications: an experimental investigation, Mater. Res. Exp. (2018), https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaddee (in press).
H. Soni, S. Narendranath, M.R. Ramesh, Effects of wire electro-discharge machining process parameters on the machined surface of Ti50Ni49Co1 shape memory alloy, Silicon (2018), https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-017-9687-x (in press).
H. Bisaria, P. Shandilya, Experimental studies on electrical discharge wire cutting of ni-rich NiTi shape memory alloy, Mater. Manufact. Process 33 (9) (2018) 977–985.
M.S. Phadke, Quality Engineering using Roust Design, Pearson Education, New York, Singapore, 2008.
D.G. Montgomery, Design and Analysis of Experiments, 7th ed., John Wiley & Sons, New Delhi, 2009.
M. Gostimirovic, P. Kovac, M. Sekulic, B. Skoric, Influence of discharge energy on machining characteristics in EDM, J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 26 (1) (2012) 173–179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, N., Gupta, K. & Davim, J.P. On wire spark erosion machining induced surface integrity of Ni55.8Ti shape memory alloys. Archiv.Civ.Mech.Eng 19, 680–693 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2019.02.004
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2019.02.004