Abstract
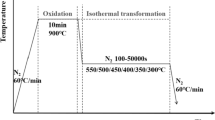
The influences of coiling temperature and cooling condition on structural transformation of the hot-rolled tertiary oxide scale formed under continuous cooling conditions were studied by thermal gravimetric analyzer. The fourth oxide scale formed under different conditions were classified and plotted. Because the oxide scale structure transformation is diffusion-controlled and the transformation law is similar to “C” curve, the eutectoid transformation nose temperature is 450 °C. Under condition of low temperature and high cooling rate, ion diffusion behavior is restricted so that the eutectoid reaction is suppressed, resulting in that the fourth oxide scale is mainly made up of pre-eutectoid Fe3O4 and FeO without eutectoid products. From scale structure transition diagram, the eutectoid reaction process was affected by coiling temperature and cooling rate, leading to various scale structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Y. Chen, W. Y. D. Yuen, ISIJ Int. 45 (2005) 52–59.
W. Sun, A. Tieu, Z. Jiang, C. Lu, JMPT 155 (2004) 1307–1312.
J. C. Mascia, Iron and Steel Eng. 35 (1998) 46–51.
N. Birks, G. H. Meier, F. S. Pettit, Introduction to High-temperature Oxidation of Metals, 2nd Ed. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2006.
T. P. Li, Metal High Temperature Oxidation and Thermal Corrosion, Chemical Industry Publishers, Beijing, 2003.
R. Y. Chen, W. Y. D. Yuen, Oxid. Met. 59 (2003) 433–468.
R. Y. Chen, W. Y. D. Yuen, Oxid. Met. 56 (2001) 111–112.
B. Ilschner, E. Mitzke, Acta Metall. 13 (1965) 855–867.
H. B. Qi, Y. H. Qian, W. Wang, H. Zhang, Baosteel Technical Research 1 (2008) 42–54.
H. Wriedt, Journal of Phase Equilibria 12 (1991) 170–200.
J. Paidassi, Acta Metall. 3 (1955) 447–451.
B. Sun, Z. Y. Liu, Y. Q. Qiu, G. D. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. 22 (2010) No. 2, 34–40.
R. Y. Chen, W. Y. D. Yuen, Oxid. Met. 53 (2000) 539–560.
T. Hiroshi, K. Yasumitsu, ISIJ Int. 52 (2012) 105–109.
J. Y. David, High Temperature Oxidation and Corrosion of Metals, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51204047); National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2011BAE13B04); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (N130407004)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Gm., Wu, Tz., Xu, R. et al. Effects of Coiling Temperature and Cooling Condition on Transformation Behavior of Tertiary Oxide Scale. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 22, 892–896 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(15)30086-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(15)30086-8