Abstract
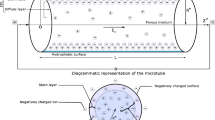
Joule heating effects on a slit microchannel filled with electrolytes are comprehensively investigated with emphasis on the thermal boundary conditions. An accurate analytical expression is proposed for the electrical field and the temperature distributions due to Joule heating are numerically obtained from the energy balance equation. The results show that a thermal design based on the average electric potential difference between electrodes can cause severe underestimation of Joule heating. In addition, the parametric study of thermal boundary conditions gives us an insight into the best cooling scenario for microfluidic devices. Other significant thermal characteristics, including Nusselt number, thermophoretic force, and entropy generation, are discussed as well. This study will provide useful information for the optimization of a bioMEMS device in relation to the thermal aspect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RAHMAT A., SHADLOO M. The electrohydrodynamic deformation of quiescent bubble under electric field[C]. 8th International SPHERIC Workshop. Trondheim, Norway, 2014, 87–94.
XUAN X. Joule heating in electrokinetic flow[J]. Electrophoresis, 2008, 29(1): 33–43.
CHAUREY V., ROHANI A. and SU Y.-H. et al. Scaling down constriction-based (electrodeless) dielectrophoresis devices for trapping nanoscale bioparticles in physiological media of high-conductivity[J]. Electrophoresis, 2013, 34(7): 1097–1104.
GAO J., SIN M. L. Y. and LIU T. et al. Hybrid electrokinetic manipulation in high-conductivity media[J]. Lab on A Chip, 2011, 11(10): 1770–5.
SHAHIDIAN A., GHASSEMI M. and KHORASANI-ZADE S. et al. Flow analysis of non-newtonian blood in a magnetohydrodynamic pump[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2009, 45(6): 2667–2670.
JAMALABADI M. Y. A. Analytical study of magneto-hydrodynamic propulsion stability[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Application, 2014, 13(3): 281–290.
DESAI S. P., VOLDMAN J. Cell-based sensors for quantifying the physiological impact of Micro-systems[J]. Integrative Biology, 2011, 3(1): 48–56.
ERICKSON D., SINTON D. and LI D. Joule heating and heat transfer in poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic systems[J]. Lab on A Chip, 2003, 3(3): 141–149.
TANG G., YAN D. and YANG C. et al. Assessment of Joule heating and its effects on electroosmotic flow and electrophoretic transport of solutes in microfluidic channels[J]. Electrophoresis, 2006, 27(3): 628–639.
De Mello A. J., HABGOOD M. N. and LANCASTER L. et al. Precise temperature control in microfluidic devices using Joule heating of ionic liquids[J]. Lab on A Chip, 2004, 4(5): 417–419.
ROSS D., GAITAN M. and LOCASCIO L. E. Tempera ture measurement in microfluidic systems using a tempe rature-dependent uorescent dye[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 73(17): 4117–4123.
ABDOLLAHZADEH JAMALABADI M. Y. Joule heating in low-voltage electroosmotic with electrolyte containing nano-bubble mixtures through microchannel rectangular orifice[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2015, 102: 407–415.
BURG B. R., BIANCO V. and SCHNEIDER J. et al. Electrokinetic framework of dielectrophoretic deposition devices[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 107(12): ID124308.
CASTELLANOS A., RAMOS A. and GONZALEZ A. et al. Electrohydrodynamics and dielectrophoresis in micro-systems: Scaling laws[J]. Journal of Physics D Applied Physics, 2003, 36(20): 2584–2597.
SRIDHARAN S., ZHU J. and HU G. et al. Joule heating effects on electroosmotic flow in insulator-based dielectrophoresis[J]. Electrophoresis, 2011, 32(17): 2274–2281.
CETIN B., LI D. Effect of Joule heating on electrokinetic transport[J]. Electrophoresis, 2008, 29(5): 994–1005.
KUA C. H., LAM Y. C. and RODRIGUEZ I. et al. Dynamic cell fractionation and transportation using moving dielectrophoresis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 79(18): 6975–6987.
JAMALABADI M. Y. A., GHASEMI M. and HAMEDI M. H. Numerical investigation of thermal radiation effects on open cavity with discrete heat sources[J]. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat and Fluid Flow, 2013, 23(4): 649–661.
JAMALABADI M. Y. A., GHASEMI M. and HAMEDI M. H. Two-dimensional simulation of thermal loading with horizontal heat sources[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2012, 226(5): 1302–1308.
JAMALABADI M. Y. A. Experimental investigation of thermal loading of a horizontal thin plate using infrared camera[J]. Journal of King Saud University Engineering Sciences, 2014, 26(2): 159–167.
VALYASHKO V. M. Hydrothermal experimental data[M]. New York, USA: John Wiley and Sons, 2008.
RAMIRES M. L. V., De CASTRO C. A. N. Thermal conductivity of aqueous potassium chloride solutions[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 2000, 21(3): 671–679.
GOLDHIRSCH I., RONIS D. Theory of thermophoresis. I. General considerations and mode-coupling analysis[J]. Physical Review A, 1983, 27(3): 1616–1634.
JAMALABADI M. Y. A., PARK J. H. and LEE C. Y. Optimal design of mhd mixed convection ow in a vertical channel with slip boundary conditions and thermal radiation effects by using entropy generation minimization method[J]. Entropy, 2015, 17(2): 866–881.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Biography: M. Y. ABDOLLAHZADEH JAMALABADI (1983-), Male, Ph. D., Assistant Professor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdollahzadeh Jamalabadi, M.Y., Park, J.H., Rashidi, M.M. et al. Effects of thermal boundary conditions on the joule heating of electrolyte in a microchannel. J Hydrodyn 28, 850–862 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60705-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60705-9