Abstract
Background
The red cell distribution width (RDW) was higher among neonates with early onset neonatal sepsis. The study aimed to determine the red cell distribution width (RDW) with positive blood culture of early onset neonatal sepsis. This was a descriptive laboratory-based study, conducted during the period from January to September 2023, done on a total of 244 blood sample containers, tested for Complete Blood Count (CBC) tests and blood culture for who were diagnosed as early onset neonatal sepsis.
Results
In this study (244) neonates were diagnosed as blood culture proven neonatal sepsis, The study showed that the cultured organism was isolated as following: 95 were Staphylococcus aureus, 70 were Candida Spp, 28 were Pseudomonas ssp, then 27 were Klebsiella ssp, 16 were Escherichia coli, after that 6 were Enterococcus feacalis and finally 2 were Listeria monocytogenes, and the RDW in this study was significantly higher in neonatal sepsis with average range (20 ± 2.5%).
Conclusions
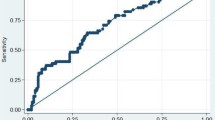
The study concluded that RDW at levels more than or equal to 17% was the most sensitive hematological marker to predict mortality of neonatal sepsis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Background
Neonatal sepsis is a syndrome characterized by systemic signs of infection [1,2,3].
The organisms are most associated with early onset neonatal sepsis range from gram positive and negative bacteria [4, 5].
Red cell distribution width (RDW) has been classically used as a screening index for iron deficiency anemia. Neonatal sepsis (NS) remains a significant contributor to morbidity and mortality [5].
The need for accurate biomarkers to aid in the timely and accurate diagnosis of NS, thus remains as important as issue. RDW is associated with inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) [6, 7].
The need for accurate biomarkers to aid in the timely and accurate diagnosis of Neonatal sepsis (NS) thus remains as important as ever. The study aimed to determine RDW with positive blood culture of neonatal sepsis.
2 Methods
2.1 Study settings and population
This was a descriptive laboratory-based study, conducted during the period from January to September 2023, performed in Obstetrics and gynecology Hospitals in Sudan including Gaafar Ibnauf Children’s, AL- Baraa, Fedeal Hospitals, from December 2022 to April 2023. The study population was term neonates aged from 1 to 28 days with culture positive proven neonatal sepsis admitted to NICU. Inclusion criteria included neonate age from one day to 28 days, diagnosed as early onset neonatal sepsis, while exclusion criteria included neonates, from 1 to 28 days not diagnosed as neonatal sepsis.
Study group was selected according to diagnosis as early onset neonatal sepsis, sample size included 244 study populations collected during the study period.
2.2 Study procedure
Blood conventional culture included sample of 2 ml of blood collected by senior nurse in 2 containers. The first one contained brain heart infusion media with sodium polysulfide as anticoagulant for aerobic organism and the second one contained thiosulfate growth media for an aerobic organism. The incubation period was 24 h initial culture, 3 days mid culture and 7-day last culture [8, 9].
For isolation of candida, we used Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) as selective culture media for only selected patients.
Gram’s staining technique was used [10]. Biochemical tests performed for primary and secondary tests for Gram positive cocci included Catalase test [11], Coagulase test [12], DNase test [13], Mannitol Salt Agar [14].
For Primary and secondary tests for Gram Negative bacilli biochemical tests included Oxidase Test [15], Kliglar iron agar (KIA) [16], Urease Utilization Test [17], Indole Test [18], Citrate utilization test [19], Motility Test [20, 21]. Also, complete blood count (CBC) was done using automated analyzer. Normal range: WBCs (6000 to 20,000/mm3), PLT (150 × 103 to 450 × 103 /mcL), RDW (15.5 ± 2.5%) [22].
3 The RDW was categorized in 3 group, Group (1): minimum 17%, Group (2): average 18–19%, and Group (3): maximum than 20%
3.1 Statistical analysis
Structured questionnaire has been used to gather data. Information included age of mother, antenatal care, antibiotic use during pregnancy, baby gender, symptoms and signs of participant, medical history, and laboratory culture isolation result. Data was analyzed by using SPSS, ver. 23. Frequency tables were constructed and test of significant was applied. The values considered as statistically significant when the p value < 0.05 at confidence level of 95%. Data was presented in form of cross tabulation, tables which were presented in the form of graphs for each variable in the objectives of the study.
4 Results
This study was conducted to determine red cell distribution width (RDW) with positive blood culture of neonatal sepsis, 244 blood proven in EDTA continuer for CBC tests and blood culture samples diagnosed as neonatal sepsis at different Khartoum hospitals participated in this study between January and April 2023.
The study population had their gender 126 (51.6%) were males and 118 (48.4%) subjects were females, as demonstrated in Table 1.
The study showed the cultured organism was isolated as following: according to the percentage of organism from highest to lowest, first 95 (38.93%) was Staphylococcus aureus, next 70 (28,6%) were Candida Spp, After that 28 (11.48%) then Pseudomonas ssp, then 27 (11.07%) were Klebsiella ssp, 16 (6.56%) were Escherichia coli, after that 6 (2.46%) were Enterococcus feacalis and finally 2 (0.82%) were Listeria monocytogenes, Table 2.
The result of RDW was categorized in 3 group, Group (1): minimum 17%: represents 107 (43.8%). Group (2): average 18–19% represents 96 (39.34%), and Group (3): maximum than 20% represent 41 (16.8%), demonstrated in Table 2.
The study showed there was insignificant correlation between isolation result and gender group of neonates, p value (0.076), Out of 126 male and 118 female the most organism is Staphylococcus aureus demonstrated in Table 3.
The results of isolated organisms showed there was significant correlation between RDW% and result of isolation p value (0.000) demonstrated in Table 4.
The study showed there was insignificant correlation between RDW% and gender p value (0.202) demonstrated in Table 5.
5 Discussion
A total of (244) patient babies with blood culture positive diagnosed as early onset neonatal sepsis who full filled the eligible criteria were enrolled in the study.
Gender distribution among the studied group revealed that (51.6%) were males and (48.4%) were females and this distribution of result agree with previous studies showed (60%) was male and (39%) was females [23].
In this study the most cultured organism was isolated as first was Staphylococcus aureus 95 (38.9%) followed by Candida ssp 70 (11%), and finally 2 (0.8%) were Listeria monocytogenes. A previous report agreed with the current findings, which is in consistent with the present study [24,25,26].
Other similar studies revealed that mean RDW was significantly higher among neonates with septic shock which are in consistent with the present study (18.53 ± 2.63%) [27,28,29].
Red cell distribution width to platelet ratio (RPR) has been reported as a useful inflammatory marker and prognostic indicator of adult inflammatory diseases. RPR may be used in diagnosis of early onset neonatal sepsis and may be a good alternative to other tools as a readily available biomarker [30].
Red blood cell distribution width to platelet ratio calculation is practical, inexpensive, and based on CBC-derived data. Calculation of RPR along with CBC can aid in the diagnosis of sepsis and estimation of outcome [31, 32].
RDW is independent predictors of prognosis and help in predicting the prognosis of preterm with neonatal sepsis in the early stage [33].
5.1 Study limitation
There data available in the study is very little. The sample size is small.
6 Conclusion
The study concluded that RDW are quickly and easily available parameters in all hospitals and especially in those in developing countries and they can be used by clinicians as cost-effective markers to predict the outcome in neonatal sepsis syndrome. The study recommend that more studies should be performed to evaluate the relationship between other hematological parameters or biomarkers with neonatal sepsis.
Data availability
Data is provided within the manuscript or supplementary information files. The data sets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CBC:
-
Complete blood count
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- KIA:
-
Kliglar iron agar
- NS:
-
Neonatal sepsis
- RDW:
-
Red cell distribution width
- RPR:
-
Red cell distribution width to platelet ratio
- SDA:
-
Sabouraud dextrose agar
- SPSS:
-
Statistical Packages for Social Sciences
References
Singh M, Alsaleem M, Gray CP. Neonatal Sepsis. 2022 Sep 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
Hayes R, Hartnett J, Semova G, Murray C, Murphy K, Carroll L, et al. Infection, Inflammation, Immunology and Immunisation (I4) section of the European Society for Paediatric Research (ESPR). Neonatal sepsis definitions from randomised clinical trials. Pediatr Res. 2023;93(5):1141–8.
Fleiss N, Schwabenbauer K, Randis TM, Polin RA. What’s new in the management of neonatal early-onset sepsis? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2023;108(1):10–4.
Briggs-Steinberg C, Roth P. Early-onset sepsis in newborns. Pediatr Rev. 2023;44(1):14–22.
Lee CC, Chiu CH. Link between gut microbiota and neonatal sepsis. J Formos Med Assoc. 2023: S0929-6646(23)00398-4.
Frater JL. Red blood cell distribution width as a biomarker in acute kidney injury: too soon? Int Urol Nephrol. 2023;56:807.
Lange A, Kostadinova L, Damjanovska S, Gad I, Syed S, Siddiqui H, et al. Red cell distribution width and absolute lymphocyte count associate with biomarkers of inflammation and subsequent mortality in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2023;50(2):166–74.
Kirk F, Vaselli NM. Blood culture-negative infective endocarditis: are we looking hard enough? Infection. 2023;51(6):1629–31.
Austin B. The value of cultures to modern microbiology. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2017;110(10):1247–56.
Kp A, Mohapatra S, Gautam H, Nityadarshini N, Das BC, Yadav VK. The Gram stain: implication in blood culture reporting. Trop Doct. 2023;53(2):256–9.
Škodová-Sveráková I, Záhonová K, Bučková B, Füssy Z, Yurchenko V, Lukeš J. Catalase and ascorbate peroxidase in Euglenozoan protists. Pathogens. 2020;9(4):317.
Shariati A, Dadashi M, Chegini Z, van Belkum A, Mirzaii M, Khoramrooz SS, et al. Tigecycline, Quinupristin/Dalfopristin, and Linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci strains: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020;9(1):56.
Abreu-Pereira CA, Klein MI, Lobo CIV, Gorayb Pereira AL, Jordão CC, Pavarina AC. DNase enhances photodynamic therapy against fluconazole-resistant Candida albicans biofilms. Oral Dis. 2023;29(4):1855–67.
Arjyal C, Kc J, Neupane S. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in shrines. Int J Microbiol. 2020;2020:7981648.
Pick E. Cell-free NADPH oxidase activation assays: a triumph of reductionism. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2087:325–411.
Yesigat T, Jemal M, Birhan W. Prevalence and associated risk factors of salmonella, Shigella, and intestinal parasites among food handlers in Motta Town, North West Ethiopia. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2020;13(2020):6425946.
Uotani T, Graham DY. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori using the rapid urease test. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3(1):9.
Kumari A, Singh RK. Medicinal chemistry of indole derivatives: current to future therapeutic prospectives. Bioorg Chem. 2019;89: 103021.
Zou Z, Liu Y, Zhu B, Zeng P. Direct identification of Mycobacterium abscessus through 16S rDNA sequence analysis and a citrate utilization test: a case report. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8(1):115–7.
Wang R, Wang F, He R, Zhang R, Yuan J. The second messenger c-di-GMP adjusts motility and promotes surface aggregation of bacteria. Biophys J. 2018;115(11):2242–9.
Dyer EM, Waterfield T, Baynes H. How to use C-reactive protein. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2019;104(3):150–3.
May JE, Marques MB, Reddy VVB, Gangaraju R. Three neglected numbers in the CBC: the RDW, MPV, and NRBC count. Cleve Clin J Med. 2019;86(3):167–72.
Ciesielski TH, Zhang X, Tacconelli A, Lutsar I, de Cabre VM, Roilides E, et al. Late-onset neonatal sepsis: genetic differences by sex and involvement of the NOTCH pathway. Pediatr Res. 2023;93(4):1085–95.
Bulut O, Akcakaya A, Bulut N, Ovali F. Elevated red cell distribution width as a useful marker in neonatal sepsis. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2021;43(5):180–5.
Liu ZY, Jiang HZ, Wang L, Chen MX, Wang HT, Zhang JX. Diagnostic accuracy of red blood cell distribution width for neonatal sepsis. Minerva Pediatr (Torino). 2022;74(2):202–12.
Martin SL, Desai S, Nanavati R, Colah RB, Ghosh K, Mukherjee MB. Red cell distribution width and its association with mortality in neonatal sepsis. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32(12):1925–30.
Weiss SL, Peters MJ, Alhazzani W, Agus MSD, Flori HR, Inwald DP, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign international guidelines for the management of septic shock and sepsis-associated organ dysfunction in children. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(Suppl 1):10–67.
Burgunder L, Heyrend C, Olson J, Stidham C, Lane RD, Workman JK, et al. Medication and fluid management of pediatric sepsis and septic shock. Paediatr Drugs. 2022;24(3):193–205.
Davis AL, Carcillo JA, Aneja RK, Deymann AJ, Lin JC, Nguyen TC, et al. American College of critical care medicine clinical practice parameters for hemodynamic support of pediatric and neonatal septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(6):1061–93.
Karabulut B, Arcagok BC. New diagnostic possibilities for early onset neonatal sepsis: red cell distribution width to platelet ratio. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2020;39(4):297–306.
Scalco R, de Oliveira GN, da Rosa CB, Wooten M, Magdesian KG, Hidai ST, Pandit P, Aleman M. Red blood cell distribution width to platelet ratio in neonatal foals with sepsis. J Vet Intern Med. 2023;37(4):1552–60.
Ellahony DM, El-Mekkawy MS, Farag MM. A study of red cell distribution width in neonatal sepsis. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2020;36(8):378–83.
Cai N, Chen ZQ, Tao M, Fan WT, Liao W. Mean platelet volume and red blood cell distribution width is associated with prognosis in premature neonates with sepsis. Open Med (Wars). 2021;16(1):1175–81.
Acknowledgements
Thanks for all participants involved in this research.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OAA and SMS conceived the design and carried out the experiments. AAI obtained, analyzed and interpreted the data. OAA and SMS wrote and revised the manuscript. AAI provides financial support for all experiments. All authors have critically reviewed and approved the final draft and are responsible for the content and similarity index of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval was obtained from the from Ministry of Health Ethical Research Committee in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki Principles, and the agreement was taken from Dentistry hospital administration before sample and data collection. Informed consent was obtained from the parents/ legally authorized representatives of subjects who are under 16, and for neonates. The patient’s information was highly secured and not used for other purposes than scientific inquiry. The aims and objectives of the study along with its procedure, methods, risks and benefits of this study were explained to each participant in easily understandable local language, and written informed consent was taken from each patient. Ethical clearance code number: MH-RES/1-023-04; Date: 7/1/2023.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, O.A.A., Seedahmed, S.M. & Idris, A.A.A. Association of red cell distribution width (RDW) with positive blood culture of neonatal sepsis in Khartoum state, Sudan. Discov Med 1, 6 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44337-024-00011-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44337-024-00011-z