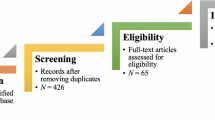
Abstract
Many AI ethics guidelines have recently been published that center the fairness, accountability, sustainability, and transparency of algorithmic decision-making. Relatively few guidelines center the ethics of the business practices and political economies in which AI systems are situated. We present the findings of a semi-systematic literature review and thematic analysis aimed at determining the extent to which the ethics of AI business practices are considered in a large sample of guidelines. Our review reveals that the political and economic implications of AI business practices are greatly underrepresented in AI ethics guidelines. In its current state, AI ethics guidelines focus disproportionately on issues of algorithmic decision-making, while the fairness, accountability, sustainability, and transparency of the business decision-making contexts in which AI systems are situated remain seriously undermined by competitive and speculative norms, ethics washing, corporate secrecy, and other harmful business practices. We discuss these challenges, and we suggest that the ontological and disciplinary scope of future AI ethics guidelines should be expanded to better contend with them.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leslie, D.: Understanding artificial intelligence ethics and safety: A guide for the responsible design and implementation of AI systems in the public sector. The Alan Turing Institute. https://www.turing.ac.uk/sites/default/files/2019-06/understanding_artificial_intelligence_ethics_and_safety.pdf (2019). Accessed 3 June 2020
Häußermann, J.J., Lütge, C.: Community-in-the-loop: Towards pluralistic value creation in AI, or—why AI needs business ethics. AI Ethics (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43681-021-00047-2
Rességuier, A., Rodrigues, R.: AI ethics should not remain toothless! A call to bring back the teeth of ethics. Big Data Soc. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/2053951720942541
Blackman, R.: A practical guide to building ethical AI. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2020/10/a-practical-guide-to-building-ethical-ai (2020). Accessed 6 June 2020
Hagendorff, R.: The ethics of AI ethics: An evaluation of guidelines. Minds Mach. 30, 99–120 (2020)
Floridi, L., Cowls, J.: A unified framework of five principles for AI in society. Harvard Data Sci. Rev. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1162/99608f92.8cd550d1
Benanav, A.: Automation and the future of work. Verso Books, London (2020)
Posada, J.: The future of work is here: Toward a comprehensive approach to artificial intelligence and labour. Ethics of AI in Context. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2007.05843 (2020)
Dyer-Witheford, N., Kjøsen, A.M., Steinhoff, J.: Inhuman power: Artificial intelligence and the future of capitalism. Pluto Press, London (2019)
Keyes, O., Huston, J., Durbin, M.: A mulching proposal: Analysing and improving an algorithmic system for turning the elderly into high-nutrient slurry. In: Extended Abstracts of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3290607.3310433
Greene, D., Hoffman, A. L., Stark, L.: Better, nicer, clearer, fairer: A critical assessment of the movement for ethical artificial intelligence and machine learning. In:Proceedings of the 52nd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (2019). https://doi.org/10.24251/HICSS.2019.258
Fjeld, J., Achten, N., Hilligoss, H., Nagy, A., Srikumar, M.: Principled artificial intelligence: Mapping consensus in ethical and rights-based approaches to principles for AI. Berkman Klein Center Research Publication No. 2020-1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3518482
Cooper, H.M.: Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowl. Soc. (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03177550
Nowell, L.S., Norris, J.M., White, D.E., Moules, N.J.: Thematic analysis: Striving to meet the trustworthiness criteria. Int. J. Qual. Methods (2017). https://doi.org/10.1177/1609406917733847
OECD: Recommendation of the council on artificial intelligence. OECD Legal Instruments https://legalinstruments.oecd.org/en/instruments/OECD-LEGAL-0449 (2019). Accessed 29 May 2020
Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence: Beijing AI principles. Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence https://www.baai.ac.cn/news/beijing-ai-principles-en.html (2019). Accessed 2 June 2020
Executive Office of the President: Preparing for the future of artificial intelligence. Obama White House Archives https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/whitehouse_files/microsites/ostp/NSTC/preparing_for_the_future_of_ai.pdf (2016). Accessed 4 June 2020
British Embassy in Mexico City: Towards an AI Strategy in Mexico: Harnessing the AI Revolution. Oxford Insights https://docs.wixstatic.com/ugd/7be025_ba24a518a53a4275af4d7ff63b4cf594.pdf (2018). Accessed 4 June 2020
Council of Europe: European ethical charter on the use of artificial intelligence in judicial systems and their environment. Council of Europe https://rm.coe.int/ethical-charter-en-for-publication-4-december-2018/16808f699c (2018). Accessed 29 May 2020
The Federal Government of Germany: Artificial intelligence strategy. Nationale Strategie Künstliche Intelligenz https://www.ki-strategie-deutschland.de/home.html?file=files/downloads/Nationale_KI-Strategie_engl.pdf (2019). Accessed 1 June 2020
UNI Global Union: Top 10 principles for workers’ data privacy and protection. The Future World of Work http://www.thefutureworldofwork.org/media/35421/uni_workers_data_protection.pdf (2017). Accessed 3 June 2020
World Economic Forum: AI procurement in a box: AI government procurement guidelines. World Economic Forum http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_AI_Procurement_in_a_Box_Project_Overview_2020.pdf (2020). Accessed 6 June 2020
Microsoft: The future computed: Artificial intelligence and its role in society. Microsoft News https://news.microsoft.com/cloudforgood/_media/downloads/the-future-computed-english.pdf (2018). Accessed 29 May 2020
Google: Responsible development of AI. Google AI https://ai.google/static/documents/responsible-development-of-ai.pdf (2019). Accessed 29 May 2020
Google: Perspectives on issues in AI governance. Google AI https://ai.google/static/documents/perspectives-on-issues-in-ai-governance.pdf (2019). Accessed 29 May 2020
European Commission High-Level Expert Group on Artificial Intelligence: Ethics guidelines for trustworthy AI. Publications Office of the European Union https://ec.europa.eu/digital-single-market/en/news/ethics-guidelines-trustworthy-ai (2019). Accessed 1 June 2020
Abrassart, C., Bengio, Y., Chichoisne, G., de Marcellis-Warin, N., Dilhac, M. et al.: Montréal declaration for a responsible development of artificial intelligence. Université de Montréal https://www.montrealdeclaration-responsibleai.com/the-declaration (2019). Accessed 3 June 2020
Floridi, L., Cowls, J., Beltrametti, M., Chatila, R., Chazerand, P., et al.: AI4People—An ethical framework for a good AI society: opportunities, risks, principles, and recommendations. Minds Mach. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11023-018-9482-5
European Commission: Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the European Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions: Artificial Intelligence for Europe. European Commission https://ec.europa.eu/transparency/regdoc/rep/1/2018/EN/COM-2018-237-F1-EN-MAIN-PART-1.PDF (2018). Accessed 28 May 2020
NITI Aayog: National strategy for artificial intelligence. National Portal of India https://niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2019-01/NationalStrategy-for-AI-Discussion-Paper.pdf (2018). Accessed 6 June 2020
National Governance Committee for the New Generation Artificial Intelligence: Governance principles for the new generation artificial intelligence—developing responsible artificial intelligence. China Daily http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201906/17/WS5d07486ba3103dbf14328ab7.html (2019). Accessed 3 June 2020
AI Now: AI Now 2019 report. AI Now Institute https://ainowinstitute.org/AI_Now_2019_Report.pdf (2019). Accessed 2 June 2020
IBM: Everyday ethics for artificial intelligence. IBM https://www.ibm.com/watson/assets/duo/pdf/everydayethics.pdf (2019). Accessed 3 June 2020
Metz, C.: Seeking ground rules for A.I. The New York Times https://www.nytimes.com/2019/03/01/business/ethical-ai-recommendations.html (2019). Accessed 28 May 2020
UNESCO & COMEST: Preliminary study on the ethics of artificial intelligence. UNESDOC Digital Library https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000367823 (2019). Accessed 29 August 2020
OECD: Recommendation of the council on artificial intelligence. OECD Legal Instruments https://legalinstruments.oecd.org/en/instruments/OECD-LEGAL-0449 (2019). Accessed 3 June 2020
G7 2018: Charlevoix common vision for the future of artificial intelligence. Global Affairs Canada https://www.international.gc.ca/world-monde/assets/pdfs/international_relations-relations_internationales/g7/2018-06-09-artificial-intelligence-artificielle-en.pdf (2018). Accessed 4 June 2020
Cihon, P.: Standards for AI governance: International standards to enable global coordination in AI research & development. Oxford Future of Humanity Institute. https://www.fhi.ox.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/Standards_-FHI-Technical-Report.pdf (2019). Accessed 3 July 2020
Artificial Intelligence Industry Alliance: Joint pledge on artificial intelligence industry self-discipline [draft for comment]. New America https://www.newamerica.org/cybersecurity-initiative/digichina/blog/translation-chinese-ai-alliance-drafts-self-discipline-joint-pledge/ (2019). Accessed 2 June 2020
IEEE: Ethically aligned design: A vision for prioritizing human well-being with autonomous and intelligent systems. IEEE Standards https://standards.ieee.org/content/dam/ieee-standards/standards/web/documents/other/ead1e.pdf?utm_medium=undefined&utm_source=undefined&utm_campaign=undefined&utm_content=undefined&utm_term=undefined (2019). Accessed 28 June 2020
Monetary Authority of Singapore. Principles to promote fairness, ethics, accountability and transparency (FEAT) in the use of artificial intelligence and data analytics in Singapore’s financial sector. Monetary Authority of Singapore https://www.mas.gov.sg/publications/monographs-or-information-paper/2018/FEAT (2018). Accessed 1 July 2020
House of Lords Select Committee on Artificial Intelligence: AI in the UK: ready, willing and able? United Kingdom Parliament https://publications.parliament.uk/pa/ld201719/ldselect/ldai/100/100.pdf (2018). Accessed 4 June 2020
Access Now: Human rights in the age of artificial intelligence. Access Now https://www.accessnow.org/cms/assets/uploads/2018/11/AI-and-Human-Rights.pdf (2018). Accessed 24 August 2020
ITI: AI policy principles. Information Technology Industry Council https://www.itic.org/resources/AI-Policy-Principles-FullReport2.pdf (2017). Accessed 15 July 2020
Government of Japan: Social principles of human-centric AI (draft). Cabinet Office https://www8.cao.go.jp/cstp/stmain/aisocialprinciples.pdf (2019). Accessed 5 August 2020
OpenAI: OpenAI charter. OpenAI https://openai.com/charter/ (2018). Accessed 17 June 2020
Center for Humane Technology: For technologists. Center for Humane Technology https://humanetech.com/techprinciples/ (2021). Accessed 3 July 2020
Smart Dubai: AI ethics principles & guidelines. Smart Dubai https://www.smartdubai.ae/pdfviewer/web/viewer.html?file=https://www.smartdubai.ae/docs/default-source/ai-principles-resources/ai-ethics.pdf?sfvrsn=d4184f8d_6 (2018). Accessed 6 July 2020
Amnesty International and Access Now: The Toronto declaration: Protecting the right to equality and non-discrimination in machine learning systems. Access Now https://www.accessnow.org/cms/assets/uploads/2018/08/The-Toronto-Declaration_ENG_08-2018.pdf (2018). Accessed 5 August 2020
Mukherjee, C., Tripathi, S., Batra, B., Singh A., & Sheppard, B. (2018). Future of work and education for the digital age: Building on the Hamburg statement and the G20 roadmap for digitalization - towards a G20 framework for artificial intelligence in the workplace. Think 20. PwC https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/issues/assets/pdf/future-of-work-education-digital-age.pdf (2018). Accessed 3 July 2020
Telefónica AI principles of Telefónica. Telefonica https://www.telefonica.com/en/web/responsible-business/our-commitments/ai-principles (2018). Accessed 20 August 2020
Axon: Axon’s AI Ethics Board. Axon https://www.axon.com/company/ai-and-policing-technology-ethics (n.d.). Accessed 7 September 2020
The Public Voice: Universal guidelines for artificial intelligence. The Public Voice https://thepublicvoice.org/ai-universal-guidelines/ (2018). Accessed 4 August 2020
Diakopoulos, N., Friedler, S., Arenas, M., Barocas, S., Hay, M., et al.: Principles for accountable algorithms and a social impact statement for algorithms. FAT/ML https://www.fatml.org/resources/principles-for-accountable-algorithms (n.d.). Accessed 4 June 2020
China Electronics Standardization Institute: Artificial intelligence standardization white paper (2018 edition). Center for Security and Emerging Technology https://cset.georgetown.edu/research/artificial-intelligence-standardization-white-paper/ (2018). Accessed 5 July 2020
Future of Life Institute: Asilomar AI principles. Future of Life Institute https://futureoflife.org/ai-principles/?cn-reloaded=1&cn-reloaded=1&cn-reloaded=1 (2017). Accessed 7 August 2020
Pichai, S. AI at Google: Our principles. Google Blog https://www.blog.google/technology/ai/ai-principles/ (2018). Accessed 27 May 2020
Schwab, K. & Vanham, P.: What is stakeholder capitalism? World Economic Forum https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2021/01/klaus-schwab-on-what-is-stakeholder-capitalism-history-relevance/ (2021) 30 January 2020
Mishra, S., Clark, J., Perrault, C. R.: Measurement in AI policy: Opportunities and challenges. arXiv preprint (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2009.09071
Metcalf, J., Moss, E., Boyd, D.: Owning ethics: Corporate logics, Silicon Valley, and the institutionalization of ethics. Soc Res 86(2), 449–476 (2019)
Yeung, K., Howes, A., Pogrebna, G.: AI governance by humans right-centered design, deliberation, and oversight: An end to ethics washing. In: Dubber, M.D., Pasquale, F., Das, S. (eds.) The Oxford Handbook of Ethics of AI. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2020)
Bietti, E.: From ethics washing to ethics bashing: A view on tech ethics from within moral philosophy. FAT* https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3513182 (2020). Accessed 13 July 2020
Partnership on AI: Tenets. Partneship on AI https://www.partnershiponai.org/tenets/ (n.d.). Accessed on 5 June 2020
OpenAI: OpenAI charter. OpenAI https://openai.com/charter/ (n.d.). Accessed 3 July 2020
Dastin, J. & Dave, P.: Exclusive: Google pledges changes to research oversight after internal revolt. Reuters https://www.reuters.com/article/us-alphabet-google-research-exclusive/exclusive-google-pledges-changes-to-research-oversight-after-internal-revolt-idUSKBN2AP1AC (2021). Accessed 5 February 2021
Xiang, A., Raji, I.D.: On the legal compatibility of fairness definitions. arXiv preprint (2019). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1912.00761
Crawford, K.: Atlas of AI: Power, politics, and the planetary costs of artificial intelligence. Yale University Press, New Haven (2021)
Crawford, K. & Joler, V.: Anatomy of an AI system. Anatomy of AI https://anatomyof.ai/ (2018). Accessed 4 June 2020
Raji, I. D., Smart, A., White, R. N., Mitchell, M., Gebru, T., Hutchinson, B., et al.: Closing the AI accountability gap: defining an end-to-end framework for internal algorithmic auditing. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2001.00973
Rahwan, I.: Society-in-the-loop: Programming the algorithmic social contract. Ethics Inf. Technol. 20, 5–14 (2018)
Parliament of Canada: Bill C-11, An Act to Enact the Consumer Privacy Protection Act and the Personal Information and Data Protection Tribunal Act and to Make Consequential and Related Amendments to Other Acts, 2nd Session, 43rd Parliament, Ottawa, 2020. Parliament of Canada https://parl.ca/DocumentViewer/en/43-2/bill/C-11/first-reading (2020). Accessed 6 February 2021
Birhane, A.: Algorithmic injustice: a relational ethics approach. Patterns (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2021.100205
Indigenous Protocol and Artificial Intelligence Working Group: Indigenous protocol and artificial intelligence. The Initiative for Indigenous Futures and the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR) (2020). https://doi.org/10.11573/spectrum.library.concordia.ca.00986506
Lewis, J. E., Arista, N., Pechawis, A., Kite, S.: Making kin with the machines. Journal of Design and Science (2018). https://doi.org/10.21428/bfafd97b
Raji, I. D., Scheuerman, M. K., Amironesei, R.: You can’t sit with us: Exclusionary pedagogy in AI ethics education. FAccT ‘21: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3442188.3445914
D’Ignazio, C., Klein, L.: Data Feminism. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA (2020)
AlgorithmWatch (2020). AI ethics guidelines global inventory. Retrieved from https://inventory.algorithmwatch.org/
Altman, M., Wood, A., Vayena, E.: A harm-reduction framework for algorithmic fairness. IEEE Secur. Priv. 16(3), 34–45 (2018)
CIO Strategy Council: Ethical design and use of automated decision systems. National Standard of Canada CAN/CIOSC 101:2019. Ottawa: CIO Strategy Council & Standards Council of Canada. https://ciostrategycouncil.com/standards/implement-standards/ (2019)
Fjeld, J., Achten, N., Hilligoss, H., Nagy, A., Srikumar, M.: Principled artificial intelligence: Mapping consensus in ethical and rights-based approaches to principles for AI. Berkman Klein Center Research Publication No. 2020-1. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3518482 (2020)
Greene, D., Hoffman, A. L., Stark, L.: Better, nicer, clearer, fairer: A critical assessment of the movement for ethical artificial intelligence and machine learning. In: Proceedings of the 52nd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 2122-2131. https://scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/bitstream/10125/59651/0211.pdf (2019)
Keyes, O., Huston, J., Durbin, M.: A mulching proposal: Analysing and improving an algorithmic system for turning the elderly into high-nutrient slurry. CHI 2019. https://ironholds.org/resources/papers/mulching.pdf (2019)
Lepri, B., Oliver, N., Letouze, E., Pentland, A., Vinck, P.: Fair, transparent, and accountable algorithmic decision-making processes: the premise, the proposed solutions, and the open challenges. Philos. Technol. 31(3), 611–627 (2018)
Metcalf, J., Moss, E., Boyd, D.: Owning ethics: corporate logics, Silicon Valley, and the institutionalization of ethics. Soc. Res. 86(2), 449–476 (2019)
Suresh, H., Guttag, J. V.: A framework for understanding unintended consequences of machine learning. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/pdf/1901.10002.pdf (2020)
Abrassart, C., Bengio, Y., Chichoisne, G., de Marcellis-Warin, N., Dilhac, M., et al.: Montréal declaration for a responsible development of artificial intelligence. Université de Montréal. https://www.montrealdeclaration-responsibleai.com/the-declaration (2019)
Access Now: Human rights in the age of artificial intelligence. https://www.accessnow.org/cms/assets/uploads/2018/11/AI-and-Human-Rights.pdf (2018)
AI Now: AI Now 2019 report. https://ainowinstitute.org/AI_Now_2019_Report.pdf (2019)
Amnesty International and Access Now: The Toronto declaration: Protecting the right to equality and non-discrimination in machine learning systems. https://www.accessnow.org/cms/assets/uploads/2018/08/The-Toronto-Declaration_ENG_08-2018.pdf (2018)
Artificial Intelligence Industry Alliance: Joint pledge on artificial intelligence industry self-discipline (draft for comment). (Trans. Webster, G.). https://www.newamerica.org/cybersecurity-initiative/digichina/blog/translation-chinese-ai-alliance-drafts-self-discipline-joint-pledge/ (2019)
Axon: Axon’s AI Ethics Board. https://www.axon.com/company/ai-and-policing-technology-ethics (2021)
Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence: Beijing AI principles. https://www.baai.ac.cn/news/beijing-ai-principles-en.html (2019)
British Embassy in Mexico City: Hacia una Estrategia de IA en México: Aprovechando la Revolución de la IA. https://docs.wixstatic.com/ugd/7be025_ba24a518a53a4275af4d7ff63b4cf594.pdf (2018)
Center for Humane Technology: For technologists. https://humanetech.com/techprinciples/ (2021)
China Electronics Standardization Institute: Artificial intelligence standardization white paper (2018 edition). (Trans. Center for Security and Emerging Technology). https://cset.georgetown.edu/research/artificial-intelligence-standardization-white-paper/ (2018)
Council of Europe: European ethical charter on the use of artificial intelligence in judicial systems and their environment. https://rm.coe.int/ethical-charter-en-for-publication-4-december-2018/16808f699c (2019)
DeepMind: Exploring the real-world impacts of AI. Retrieved from https://deepmind.com/about/ethics-and-society (n.d.)
Diakopoulos, N., Friedler, S., Arenas, M., Barocas, S., Hay, M., et al.: Principles for accountable algorithms and a social impact statement for algorithms. FAT/ML. https://www.fatml.org/resources/principles-for-accountable-algorithms (n.d.)
European Commission: Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the European Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions: Artificial Intelligence for Europe. https://ec.europa.eu/transparency/regdoc/rep/1/2018/EN/COM-2018-237-F1-EN-MAIN-PART-1.PDF (2018)
European Commission High-Level Expert Group on Artificial Intelligence: Ethics guidelines for trustworthy AI. https://ec.europa.eu/digital-single-market/en/news/ethics-guidelines-trustworthy-ai (2019)
Executive Office of the President: Preparing for the future of artificial intelligence. https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/whitehouse_files/microsites/ostp/NSTC/preparing_for_the_future_of_ai.pdf (2016)
Floridi, L., Cowls, J., Beltrametti, M., Chatila, R., Chazerand, P., et al.: AI4People—An ethical framework for a good AI society: opportunities, risks, principles, and recommendations. Minds Mach. 28, 689–707 (2018)
Future of Life Institute: Asilomar AI principles. https://futureoflife.org/ai-principles/?cn-reloaded=1&cn-reloaded=1&cn-reloaded=1 (2017)
Government of Japan: Social principles of human-centric AI (draft). Retrieved from https://www8.cao.go.jp/cstp/stmain/aisocialprinciples.pdf (2019)
House of Lords Select Committee on Artificial Intelligence: AI in the UK: ready, willing and able? https://publications.parliament.uk/pa/ld201719/ldselect/ldai/100/100.pdf (2018)
IA Latam: Declaración de ética ia-latam para el diseño, desarrollo y uso de la inteligencia artificial. https://ia-latam.com/etica-ia-latam/ (n.d.).
IBM: Everyday ethics for artificial intelligence. https://www.ibm.com/watson/assets/duo/pdf/everydayethics.pdf (2019)
IEEE: Ethically aligned design: A vision for prioritizing human well-being with autonomous and intelligent systems (1st ed.). https://standards.ieee.org/content/dam/ieee-standards/standards/web/documents/other/ead1e.pdf?utm_medium=undefined&utm_source=undefined&utm_campaign=undefined&utm_content=undefined&utm_term=undefined (2019)
ITI: AI policy principles. https://www.itic.org/resources/AI-Policy-Principles-FullReport2.pdf (2017)
Leslie, D.: Understanding artificial intelligence ethics and safety: A guide for the responsible design and implementation of AI systems in the public sector. The Alan Turing Institute. https://www.turing.ac.uk/sites/default/files/2019-06/understanding_artificial_intelligence_ethics_and_safety.pdf (2019)
Metz, C.: Seeking ground rules for A.I. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2019/03/01/business/ethical-ai-recommendations.html (2019)
Microsoft: The future computed: Artificial intelligence and its role in society. https://news.microsoft.com/cloudforgood/_media/downloads/the-future-computed-english.pdf (2018)
Monetary Authority of Singapore: Principles to promote fairness, ethics, accountability and transparency (FEAT) in the use of artificial intelligence and data analytics in Singapore’s financial sector. https://www.mas.gov.sg/publications/monographs-or-information-paper/2018/FEAT (2018)
Mukherjee, C., Tripathi, S., Batra, B., Singh A., Sheppard, B.: Future of work and education for the digital age: Building on the Hamburg statement and the G20 roadmap for digitalization - towards a G20 framework for artificial intelligence in the workplace. Think 20. https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/issues/assets/pdf/future-of-work-education-digital-age.pdf (2018)
National Governance Committee for the New Generation Artificial Intelligence: Governance principles for the new generation artificial intelligence—developing responsible artificial intelligence. China Daily. http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201906/17/WS5d07486ba3103dbf14328ab7.html (2019)
NITI Aayog: National strategy for artificial intelligence. https://niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2019-01/NationalStrategy-for-AI-Discussion-Paper.pdf (2018)
OECD: Recommendation of the council on artificial intelligence. https://legalinstruments.oecd.org/en/instruments/OECD-LEGAL-0449 (2019)
OpenAI: OpenAI charter. https://openai.com/charter/ (2018)
Partnership on AI: Tenets. Retrieved from https://www.partnershiponai.org/tenets/ (n.d.)
Pichai, S.: AI at Google: Our principles. Google. https://www.blog.google/technology/ai/ai-principles/ (2018)
Schoenauer, M., Bonnet, Y., Berthet, C., Cornut, A-C., Levin, F., Rondepierre, B.: For a meaningful artificial intelligence: Towards a French and European strategy. https://www.aiforhumanity.fr/pdfs/MissionVillani_Report_ENG-VF.pdf (2018)
Smart Dubai: AI ethics principles & guidelines. https://www.smartdubai.ae/pdfviewer/web/viewer.html?file=https://www.smartdubai.ae/docs/default-source/ai-principles-resources/ai-ethics.pdf?sfvrsn=d4184f8d_6 (2018)
Telefónica: AI principles of Telefónica. https://www.telefonica.com/en/web/responsible-business/our-commitments/ai-principles (2018)
Telia Company: Guiding principles on trusted AI ethics. https://www.teliacompany.com/globalassets/telia-company/documents/about-telia-company/public-policy/2018/guiding-principles-on-trusted-ai-ethics.pdf (2019)
Tencent Institute: Six principles of AI. http://www.kejilie.com/iyiou/article/ZRZFn2.html (2017)
The Federal Government of Germany: Artificial intelligence strategy. https://www.ki-strategie-deutschland.de/home.html?file=files/downloads/Nationale_KI-Strategie_engl.pdf (2018)
The Public Voice: Universal guidelines for artificial intelligence. https://thepublicvoice.org/ai-universal-guidelines/ (2018)
UNI Global Union: Top 10 principles for workers’ data privacy and protection. http://www.thefutureworldofwork.org/media/35421/uni_workers_data_protection.pdf (2017)
Cihon, P.: Standards for AI governance: International standards to enable global coordination in AI research & development. Oxford: Future of Humanity Institute. https://www.fhi.ox.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/Standards_-FHI-Technical-Report.pdf (2019)
G7 2018: Charlevoix common vision for the future of artificial intelligence. https://www.international.gc.ca/world-monde/assets/pdfs/international_relations-relations_internationales/g7/2018-06-09-artificial-intelligence-artificielle-en.pdf (2018)
Google: Responsible development of AI. https://ai.google/static/documents/responsible-development-of-ai.pdf (2019)
Google: Perspectives on issues in AI governance. https://ai.google/static/documents/perspectives-on-issues-in-ai-governance.pdf (2019)
UNESCO & COMEST: Preliminary study on the ethics of artificial intelligence. SHS/COMEST/EXTWG-ETHICS-AI/2019/1. https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000367823 (2019)
World Economic Forum: AI procurement in a box: AI government procurement guidelines. http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_AI_Procurement_in_a_Box_Project_Overview_2020.pdf (2020)
Funding
The authors received funding for this research from University College London-University of Toronto, Fund for Collaborative Projects and Exchange Activities in Artificial Intelligence, Project title: AI Governance: Building ethical frameworks to balance risk and innovation, (PIs: R. Alexander and K. Lyons, UofT and J. Bunn and E. Lomas, UCL): https://ei4ai.wordpress.com/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Andrés De los Ríos is an employee of Doblin, a Deloitte business. Andrés’s employer was not involved in the research or writing of this manuscript, did not in any way endorse the research and writing of this manuscript, and provided none of the authors with any financial compensation for our work on this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attard-Frost, B., De los Ríos, A. & Walters, D.R. The ethics of AI business practices: a review of 47 AI ethics guidelines. AI Ethics 3, 389–406 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43681-022-00156-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43681-022-00156-6