Abstract
Child sexual abuse is a growing problem, representing an egregious abuse of power, trust, and authority with far-reaching implications for the victims. This review study highlights the intricate psychological impacts of child sexual abuse, addressing both short and long-term consequences. Existing literature highlights the deep impacts on the victims’ psychological health and well-being, necessitating an in-depth examination of the subject. Drawing from a sample of n = 19 research articles selected through stringent inclusion and exclusion criteria and the PRISMA approach, this study synthesizes results from publications spanning 2010 to 2022. The review reveals various detrimental impacts on the victims’ psychological well-being, including short-term consequences, i.e., isolation, bullying, stress, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Long-term effects encompass PTSD in later life, disrupted intimate relationships, social and emotional health concerns, revictimization, and more. In conclusion, the study emphasizes the lack of a definitive number of impacts, highlighting the need to discuss and raise awareness about child sexual abuse. This increased awareness is important for parents, guardians, and responsible authorities to effectively counteract these crimes against children. Also, providing emotional support to victims is important to mitigate the long-term impacts. The researchers offer implications and discuss limitations, providing an extensive overview and foundation for future research and interventions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Child sexual abuse is prevalent across class, race, and ethnicity, with both short-term and long-term impacts. It mainly involves an interaction between the abuser and the child, in which the child is the focus of the sexual stimulation of an observer or the offender (Wagenmans et al. 2018). Child sexual abuse is anticipated as silencing the minor, and consequently, reporting such incidents is much less. Even without knowing the full ratio of the relevant incidents, experts agree that 500,000 children face sexual abuse yearly (YWCA.org 2017). This sexual offence against children has always been an existing phenomenon in all societies and historical eras. For instance, ancient civilizations openly adopted child sexual abuse as a normal, cultural, and social practice aimed at the learning and development of children (Ali 2019). Despite the perceptions about child sexual abuse historically varied, we found varying perceptions ranging from acceptance (justifiable) to rejection (children’s rights violation) (DiLillo et al. 2014). Child sexual abuse is not limited only to penetration; instead, showing a child pornographic photos, voyeurism, touching a child’s genitals, and even making the child touch or see the perpetrator’s private body parts is also considered sexual abuse (National Sexual Violence Resource Center 2011). It is also notable that both boys and girls are strongly susceptible to sexual abuse. However, girls are more vulnerable as they confront sexual abuse three times more than boys, while boys are more likely to be severely injured or die after sexual molestation (National Sexual Violence Resource Center 2011). A report by the World Health Organization in 2006 revealed that more than 20% of women and 8% of men in 39 countries reported that they had faced sexual abuse during childhood.
Similarly, data from 2012 to 2013 shows that 2% of boys and 4% of girls experience some sexual abuse every year (Chan et al. 2013). Another report (UNICEF 2020a) revealed that more than 120 million individuals worldwide face forced sexual acts during their childhood. Most are females (89%), and 11% are males. Globally, this statistic is much higher as every one out of four girls and one in every six boys during the early years of their lives (YWCA.org 2017).
Similarly, sexual abuse of children is possible in almost every social setting and location, i.e., schools, roads, justice institutions, and homes. Also, it is prevalent equally among all socio-economic classes and age groups; children facing sexual abuse sometimes cannot realize their molestation (Selengia et al. 2020). Around 92.0 of the reported incidents were linked by acquittances (closed relatives), indicating the prevalence of incestuous abuse (Ali et al. 2021). Notably, there are three dynamic factors behind child sexual abuse, i.e., psychological, economic, and social. For instance, social factors involve one’s personal experience of sexual exploitation during childhood (Middleton et al. 2017). Economic factors involve poverty. For example, parents may ask their girl child to look for a capable man to take care of her primary needs, which may further lead to engaging in sexual activities in return for monetary support (Simuforosa 2015, p. 1792).
On the other hand, psychological factors are mainly defined as sexual interest in children due to a mental disorder (Tenbergen et al. 2015). However, the economic factors responsible for perpetuating child sexual abuse mainly involve forcibly engaging children in sexual acts, selling or buying children pornography, and all the other relevant factors that lead to the economic benefits for the perpetrators (Ali 2019). Notably, the impacts of child sexual use are detrimental from different aspects. For instance, these impacts are immediate yet prolonged, indicating their severity during adulthood. According to (Downing et al. 2021), stress-induced variations in the pro-inflammatory substances, i.e., alterations in gene expression and cortisol, mediate these detrimental impacts.
Additionally, risky sexual behaviours against children and the opposite gender are further attributed to the impacts of child sexual abuse (Fisher et al. 2017, p. 11). Child sexual abuse poses an influential societal challenge, demanding careful examination to understand its complexities fully.
Aim and purpose
This research aims to scrutinize the role of Child Sexual Abuse as a risk factor for causing several psychological concerns among the victims. The researcher has reviewed some studies on Child Sexual Abuse and its impacts. Drawing on the aims of this article, the study aims to examine (1) the short-term psychological impacts of Child Sexual Abuse and (2) the long-term psychological impacts of Child Sexual Abuse according to studies conducted during the past twelve years (2010–2022). The overarching goal is to provide a comprehensive synthesis of existing literature, shedding light on the multifaceted consequences of child sexual abuse over both short and long-term durations. By systematically analyzing and assessing a selected set of articles, this study seeks to contribute to the understanding of prevalent themes, methodologies, and gaps in the existing literature surrounding the psychological impacts of child sexual abuse. The significance of this work extends to informing future research, interventions, and policymaking related to child protection and well-being. Finally, the aim is to facilitate the development of targeted and effective strategies for preventing, intervening, and supporting individuals affected by children.
In response to the urgent need for a comprehensive understanding, this review study uses the PRISMA approach to navigate existing literature. Addressing the CSA in current knowledge, we highlight the major difficulties associated with unravelling the complexities of child sexual abuse. This review not only synthesizes an extensive body of research but also discusses their findings and insights to overcome the inherent challenges in comprehending the short and long-term impacts of child sexual abuse. Our study seeks to make a distinctive contribution by explaining the intercity of this fragile subject matter, thus laying the groundwork for more effective interventions and support systems. It addresses the following research questions based on the aims and purposes of current research.
RQ1. What constitutes Child Sexual Abuse, and how can it be accurately defined within the current literature?
RQ2. How does Child Sexual Abuse affect the mental health and overall well-being of individuals, considering both short-term and long-term impacts?
Methods
This study is based on the systematic literature review approach. The review-based studies are a significant part of the existing literature as they closely witness the ongoing trends and complexities in the field under study (Ali and Pasha 2022). Besides, the relevant studies also highlight the major findings to further the gap and conduct an in-depth analysis of the other aspects of the same concern.
Assumptions and justifications
In the context of this systematic literature review, certain assumptions were made to facilitate the synthesis and analysis of the selected studies. These assumptions are integral to the nature of the review process. First, it was deemed that the definitions of key terms, i.e., “child sexual abuse” and “psychological impacts,” were relatively consistent across the selected studies. This assumption is grounded in the anticipation that researchers within the field comply with widely accepted definitions and classifications. While variations in terminologies exist, a comprehensive screening process and compliance with inclusion criteria mitigated possible discrepancies. The study focused on articles with clear and relevant definitions, assuring homogeneity in the selected literature.
Further, the decision to include articles published from 2010 onwards was based on the assumption that recent research mirrors current trends and developments in comprehending the psychological impacts of child sexual abuse. The rationale is rooted in the dynamic nature of research, focusing on current perspectives. This assumption allows for analyzing the most recent insights into the subject matter and recognizing the evolving nature of societal attitudes and academic discourse.
Evaluation of assumptions
While these assumptions were important for the systematic review process, it is important to acknowledge their probable impact on the results. A few considerations emphasize how these assumptions may affect the outcomes. For example, despite efforts to ensure consistency, variations in definitions across studies may introduce complexities in interpreting psychological impacts. This could influence the synthesis of results, and readers should be aware of the potential heterogeneity in conceptualizing key terms. Besides, the focus on recent publications assumes that newer research accurately represents the current landscape. However, this may bias contemporary perspectives, potentially bypassing practical insights from earlier studies.
Thus, considering the problem’s complexity and continuous research, the researcher selected three specialized platforms: PubMed, Science Direct, and APA PsycNet. However, the selection criteria were not restricted to any age, gender, race, ethnicity, nationality, and language. The keywords for the search were “impacts of child sexual abuse, child sexual abuse, psychological effects of child sexual abuse, short-term effects of child sexual abuse, and long-term effects of child sexual abuse. Later the researcher tabulated the data using Microsoft Excel, which further helped calculate the included articles’ percentages and frequencies. The researcher used the PRISMA method for systematic review, as suggested by (Page and McKenzie 2021). Table 1 summarizes the inclusion and exclusion criteria used in the current study:
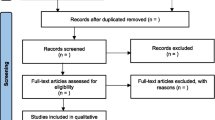
Based on the PRISMA method of screening, evaluation and Selection, the researchers gathered a total of 113 records from the selected database. After removing the duplicates, 106 total articles were further screened for full-text availability (93). Finally, the researchers selected n = 19 articles adhering to the selection criteria (See Fig. 1).
Table 2 summarizes the frequencies and percentages of the literature according to their database. It is observable that most of the articles were from PubMed (n = 11 or 57.8). APA PsyNet provided n = 7 or 36.8% articles, while n = 1 (5.2%) article was obtained from Science Direct.
Table 3 summarizes the frequencies and percentages of the selected literature according to their publication years. As visible, most of the studies (n = 12, 63.1%) were published from 2015 to 2020, indicating that these years focused mainly on research scholars in psychology, communication, sociology, criminology, and other fields. These results also reflect the prevalence of the relevant concern demanding a strong consideration towards children’s rights and health protection (Ali and Pasha 2022). Followed by 04 or 21.0% of studies published between 2010–2015, n = 03 or 1.7% of studies published until the end of November 2022.
Concerning the frequencies and percentages of the cited literature according to their designs, most studies (09 or 47.3%) were based on a review approach. Followed by experimental design (n = 06 or 31.5%), 03 or 15.7% of studies were based on the perspective method. Finally, online n = 1 (5.2%) of the study was based on the case study method, and the same number of studies (n = 1, 5.2%) was categorized as “other” (See Table 4). Additionally, n = 11 or 7.8% of studies were based on a qualitative approach, n = 11 or 57.8% were based on the quantitative approach, and only one study was based on the mixed method approach (See Table 5).
The researchers calculated the frequencies and percentages of the cited literature according to the data-gathering approaches used by the relevant researchers (See Table 3). Most studies (n = 13, 68.4%) were based on the survey method. Besides, the interview approach was preferred in 04% of studies. While n = 1 (5.2%) study was based on the literature review approach, and the same number of literature (n = 1, 5.2%) was categorized as “other”.
Validation of selected methodology
The methodology used in this systematic literature review underwent a thorough validation process to ensure its reliability and comprehensiveness. Key elements of the validation process are.
-
1.
Adherence to PRISMA Guidelines: The systematic review methodology rigorously adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, as Page and McKenzie (2021) recommended. PRISMA guidelines are widely recognized and accepted standards for conducting systematic reviews, assuring a systematic and transparent approach to literature synthesis.
-
2.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria: Establishing clear and strict inclusion and exclusion criteria contributed to the robustness of the methodology. These criteria were designed to select studies that specifically addressed the psychological impacts of child sexual abuse, enhancing the relevance and reliability of the synthesized literature.
-
3.
Search Strategy: The search strategy employed in selecting articles was exhaustive, using three specialized platforms—PubMed, Science Direct, and APA PsycNet. The chosen keywords were carefully selected to encompass diverse dimensions of child sexual abuse and its psychological impacts, minimizing the risk of overlooking pertinent studies.
-
4.
Data Tabulation and Analysis: Using Microsoft Excel for data tabulation provided a structured and organized approach to handling the extensive information extracted from the selected articles. This facilitated a systematic calculation of frequencies and percentages, assuring accuracy and consistency in reporting.
-
5.
PRISMA Flow Chart: A PRISMA flow chart (Fig. 1) visually represents the systematic article selection, screening, and inclusion process. This chart improves transparency and serves as a visual validation of the methodological stringency applied in the study.
While this systematic review does not involve the same type of validation as experimental or modelling studies, the validation lies in compliance with established guidelines, rigorous criteria for article selection, and transparent reporting of the review process. These elements collectively contribute to the robustness and credibility of the methodology used in this study.
Review of literature
Defining child sexual abuse
According to (Pulverman et al. 2018), the definition of child sexual abuse has been a major concern for many researchers since the 1970s. The prevalent cases and recent concerns indicate that providing and establishing the definition of child sexual abuse is urgent and needs strong consideration. Notably, it is important to keep the complexity and sensitivity of the relevant issue under consideration when providing a potential definition of child sexual abuse (Pulverman et al. 2018) theoretically defined child sexual abuse as the unconscionability of the acts, which further indicates four types of activities such as the relationship of power between an adult and child, the child in the lower position facing inequality, the child’s susceptibility is exploited based on their detriment, and truancy of true consent (Table 6).
Defining sexual abuse can vary on a different basis. For instance, (Vaillancourt-Morel et al. 2016) argue that child sexual abuse mainly relies on the legal definition. Several self-reported cases of child sexual abuse remained affirmed, leading to further legal actions, yet some cases indicate doubtful accusations. As in the empirical study (Vaillancourt-Morel et al. 2016), results indicated 21.3% sexual abuse among females and 19.6% among males. At the same time, 7.1% of females and 3.8% remained consistent with self-defined child sexual abuse. However, (Ma 2018) stated that the relevant definition could vary according to the prevalence estimation. Besides, this definition is based on five criteria, including the age of the childhood, the age of the perpetrator or the age difference between the victim and the perpetrator, the relationship between the victim and the perpetrator, the type of sexual acts performed by the perpetrator, and the extension of the coercion. According to (Pulverman et al. 2018), child sexual abuse can be defined as unwanted sexual activities between an adult and a child, including vaginal, oral, and anal penetration. Besides, online child sexual abuse, including online sex, child pornography, and others, is also considered a vital type of child sexual abuse.
Impacts of child sexual abuse
Child sexual abuse is strongly detrimental to children’s physical and psychological health. In this regard, researchers and medical experts claim physical consequences as serious as brain damage and immediate death. Minor injuries are also found in some cases. However, death is the most common physical outcome of child sexual abuse (Habes et al. 2022). As noted by (Beltran 2010), no single impact patterns exist. Sometimes, a victim does not show any prominent impacts that may impede the development of a psychological syndrome that adversely affects a child’s social, emotional and cognitive abilities. Some researchers claim that only 20–30% of children remain emotionally and physically stable after sexual molestation. However, although they remain normal, internally, they develop latent effects of sexual abuse. The short-term and immediate psychological impacts of sexual abuse may involve painful emotions, Post-traumatic stress disorder, cognitive distortions, and disturbed mood. These victims respond to sexual abuse in diverse ways that can be changed over time. However, the psychological harm is still severe and can result in even adverse consequences. During sexual abuse, victims can feel fear, anxiety, self-blame, guilt, confusion, and anger. They feel self-conscious and humiliated, unable to talk about what happened, which can result in stress and frustration (Pulverman et al. 2018). Table 1 below provides a summary of studies witnessing the physical and psychological consequences of child sexual abuse (Table 7).
(Batool and Abtahi 2017) named short-term effects “initial effects”, as these reactions mainly occur during the first two years of abuse. Previous studies revealed that 66.0% of children were emotionally disturbed due to sexual abuse, 5.2% were mild to moderately disturbed, and 24.0% remained stable after the sexual abuse. Similarly, a study conducted by (Fontes et al. 2017) also witnessed the short-term impacts of sexual abuse on the mental health of the victims. Results gathered by using the Propensity Score Matching technique revealed that 13.3% of sexually abused children reported a greater feeling of loneliness, 7.5% were having difficulty in making friends, and 9.5% reported insomnia. Despite these effects differing among male and female children, both were equally confronting to the relevant mental disturbances.
Further, regarding the long-term effects of child sexual abuse, (Petersen et al. 2014) stated that it results in both short and long-term effects. A survivor may feel peer rejection, confusion, lack of self-confidence, conduct disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, and aggression. Similarly, in the later years, the survivor may also develop other extreme psychiatric disorders such as depression, low economic productivity, drug addiction and even severe medical illness. According to (Hodder and Gow 2012), long-term child sexual abuse can also result in substance abuse, long-term depression, negative attributions, and even eating disorders. Most recently, practitioners also found even more chronic mental disorders such as delusions, schizophrenia, and personality disorders. However, children who have experienced abuse involving penetration are more likely to develop these chronic psychotic and schizophrenic disorders. Likewise, sexually abused children also have low self-esteem and overly sexualized behaviour, which, in many cases, results in teen pregnancy and motherhood and even an increased vulnerability to another victimization (Townsend 2013). Besides, socially isolated children with a disability or emotional disorder are comparatively more vulnerable to victimization. Once the abuse has happened, they also face threats to end the relationship if they refuse to perform sex or threats to publicly share their sexual images (UNICEF 2020b) (Table 8).
Wagenmans et al. (2018) highlighted the occurrence of prolonged and severe psychological disorders among individuals who previously experienced child sexual abuse. As noted, the prolonged effects are more common when there is a repetitive and interpersonal nature of abuse, mostly leading to develop Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) in later years. Those with a history of Child Sexual Abuse risk developing issues in interpersonal relationships, emotional regulation, and self-concept that result in “Complex PTSD” (p. 2). As (Gupta and Garg 2020) noted, child sexual abuse indicates an increased self-harming behaviour, fear, depression, impaired brain development, and others that are criteria for developing Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Notably, this sexual abuse is not limited to physical and sexual harm; it also involves emotional abuse that further indicates the severity of the relevant issue today. It is also worth mentioning that most victims report sexual abuse in their later life. These victims also indicate their revictimization as one of the most consistent outcomes of child sexual abuse (Papalia et al. 2021). The term revictimization is also defined as any further victimization even during childhood, adolescence, or adulthood after the first incident of sexual abuse during childhood (P.1). However, there can be different factors, including sex, mental health issues, age at initial abuse, and others as different determinants of revictimization (Papalia et al. 2021). (MacIntosh and Ménard 2021) synthesized the status of research witnessing the long-term impacts of child sexual abuse over the past thirty years. As noted, different researchers have witnessed different impacts. Disturbed academic functioning, substance abuse and alcoholism in later years, revictimization and developing Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Besides, sexual disorders, sex-related cognitions, disturbed intimate relationships, and emotional aspects of sexuality remain highlighted, witnessed, and still need much more consideration. Finally, the study by (Schreier et al. 2017) highlighted another important dimension regarding the impacts of child sexual abuse, as their focus was on the victims’ siblings as an important factor to determine in post-abuse scenarios. As noted, siblings can confront several emotional responses after disclosing the child’s sexual abuse. Siblings’ reactions are important as negative behaviour can increase the post-abuse stress among the victim and the family. Thus, it is concluded that the siblings should also be provided clinical services to reduce the negative impacts of child sexual abuse. Siblings also indicate symptoms of distress on an average level that needs strong consideration.
Conclusion
The gathered evidence unequivocally highlights the pervasive and profound negative impacts of child sexual abuse on the psychological health, cognitive development, and overall well-being of victims. The complex dynamics of the relationship between the abuser and the child, initially built on trust and affection, morph into a distressing paradigm of power, domination, victimization, and, in some examples, revictimization. The susceptibility of children in such situations places their psychological health at considerable risk, necessitating urgent and effective preventive measures to protect their well-being. This study serves to highlight the enduring and detrimental repercussions of child sexual abuse that can persist throughout a child’s life. The complexities of the psychological toll highlight the need for targeted interventions and support mechanisms. Our findings indicate that discussions and heightened awareness surrounding child sexual abuse are imperative. It is not merely a matter of quantifying impacts but a call to action to proactively empower parents, guardians, and responsible authorities to counteract these blatant crimes against children. Thus, our study affirms the critical importance of providing emotional support to victims, recognizing it as an integral component in mitigating the long-term impacts of child sexual abuse. By shedding light on the deep consequences and supporting awareness, we aim to contribute to the collective efforts toward a safer environment for children, free from the effects of sexual abuse.
Implications
Incidents of child sexual abuse are prevalent, especially since access to vulnerable children is even more feasible due to social media and other digital platforms (Ali et al. 2021). Consequently, children are at increased risk of maltreatment, particularly sexual abuse. Consequently, this research has some implications for the service and police departments, parents, and mental healthcare practitioners across the globe.
-
1.
Families should receive prevention support and guidance through proper risk assessment and multi-level parent education (Tener et al. 2020). Parents informing the children about the protection measures can also help them prevent any detrimental incident that may further nullify the impacts of sexual abuse.
-
2.
Providing mental healthcare services to the victims, their families, and their siblings, as also emphasized by (Schreier et al. 2017), also ensures the children’s mental well-being and development, especially among those who have been through any abusive exposure.
-
3.
Besides psychological impacts, there are other detrimental impacts that child faces after sexual abuse that necessitate the provision of adequate healthcare services. These healthcare services aim to ensure the different consequences of abuse and that the victim may overcome the incident (Rahnavardi et al. 2022).
-
4.
Medical healthcare providers, including staff, should also support and guide the victim and their families. Although exposure to a CSA victim can be traumatizing for healthcare practitioners, their behaviour and support patterns can help the victims cope with the challenges, especially with the psychological impacts (Pérez-Fuentes et al. 2013).
-
5.
A victim can also face other consequences that may further worsen the impact of sexual abuse, including bullying. Schools and teachers can also effectively nullify these impacts by supporting and scrutinizing the victims. The focus should be on avoiding any further outcomes on their mental health (Sawyerr and Bagley 2017).
-
6.
Implementing laws and active consideration towards welfare programs and training sessions for children, parents, and teachers as caregivers can also mitigate the impacts of child sexual abuse (Batool and Abtahi 2017).
Limitations and recommendations
Although this study synthesized the findings of recent literature witnessing both short-term and long-term impacts of child sexual abuse, it also contains some primary limitations. First, this study does not involve human subjects or clinical trials that may witness the impacts under study in a particular setting. Second, the Selection of the cited articles was strict and based on only three databases, limiting its scope. Third, the research does not provide any country-specific evidence. Instead, the cited literature is scattered and based on studies from around the world. Finally, although the study empirically witnesses the impacts of child sexual abuse, there are many regions where empirical research on child sexual abuse, its impacts, and causes are understudied. Consequently, this study emphasizes conducting more research on the impacts of child sexual abuse, its prevalence, and causal factors that may further provide strong insights regarding the relevant issue and help propose implications and nullify its impacts.
Data availability
No data is associated with this research project.
Code availability
No codes are available for this study.
References
Ali S (2019) Understanding paedophilia through different perspectives, 1st edn. LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing
Ali S, Haykal HA, Youssef EYM (2021) Child sexual abuse and the internet—a systematic review. Human Arenas. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42087-021-00228-9
Ali S, Pasha SA (2022) A systematic review of the technology enabled child sexual abuse (OCSA) & its impacts. J Leg Ethical Regul Issues 25(5S):1–20
Batool S, Abtahi A (2017) Psychosocial impact of childhood sexual abuse: perspective of victims. J Arts Soc Sci 4(2):36–48
Beltran NP (2010) Long-term psychological consequences of child sexual abuse. Papeles Del Psicólogo 31(2):191–201
Chan KL, Yan E, Brownridge DA, Ip P (2013) Associating child sexual abuse with child victimization in China. J Paediatr 162(5):1028–1034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.10.054
DiLillo DK, Fortier MA, Perry AR (2014) Child abuse and neglect psychology. Department of Faculty Publications, Department of Child Abuse and Neglect. November 2005
Downing NR, Akinlotan M, Thornhill CW (2021) The impact of childhood sexual abuse and adverse childhood experiences on adult health-related quality of life. Child Abuse Negl 120(May):105181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2021.105181
Fisher C, Goldsmith A, Hurcombe R, Soares C (2017) The impacts of child sexual abuse: a rapid evidence assessment. IICSA Research Team, USA
Fontes LFC, Conceição OC, Machado S (2017) Violência sexual na adolescência, perfil da vítima e impactos sobre a saúde mental. Ciencia E Saude Coletiva 22(9):2919–2928. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-81232017229.11042017
Gupta S, Garg S (2020) Causes and effects of child sexual abuse. Int J Innov Sci Res Technol 5(5):1867–1870. https://doi.org/10.38124/ijisrt20may650
Habes M, Elareshi M, Ali S, Ziani A (2022) Analyzing the portrayals of child sexual abuse of Urdu newspapers in developing countries. Pertanika J Soc Sci Humanit 30(4). https://doi.org/10.47836/pjssh.30.4.03
Hodder L, Gow K (2012) The long-term effects of childhood sexual abuse. In: Individual trauma: recovering from deep wounds and exploring the potential for renewal, vol 11, pp 101–114. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005053-199903000-00004
Ma Y (2018) Prevalence of childhood sexual abuse in China: a meta-analysis. J Child Sex Abuse 27(2):107–121. https://doi.org/10.1080/10538712.2018.1425944
MacIntosh HB, Ménard AD (2021) Where are we now? A consolidation of the research on long-term impact of child sexual abuse. J Child Sex Abuse 30(3):253–257. https://doi.org/10.1080/10538712.2021.1914261
Mathews B, Collin-Vézina D (2019) Child sexual abuse: toward a conceptual model and definition. Trauma Violence Abuse 20(2):131–148. https://doi.org/10.1177/1524838017738726
Middleton W, Sachs A, Dorahy MJ (2017) The abused and the abuser: victim–perpetrator dynamics. J Trauma Dissociation 18(3):249–258. https://doi.org/10.1080/15299732.2017.1295373
National Sexual Violence Resource Center (2011) Overview: what is child sexual abuse?
Page MJ, McKenzie JE (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Systematic Reviews. Full Text. https://systematicreviewsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4
Papalia N, Mann E, Ogloff JRP (2021) Child sexual abuse and risk of revictimization: impact of child demographics, sexual abuse characteristics, and psychiatric disorders. Child Maltreat 26(1):74–86. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077559520932665
Pérez-Fuentes G, Olfson M, Villegas L, Morcillo C, Wang S, Blanco C (2013) Prevalence and correlates of child sexual abuse: a national study. Compr Psychiatry 54(1):16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2012.05.010
Petersen AC, Joseph J, Feit M (2014) New directions in child abuse and neglect research. New Directions Child Abuse Neglect Res. https://doi.org/10.17226/18331
Pratiwi AA, Asyary A (2017) The impact of child sexual abuse. J Ultimate Public Health 1(1):13–17. https://doi.org/10.22236/jump-health.v1.i1.p13-17
Pulverman CS, Kilimnik CD, Meston CM (2018) The impact of childhood sexual abuse on women’s sexual health: a comprehensive review. Sexual Med Rev 6(2):188–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.12.002
Rahnavardi M, Shahali S, Montazeri A, Ahmadi F (2022) Health care providers’ responses to sexually abused children and adolescents: a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res 22(1):441. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-022-07814-9
Sawyerr A, Bagley C (2017) Child sexual abuse and adolescent and adult adjustment: a review of British and world evidence, with implications for social work, and mental health and school counselling. Adva Appl Soc 7(1):Article 1. https://doi.org/10.4236/aasoci.2017.71001
Schreier A, Pogue JK, Hansen DJ (2017) Impact of child sexual abuse on non-abused siblings: a review with implications for research and practice. Aggress Violent Behav 34:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2016.11.011
Selengia V, Thuy HNT, Mushi D (2020) Prevalence and patterns of child sexual abuse in selected countries of Asia and Africa: a review of literature. Open J Social Sci 08(09):146–160. https://doi.org/10.4236/jss.2020.89010
Simuforosa M (2015) Factors contributing to child sexual abuse: an ecological analysis. Int J Curr Res 7(6). http://www.journalcra.com
Tenbergen G, Wittfoth M, Frieling H, Ponseti J, Walter M, Walter H, Beier KM, Schiffer B, Kruger THC (2015) The neurobiology and psychology of pedophilia: recent advances and challenges. Front Human Neurosci 9(June). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00344
Tener D, Marmor A, Katz C, Newman A, Silovsky JF, Shields J, Taylor E (2020). Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier connect, the company’s public news and information.
Townsend C (2013) Prevalence and consequences of child sexual abuse compared with other childhood experiences. Darkness to Light, pp 1–19
UNICEF (2020a) Sexual violence against children. UNICEF. https://www.unicef.org/protection/sexual-violence-against-children
UNICEF (2020b) Sexual violence against children. UNICEF
Vaillancourt-Morel M-P, Godbout N, Bédard MG, Charest É, Briere J, Sabourin S (2016) Emotional and sexual correlates of child sexual abuse as a function of self-definition status. Child Maltreat 21(3):228–238. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077559516656069
Wagenmans A, Van Minnen A, Sleijpen M, De Jongh A (2018) El impacto del abuso sexual infantil en los resultados del tratamiento intensivo centrado en el trauma para el TEPT. Eur J Psychotraumatology 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/20008198.2018.1430962
Young Women’s Christian Association (2017) Child Sexual Abuse Facts. https://ywcaweekwithoutviolence.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/20190809-WWV19-CSAFactSheet-1.pdf
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The authors did not receive any funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.A. conceived the first draft of the manuscript. Dr. S.A.P. gathered data and conducted the analysis. Dr. A.C. revised the manuscript and formatted the language and references. Dr. E.Y. contributed in the final revisions and also contributed to restructuring the questions and validation of selected methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This research is approved by the research and ethics committee, Birmingham City University, UK and the Directorate of BASR, Allama Iqbal Open University Islamabad, Pakistan.
Conflict of interest
The authors do not declare any conflicting interests.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, S., Pasha, S., Cox, A. et al. Examining the short and long-term impacts of child sexual abuse: a review study. SN Soc Sci 4, 56 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-024-00852-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-024-00852-6