Abstract
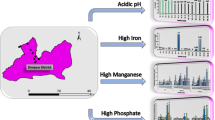
The availability of safe and clean drinking water is very limited across the world. However, it is essential to have access to safe and quality drinking water to lead a healthy life and achieve Sustainable Development Goal 6.1 by 2030. This study examines the quality of drinking water in Palghat village of South Twenty-Four Parganas, West Bengal, considering households’ level factors. A total of 78 households were selected for the study, which represents 15% of the total households. A cross-sectional research design was used and purposive sampling method was applied to conduct the household-level survey. Different improved sources of water were selected using random sampling techniques for the analysis of water quality. The water quality was determined using the water quality index (WQI). We found that 53.8% of the households in the village were dependent on tube wells for drinking water. Besides, 82.1% of the households were directly consuming drinking water without purification. The study depicts that the ordinary tube wells are slightly contaminated with arsenic heavy metals (\(0.05 \mathrm{mg}/\mathrm{L}\)), and the overall water quality of the village is 'unfit for consumption' (WQI: 190.87). Therefore, the authors suggest paying special attention to the water quality of the ordinary hand pumps in the study area. Besides, monitoring of shallow tube wells and spreading public awareness about clean and safe drinking water can improve the water quality and human health in the region.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data was collected through a primary survey with proper consent from the households. Household-level data will be available with reasonable request to the corresponding author. Furthermore, physico-chemical parameters of different improved water sources data are available in the manuscript.
References
Addisie M (2022) Evaluating drinking water quality using water quality parameters and esthetic attributes. Air Soil Water Res 15:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/11786221221075005
Akter T, Jhohura FT, Akter F, Chowdhury TR, Mistry SK, Dey D, Barua MK, Islam MA, Rahman M (2016) Water Quality Index for measuring drinking water quality in rural Bangladesh: a cross-sectional study. J Health Popul Nutr 35(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41043-016-0041-5
Atta HS, Omar MAS, Tawfik AM (2022) Water quality index for assessment of drinking groundwater purpose case study: area surrounding Ismailia Canal, Egypt. J Eng Appl Sci 69(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s44147-022-00138-9
Bain R, Cronk R, Wright J, Yang H, Slaymaker T, Bartram J (2014) Fecal contamination of drinking-water in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med 11(5):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001644
Basu A, Saha D, Saha R, Ghosh T, Saha B (2014) A review on sources, toxicity and remediation technologies for removing arsenic from drinking water. Res Chem Intermed 40(2):447–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-012-1000-4
Chakraborti D, Das B, Rahman MM, Chowdhury UK, Biswas B, Goswami AB, Nayak B, Pal A, Sengupta MK, Ahamed S, Hossain A, Basu G, Roychowdhury T, Das D (2009) Status of groundwater arsenic contamination in the state of West Bengal, India: a 20-year study report. Mol Nutr Food Res 53(5):542–551. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200700517
Chen J, Wu H, Qian H, Gao Y (2017) Assessing nitrate and fluoride contaminants in drinking water and their health risk of rural residents living in a semiarid region of Northwest China. Expo Health 9(3):183–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0231-9
Dahunsi SO, Owamah HI, Ayandiran TA, Oranusi SU (2014) Drinking water quality and public health of selected towns in South Western Nigeria. Water Qual Expo Health 6(3):143–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-014-0118-6
De A, Mridha D, Joardar M, Das A, Chowdhury NR, Roychowdhury T (2022) Distribution, prevalence and health risk assessment of fluoride and arsenic in groundwater from lower Gangetic plain in West Bengal, India. Groundw Sustain Dev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2021.100722
Directorate of Census Operations, West Bengal (2014) India—Census of India 2011—West Bengal—Series 20—Part XII A - District Census Handbook, South Twenty Four Parganas. https://censusindia.gov.in/nada/index.php/catalog/1362
EPA (2017) Drinking Water [Reports and Assessments]. https://www.epa.gov/report-environment/drinking-water
Farzan SF, Karagas MR, Chen Y (2013) In utero and early life arsenic exposure in relation to long-term health and disease. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 272(2):384–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.06.030
Ghosh AK, Sarkar D, Bhattacharya P, Maurya UK, Nayak DC (2006) Mineralogical study of some arsenic contaminated soils of West Bengal, India. Geoderma 136(1):300–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.03.044
Ghosh GC, Khan MJH, Chakraborty TK, Zaman S, Kabir AHME, Tanaka H (2020) Human health risk assessment of elevated and variable iron and manganese intake with arsenic-safe groundwater in Jashore, Bangladesh. Sci Rep 10(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62187-5
Gruber JS, Ercumen A, Colford JM (2014) Coliform bacteria as indicators of diarrheal risk in household drinking water: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 9(9):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107429
Ho L, Alonso A, Eurie Forio MA, Vanclooster M, Goethals PLM (2020) Water research in support of the sustainable development goal 6: a case study in Belgium. J Clean Prod 277:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124082
Ishaque W, Tanvir R, Mukhtar M (2022) Climate change and water crises in Pakistan: implications on water quality and health risks. J Environ Public Health 2022:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5484561
Islam MdS, Mostafa MG (2021) Influence of chemical fertilizers on arsenic mobilization in the alluvial Bengal delta plain: a critical review. J Water Supply Res Technol-Aqua 70(7):948–970. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2021.043
Islam M, Sarkar MK, Afrin T, Rahman SS, Talukder R, Howlader B, Khaleque A (2016) A study on the total dissolved solids and hardness level of drinking mineral water in Bangladesh. Am J Appl Chem 4:164–169. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajac.20160405.11
Islam M, Ercumen A, Naser AM, Unicomb L, Rahman M, Arnold BF, Colford JM Jr, Luby SP (2017) Effectiveness of the hydrogen sulfide test as a water quality indicator for diarrhea risk in rural Bangladesh. Am J Trop Med Hyg 97(6):1867–1871. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.17-0387
Johnson SF (2019) Methemoglobinemia: infants at risk. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care 49(3):57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cppeds.2019.03.002
Khan S, Shahnaz M, Jehan N, Rehman S, Shah MT, Din I (2013) Drinking water quality and human health risk in Charsadda district, Pakistan. J Clean Prod 60:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.02.016
Khan D, Nafees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Bajwa R, Shakoor M, Arshad M, Ali S, Chatha SAS, Deeba F, Murad W, Malook I, Zhu S (2017) Drinking water quality status and contamination in Pakistan. BioMed Res Int 2017:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7908183
Kumar V, Bharti PK, Talwar M, Tyagi AK, Kumar P (2017) Studies on high iron content in water resources of Moradabad district (UP), India. Water Sci 31(1):44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wsj.2017.02.003
Leurs LJ, Schouten LJ, Mons MN, Goldbohm RA, van den Brandt PA (2010) Relationship between tap water hardness, magnesium, and calcium concentration and mortality due to ischemic heart disease or stroke in the Netherlands. Environ Health Perspect 118(3):414–420. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0900782
Li P, Wu J (2019) Drinking water quality and public health. Expo Health 11(2):73–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00299-8
Ma J, Wu S, Shekhar NVR, Biswas S, Sahu AK (2020) Determination of physicochemical parameters and levels of heavy metals in food waste water with environmental effects. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2020:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8886093
Maity S, Biswas R, Sarkar A (2020) Comparative valuation of groundwater quality parameters in Bhojpur, Bihar for arsenic risk assessment. Chemosphere 259:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127398
Meride Y, Ayenew B (2016) Drinking water quality assessment and its effects on residents health in Wondo genet campus, Ethiopia. Environ Syst Res 5(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-016-0053-6
Noubactep C (2010) Metallic iron for safe drinking water worldwide. Chem Eng J 165(2):740–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.09.065
Osta MEL, Masoud M, Alqarawy A, Elsayed S, Gad M (2022) Groundwater suitability for drinking and irrigation using water quality indices and multivariate modeling in Makkah Al-Mukarramah Province. Saudi Arabia Water 14(3):1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030483
Parks JL, McNeill L, Frey M, Eaton AD, Haghani A, Ramirez L, Edwards M (2004) Determination of total chromium in environmental water samples. Water Res 38(12):2827–2838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.04.024
Parvin F, Haque MM, Tareq SM (2022) Recent status of water quality in Bangladesh: a systematic review, meta-analysis and health risk assessment. Environ Chall 6:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100416
Prasanth SVS, Magesh NS, Jitheshlal KV, Chandrasekar N, Gangadhar K (2012) Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the coastal stretch of Alappuzha District, Kerala. India Appl Water Sci 2(3):165–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-012-0042-5
Rahman MM, Dong Z, Naidu R (2015) Concentrations of arsenic and other elements in groundwater of Bangladesh and West Bengal, India: potential cancer risk. Chemosphere 139(2015):54–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.051
Rahmanian N, Ali SHB, Homayoonfard M, Ali NJ, Rehan M, Sadef Y, Nizami AS (2015) Analysis of physiochemical parameters to evaluate the drinking water quality in the state of Perak, Malaysia. J Chem 2015:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/716125
Ray B, Abedin MdA, Shaw R (2020) Safe drinking water solutions in parts of west bengal, india: combating health issues through participatory water management. In: Chan YYE, Shaw R (eds) Public health and disasters: health emergency and disaster risk management in Asia. Springer, Singapore, pp 185–200
Rehman K, Fatima F, Waheed I, Akash MSH (2018) Prevalence of exposure of heavy metals and their impact on health consequences. J Cell Biochem 119(1):157–184. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26234
Roy C, Sati VP, Biswas A, Kumar S (2023) Status of drinking water, sanitation facilities, and hygiene in West Bengal: Evidence from the National Family Health Survey of India (NFHS), 2019–2021. J Water Sanit Hyg Dev 13(1):50–62. https://doi.org/10.2166/washdev.2023.228
Roychowdhury T (2010) Groundwater arsenic contamination in one of the 107 arsenic-affected blocks in West Bengal, India: Status, distribution, health effects and factors responsible for arsenic poisoning. Int J Hyg Environ Health 213(6):414–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2010.09.003
Saha JC, Dikshit AK, Bandyopadhyay M, Saha KC (1999) A review of arsenic poisoning and its effects on human health. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 29(3):281–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389991259227
Samadder SR, Prabhakar R, Khan D, Kishan D, Chauhan MS (2017) Analysis of the contaminants released from municipal solid waste landfill site: a case study. Sci Total Environ 580:593–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.003
Singh N, Singh RP, Mukherjee S, McDonald K, Reddy KJ (2014) Hydrogeological processes controlling the release of arsenic in parts of 24 Parganas district, West Bengal. Environ Earth Sci 72(1):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2940-8
Slekiene J, Mosler HJ (2019) The link between mental health and safe drinking water behaviors in a vulnerable population in rural Malawi. BMC Psychol 7(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-019-0320-1
Srivastava S, Flora SJS (2020) Fluoride in drinking water and skeletal fluorosis: a review of the global impact. Curr Environ Health Rep 7(2):140–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-020-00270-9
Stevenson M, Bravo C (2019) Advanced turbidity prediction for operational water supply planning. Decis Support Syst 119:72–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2019.02.009
Taylor M, Elliott HA, Navitsky LO (2018) Relationship between total dissolved solids and electrical conductivity in Marcellus hydraulic fracturing fluids. Water Sci Technol 77(8):1998–2004. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.092
Toivettula A, Varis O, Vahala R, Juvakoski A (2023) Making waves: mental health impacts of inadequate drinking water services — from sidenote to research focus. Water Res 243(2023):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120335
Tyagi S, Sharma B, Singh P (2013) Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. Am J Water Resour 1(3):34–38. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajwr-1-3-3
Uddin MG, Nash S, Rahman A, Olbert AI (2022) A comprehensive method for improvement of water quality index (WQI) models for coastal water quality assessment. Water Res 219:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118532
Wang Q, Yang Z (2016) Industrial water pollution, water environment treatment, and health risks in China. Environ Pollut 218:358–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.07.011
WHO (2022) Drinking-water [Government Agency]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water
Xue L, Zhao Z, Zhang Y, Liao J, Wu M, Wang M, Sun J, Gong H, Guo M, Li S, Zheng Y (2020) Dietary exposure to arsenic and human health risks in western Tibet. Sci Total Environ 731:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138840
Yan H, Zhuo X, Shen B, Xiang P, Shen M (2016) Determination of nitrite in whole blood by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection and a case of nitrite poisoning. J Forensic Sci 61(1):254–258. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.12918
Yuan W, Yang N, Li X (2016) Advances in understanding how heavy metal pollution triggers gastric cancer. BioMed Res Int 2016:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7825432
Zhang L, Huang D, Yang J, Wei X, Qin J, Ou S, Zhang Z, Zou Y (2017) Probabilistic risk assessment of Chinese residents’ exposure to fluoride in improved drinking water in endemic fluorosis areas. Environ Pollut 222:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.074
Acknowledgements
Chandan Roy is a recipient of Indian Council of Social Science Research Doctoral Fellowship. His/her article is largely an outcome of his/her doctoral work sponsored by ICSSR. However, the responsibility for the facts stated, opinions expressed and the conclusions drawn is entirely that of the author.
Funding
Indian Council of Social Science Research, RFD/2022-23/GEN/HLTH/240, Chandan Roy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CR contributed to the conceptualization and study design. CR and SP performed the household-level survey. CR performed the physicochemical analysis of water samples and statistical analysis. CR interpreted the results and discussed the findings. CR, SK, VPS, and SP finalized the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, C., Kumar, S., Sati, V.P. et al. Investigating the physico-chemical properties of drinking water: a case study of South Twenty-Four Parganas, West Bengal. SN Soc Sci 3, 187 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-023-00778-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-023-00778-5