Abstract
Background
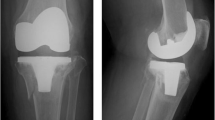
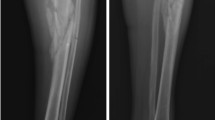
Treatment of tibia (upper third and diaphysis) fracture together with severe osteoarthritis (OA) poses challenge to an orthopedic surgeon. Traditionally, it is treated through three-stage surgeries, first fracture fixation followed by implant removal and finally surgery of total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Herein, we describe a novel TKA procedure using long-stemmed tibia component. This one-step technique not only addresses arthritis of the knee joint but also helps in assisting fixation of the fracture.
Materials and Methods
We reported outcomes of three female non-diabetic patients with OA who developed tibia shaft fracture following trauma. Range of motion and quadriceps strengthening exercise were initiated immediately after the procedure. X-rays anteroposterior and lateral views of the operated limbs were obtained at post-operative week-6 and week-12. We allowed the patients’ toe touch weight-bearing immediately after the surgery. The patients were progressed to full weight-bearing after confirming radiological union on the X-rays.
Results
At follow-up, all treated patients were able to mobilize with good range of motion of the operated knee and with union of the fracture. The American Knee society scores and WOMAC pain and stiffness scores improved significantly.
Conclusion
This novel technique offers one-stage solution to the complex situation of osteoarthritis of the knee with associated tibia shaft fracture, thereby reducing future hospital admissions/surgeries and associated costs and complications. Further, it allows faster rehabilitation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- OA:
-
Osteoarthritis
- TKA:
-
Total knee arthroploasty
- IM:
-
Intramedullary
- AP:
-
Antero-posterior
References
Court-Brown, C. M., & McBirnie, J. (1995). The epidemiology of tibial fractures. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British Volume, 77(3), 417–421
Madadi, F., VahidFarahmandi, M., Eajazi, A., DaftariBesheli, L., Madadi, F., & Nasri, L. M. (2010). Epidemiologyofadulttibialshaftfractures:A7-yearstudyinamajorreferralorthopediccenterin Iran. Medical science monitor. International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research, 16(5), 217–221
Grutter, R., Cordey, J., Buhler, M., Johner, R., & Regazzoni, P. (2000). The epidemiology of diaphyseal fractures of the tibia. Injury, 31(Suppl 3), C64–C67
Kelsey, J. L., Keegan, T. H., Prill, M. M., Quesenberry, C. P., Jr., & Sidney, S. (2006). Risk factors for fracture of the shafts of the tibia and fibula in older individuals. Osteoporosis International, 17(1), 143–149 A Journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA.
Clement, N. D., Beauchamp, N., Duckworth, A. D., & Mcqueen, M. (2013). The outcome of tibialdiaphyseal fractures in the elderly. Bone and Joint Journal, 95-B(9), 1255–1262
Mittal, A., Bhosale, P. B., Suryawanshi, A. V., & Purohit, S. (2013). One-stage long-stem total knee arthroplasty for arthritic knees with stress fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery (Hong Kong), 21(2), 199–203
Karladani, A. H., Granhed, H., Edshage, B., Jerre, R., & Styf, J. (2000). Displaced tibial shaft fractures: A prospective randomized study of closed intramedullary nailing versus cast treatment in 53 patients. ActaOrthopaedicaScandinavica, 71(2), 160–167
Karladani, A. H., & Styf, J. (2001). Percutaneous intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures: A new approach for prevention of anterior knee pain. Injury, 32(9), 736–739
Karladani, A. H., Svantesson, U., Granhed, H., & Styf, J. (2001). Postural control and torque of the knee joint after healed tibial shaft fracture. Injury, 32(1), 57–60
Yu, J., Li, L., Wang, T., Sheng, L., Huo, Y., Yin, Z., et al. (2015). Intramedullary nail versus plate treatments for distal tibial fractures: A meta-analysis. International Journal of Surgery (London, England), 16(Pt A), 60–68
Sawant, M. R., Bendall, S. P., Kavanagh, T. G., & Citron, N. D. (1999). Nonunion of tibial stress fractures in patients with deformed arthritic knees. Treatment using modular total knee arthroplasty. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British Volume, 81(4), 663–666
Tomlinson, M. P., Dingwall, I. M., & Phillips, H. (1995). Total knee arthroplasty in the management of proximal tibial stress fractures. The Journal of Arthroplasty, 10(5), 707–713
Moskal, J. T., & Mann, J. W., 3rd. (2001). Simultaneous management of ipsilateral gonarthritis and ununitedtibial stress fracture: Combined total knee arthroplasty and internal fixation. The Journal of Arthroplasty, 16(4), 506–511
Mullaji, A., & Shetty, G. (2010). Total knee arthroplasty for arthritic knees with tibiofibular stress fractures: Classification and treatment guidelines. The Journal of Arthroplasty, 25(2), 295–301
Sounderrajan, D., Rajkumar, N., Dhanasekararaja, P., & Rajasekaran, S. (2018). Proximal tibia stress fracture with osteoarthritis of knee: Radiological and functional analysis of one stage TKA with long stem. SICOT-J, 4, 13
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the help provided by Dr Udita Chandra in manuscript editing.
Funding
No funding was obtained.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed significantly to the preparation of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
There are no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Institutional review board approval was obtained before the study. Also all patients were consented.
Ethical Standard Statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for Publication
We hereby give our consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Londhe, S.B., Shah, R.V., Agrawal, P.O. et al. An Early Experience with a Novel Technique of Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritic Knee with Coexistent Traumatic Tibia Diaphysis Fracture. JOIO 56, 110–115 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-021-00406-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-021-00406-5