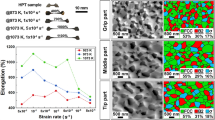
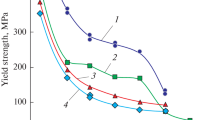
Abstract
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are a new class of engineering materials with unique mechanical and functional properties. Superplastic forming of HEAs might be a viable route for actual applications of these alloys. Accordingly, the superplastic behaviors of HEAs and medium-entropy alloys (MEAs) were summarized in this monograph, along with reviewing the basics of high-entropy alloys and fine-grained superplasticity. Moreover, the HEAs were introduced and the phase formation rules were discussed. Furthermore, the influences of grain refinement (by thermomechanical processing and severe plastic deformation (SPD) methods) and deformation conditions (temperature and strain rate) with special attention to the high strain rate superplasticity were summarized. The significance of thermal stability of the microstructure against grain coarsening was noticed, where the effects of multi-phase microstructure, formation of pinning particles, and favorable effects of the addition of alloying elements were explained. The effects of deformation temperature and strain rate on the thermally activated grain boundary sliding (GBS), precipitation of secondary phases (especially the Cr-rich σ phase), dissolution of phases, deformation-induced (dynamic) grain growth, partial melting, and dynamic recrystallization (DRX) were discussed for different HEAs and MEAs. The final part of this overview article is dedicated to the future prospects and research directions.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors stated that the processed data required to reproduce these findings were available in this manuscript.
References
Li Z, Zhao S, Ritchie RO, Meyers MA. Mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys with emphasis on face-centered cubic alloys. Prog Mater Sci. 2019;102:296–345.
Zhang W, Liaw PK, Zhang Y. Science and technology in high-entropy alloys. Sci China Mater. 2018;61:2–22.
Yeh JW, Chen SK, Lin SJ, Gan JY, Chin TS, Shun TT, Tsau CH, Chang SY. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv Eng Mater. 2004;6:299–303.
Cantor B, Chang I, Knight P, Vincent A. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2004;375:213–8.
George EP, Raabe D, Ritchie RO. High-entropy alloys. Nat Rev Mater. 2019;4:515–34.
Nguyen NTC, Asghari-Rad P, Sathiyamoorthi P, Zargaran A, Lee CS, Kim HS. Ultrahigh high-strain-rate superplasticity in a nanostructured high-entropy alloy. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2736.
Kuznetsov AV, Shaysultanov DG, Stepanov ND, Salishchev GA, Senkov ON. Tensile properties of an AlCrCuNiFeCo high-entropy alloy in as-cast and wrought conditions. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2012;533:107–18.
Langdon TG. Seventy-five years of superplasticity: historic developments and new opportunities. J Mater Sci. 2009;44:5998–6010.
Kawasaki M, Langdon TG. Principles of superplasticity in ultrafine-grained materials. J Mater Sci. 2007;42:1782–96.
Reddy SR, Bapari S, Bhattacharjee PP, Chokshi AH. Superplastic-like flow in a fine-grained equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Mater Res Lett. 2017;5:408–14.
Masuda H, Sato E. Diffusional and dislocation accommodation mechanisms in superplastic materials. Acta Mater. 2020;197:235–52.
Asghari-Rad P, Nguyen NTC, Zargaran A, Sathiyamoorthi P, Kim HS. Deformation-induced grain boundary segregation mediated high-strain rate superplasticity in medium entropy alloy. Scripta Mater. 2022;207:114239.
Gifkins RC. Grain-boundary sliding and its accommodation during creep and superplasticity. Metall Trans A. 1976;7:1225–32.
Ball A, Hutchison MM. Superplasticity in the aluminium–zinc eutectoid. Metal Sci J. 1969;3:1–7.
Mirzadeh H. High strain rate superplasticity via friction stir processing (FSP): a review. Mater Sci Eng A. 2021;819:141499.
Figueiredo RB, Langdon TG. Strategies for achieving high strain rate superplasticity in magnesium alloys processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Scripta Mater. 2009;61:84–7.
Kim WJ, Moon IK, Han SH. Ultrafine-grained Mg–Zn–Zr alloy with high strength and high-strain-rate superplasticity. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2012;538:374–85.
Orozco-Caballero A, Álvarez-Leal M, Hidalgo-Manrique P, Cepeda-Jiménez CM, Ruano OA, Carreño F. Grain size versus microstructural stability in the high strain rate superplastic response of a severely friction stir processed Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2017;680:329–37.
Giuliano G. Superplastic forming of advanced metallic materials. Woodhead Publishing; 2011.
Kassner ME, Pérez-Prado MT. Fundamentals of creep in metals and alloys. Elsevier; 2004.
Shahmir H, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG. Developing superplasticity in high-entropy alloys processed by severe plastic deformation. Mater Sci Forum. 2018;941:1059–64.
Gao MC, Yeh JW, Liaw PK, Zhang Y. High-entropy alloys. Springer; 2016.
Miracle DB, Senkov ON. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017;122:448–511.
Li W, Xie D, Li D, Zhang Y, Gao Y, Liaw PK. Mechanical behavior of high-entropy alloys. Prog Mater Sci. 2021;118:100777.
Daryoush S, Mirzadeh H, Ataie A. Amorphization, mechano-crystallization, and crystallization kinetics of mechanically alloyed AlFeCuZnTi high-entropy alloys. Mater Lett. 2022;307:131098.
Takeuchi A, Inoue A. Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater Trans. 2005;46:2817–29.
Daryoush S, Mirzadeh H, Ataie A. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys by mechanical alloying: a review of principles and magnetic properties. J Ultraf Grain Nanostruct Mater. 2021;54:112–20.
Guo S, Ng C, Lu J, Liu CT. Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J Appl Phys. 2011;109:103505.
Dwivedi A, Koch CC, Rajulapati KV. On the single phase fcc solid solution in nanocrystalline Cr-Nb-Ti-V-Zn high-entropy alloy. Mater Lett. 2016;183:44–7.
Shivam V, Sanjana V, Mukhopadhyay NK. Phase evolution and thermal stability of mechanically alloyed AlCrFeCoNiZn High-entropy alloy. Trans Indian Inst Met. 2020;73:821–30.
Vaidya M, Muralikrishna GM, Murty BS. High-entropy alloys by mechanical alloying: a review. J Mater Res. 2019;34:664–86.
Srivatsan TS, Gupta M. High entropy alloys: innovations, advances, and applications. CRC Press; 2021.
Kuznetsov AV, Shaisultanov DG, Stepanov N, Salishchev GA, Senkov ON. Superplasticity of AlCoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater Sci Forum. 2013;735:146–51.
Shaysultanov DG, Stepanov ND, Kuznetsov AV, Salishchev GA, Senkov ON. Phase composition and superplastic behavior of a wrought AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. JOM. 2013;65:1815–28.
Stepanov N, Shaysultanov DG, Salishchev GA, Senkov ON. Mechanical behavior and microstructure evolution during superplastic deformation of the fine-grained AlCoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater Sci Forum. 2016;838:302–7.
Munitz A, Kaufman MJ, Nahmany M, Derimow N, Abbaschian R. Microstructure and mechanical properties of heat treated Al1.25CoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2018;714:146–59.
Cantor B. Multicomponent high-entropy Cantor alloys. Prog Mater Sci. 2020;120:100754.
Najafkhani F, Kheiri S, Pourbahari B, Mirzadeh H. Recent advances in the kinetics of normal/abnormal grain growth: a review. Arch Civil Mech Eng. 2021;21:29.
Shahmir H, He J, Lu Z, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG. Evidence for superplasticity in a CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A. 2017;685:342–8.
Schuh B, Mendez-Martin F, Völker B, George EP, Clemens H, Pippan R, Hohenwarter A. Mechanical properties, microstructure and thermal stability of a nanocrystalline CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy after severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater. 2015;96:258–68.
Shahmir H, Nili-Ahmadabadi M, Shafiee A, Langdon TG. Effect of a minor titanium addition on the superplastic properties of a CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A. 2018;718:468–76.
Watanabe H, Murata T, Nakamura S, Ikeo N, Mukai T, Tsuchiya K. Effect of cold-working on phase formation during heat treatment in CrMnFeCoNi system high-entropy alloys with Al addition. J Alloys Compd. 2021;872:159668.
Jeong HT, Kim WJ. Calculation and construction of deformation mechanism maps and processing maps for CoCrFeMnNi and Al0.5CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2021;869:159256.
Nguyen NTC, Moon J, Sathiyamoorthi P, Asghari-Rad P, Kim GH, Lee CS, Kim HS. Superplasticity of V10Cr15Mn5Fe35Co10Ni25 high-entropy alloy processed using high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A. 2019;764:138198.
Nene SS, Liu K, Sinha S, Frank M, Williams S, Mishra RS. Superplasticity in fine grained dual phase high entropy alloy. Materialia. 2020;9:100521.
Nguyen NTC, Asghari-Rad P, Bae JW, Sathiyamoorthi P, Kim HS. Superplastic behavior in high-pressure torsion-processed Mo7.5Fe55Co18Cr12.5Ni7 medium-entropy alloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 2021;52:1–7.
Sohn SS, Kim DG, Jo YH, da Silva AK, Lu W, Breen AJ, Gault B, Ponge D. High-rate superplasticity in an equiatomic medium-entropy VCoNi alloy enabled through dynamic recrystallization of a duplex microstructure of ordered phases. Acta Mater. 2020;194:106–17.
Picak S, Yilmaz HC, Karaman I. Simultaneous deformation twinning and martensitic transformation in CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy at high temperatures. Scripta Mater. 2021;202:113995.
Hoseini-Athar MM, Mahmudi R, Babu RP, Hedström P. Microstructure and superplasticity of Mg–2Gd–xZn alloys processed by equal channel angular pressing. Mater Sci Eng A. 2021;808:140921.
Suryanarayana C. Synthesis of nanocomposites by mechanical alloying. J Alloy Compd. 2011;509:S229–34.
Picak S, Wegener T, Sajadifar SV, Sobrero C, Richter J, Kim H, Niendorf T, Karaman I. On the low-cycle fatigue response of CoCrNiFeMn high entropy alloy with ultra-fine grain structure. Acta Mater. 2021;205:116540.
Shahmir H, Mousavi T, He J, Lu Z, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG. Microstructure and properties of a CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Mater Sci Eng A. 2017;705:411–9.
Shivam V, Basu J, Pandey VK, Shadangi Y, Mukhopadhyay NK. Alloying behaviour, thermal stability and phase evolution in quinary AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Adv Powder Technol. 2018;29:2221–30.
Yadav S, Sarkar S, Aggarwal A, Kumar A, Biswas K. Wear and mechanical properties of novel (CuCrFeTiZn)100-xPbx high entropy alloy composite via mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Wear. 2018;410:93–109.
Harwani D, Badheka V, Patel V, Li W, Andersson J. Developing superplasticity in magnesium alloys with the help of friction stir processing and its variants—a review. J Market Res. 2021;12:2055–75.
Funding
This work received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
The manuscript has been prepared by the contribution of all the authors, it is the original authors work, it has not been published before, it has been solely submitted to this journal, and if accepted, it will not be submitted to any other journal in any language.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motallebi, R., Savaedi, Z. & Mirzadeh, H. Superplasticity of high-entropy alloys: a review. Archiv.Civ.Mech.Eng 22, 20 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-021-00344-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-021-00344-x