Abstract
Polypogon monspeliensis (L.) Desf. is an annual monocot weed belonging to Poaceae family, with reported folkloric medicinal uses. In this work, the hepatoprotective potentials of the aerial parts methanolic extract were assessed by in vitro CCl4 anti-hepatotoxicity on human liver-derived HepG2 cell line. In silico molecular docking studies of the UHPLC/QTOF-MS/MS investigated compounds explored to ensure the in vitro hepatoprotective potentials. In vitro hepatoprotective examination exhibited comparable effect of P. monspeliensis and positive control, silymarin. Annotation of the secondary metabolites was performed by UHPLC/QTOF-MS/MS, which allowed the tentative identification of 35 metabolites based on their exact mass information, fragmentation characteristics, and retention time values. Formononetin and linarin were the major identified components. Notably, linarin displayed a significant binding score of -6.74 kcal/mol, surpassing the binding scores of the co-crystallized ligand 703 (-6.05 kcal/mol) and the reference silybin A (-5.89 kcal/mol) assuring its prominent in vitro hepatoprotective activities. Additionally, the established absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion properties unveiled the hepatoprotective properties of both formononetin and linarin. The results assured that P. monspeliensis is a promising hepatoprotective agent, with special consideration for formononetin and linarin.
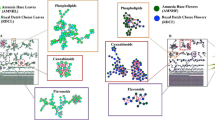
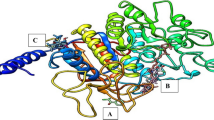
Graphical Abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abdallah SH, Mostafa NM, MaEH Mohamed, Nada AS, Singab ANB (2022) UPLC-ESI-MS/MS profiling and hepatoprotective activities of stevia leaves extract, butanol fraction and stevioside against radiation-induced toxicity in rats. Nat Prod Res 36:5619–5625. https://doi.org/10.21608/ajps.2021.153559
Abdel Maboud T (2021) Cytotoxic potentials and phytoconstituents profiling of Blepharis edulis (Forssk.) Pers. using UHPLC/Q-TOF-MS-MS. Al-Azhar J Pharm Sci 63:37–56. https://doi.org/10.21608/ajps.2021.153559
Benayad Z, Gómez-Cordovés C, Es-Safi NE (2014) Characterization of flavonoid glycosides from fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) crude seeds by HPLC–DAD–ESI/MS analysis. Int J Mol Sci 15:20668–20685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120668
Brenton AG, Godfrey AR (2010) Accurate mass measurement: terminology and treatment of data. J Am Soc Mass Spectr 21:1821–1835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasms.2010.06.006
Carter PH, Scherle PA, Muckelbauer JA, Voss ME, Liu R-Q, Thompson LA, Tebben AJ, Solomon KA, Lo YC, Li Z (2001) Photochemically enhanced binding of small molecules to the tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 inhibits the binding of tnf-α. P Natl Acad Sci 98:11879–11884. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.21117839
Chaturvedi S, Malik MY, Azmi L, Shukla I, Naseem Z, Rao C, Agarwal NK (2018) Formononetin and biochanin a protects against ritonavir induced hepatotoxicity via modulation of nfκb/pakt signaling molecules. Life Sci 213:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.10.023
Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V (2017) Swissadme: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep 7:42717. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717
Dakshini K (1995) Allelopathic potential of an annual weed, Polypogon monspeliensis, in crops in India. Plant Soil 173:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011462
Elmaaty AA, Darwish KM, Khattab M, Elhady SS, Salah M, Hamed MI, Al-Karmalawy AA, Saleh MM (2021) In a search for potential drug candidates for combating COVID-19: computational study revealed salvianolic acid b as a potential therapeutic targeting 3CLpro and spike proteins. J Biomol Struct Dyn 40:8866–8893. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2021.1918256
Fatima I, Kanwal S, Mahmood T (2019) Microbiostatic, antioxidative and cytotoxic potentiation of some grasses of Bahawalpur. Pakistan J Trad Chin Med 39:482
Fayek NM, Farag MA, Abdel Monem AR, Moussa MY, Abd-Elwahab SM, El-Tanbouly ND (2019) Comparative metabolite profiling of four citrus peel cultivars via ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time-of-flight-mass spectrometry and multivariate data analyses. J Chromatogr Sci 57:349–360. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmz006
Ferreres F, Llorach R, Gil-Izquierdo A (2004) Characterization of the interglycosidic linkage in di-, tri-, tetra-and pentaglycosylated flavonoids and differentiation of positional isomers by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectr 39:312–321. https://doi.org/10.1002/jms.586
Harun N, Chaudhry AS, Shaheen S, Ullah K, Khan F (2017) Ethnobotanical studies of fodder grass resources for ruminant animals, based on the traditional knowledge of indigenous communities in central Punjab Pakistan. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed 13:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13002-017-0184-5
Jin F, Wan C, Li W, Yao L, Zhao H, Zou Y, Peng D, Huang W (2017) Formononetin protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity through enhanced nrf2 activity. PLoS ONE 12:e0170900. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170900
Karimi G, Vahabzadeh M, Lari P, Rashedinia M, Moshiri M (2011) “Silymarin”, a promising pharmacological agent for treatment of diseases. Iranian J Basic Med Sci 14:308
Khan MA, Qaiser M (2006) Halophytes of Pakistan: characteristics, distribution and potential economic usages. In: Khan MA, Böer B, Kust GS, Barth HJ (eds) Sabkha Ecosystems. Tasks for Vegetation Science, vol 42. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-5072-5_11.
Khattab M, Al-Karmalawy AA (2021) Computational repurposing of benzimidazole anthelmintic drugs as potential colchicine binding site inhibitors. Future Med Chem 13:1623–1638. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc-2020-0273
Krawczyk-Łebek A, Dymarska M, Janeczko T, Kostrzewa-Susłow E (2022) 4′-Methylflavanone glycosides obtained using biotransformation in the entomopathogenic filamentous fungi cultures as potential anticarcinogenic, antimicrobial, and hepatoprotective agents. Int J Mol Sci 23:5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105373
Levy DD, Zeiger E, Escobar PA, Hakura A, Bas-Jan M, Kato M, Moore MM, Sugiyama K-I (2019) Recommended criteria for the evaluation of bacterial mutagenicity data (Ames test). Mutat Res 848:403074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2019.07.004
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (1997) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliver Rev 23:3–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(96)00423-1
Ma B-X, Meng X-S, Tong J, Ge L-L, Zhou G, Wang Y-W (2018) Protective effects of Coptis chinensis inflorescence extract and linarin against carbon tetrachloride-induced damage in hepg2 cells through the mapk/keap1-nrf2 pathway. Food Funct 9:2353–2361. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FO00078F
Manjunatha B, Bodke YD, Kumaraswamy H, Pasha KM, Prashanth N (2022) Synthesis, computational, hepatoprotective, antituberculosis and molecular docking studies of some coumarin derivatives. J Mol Struct 1254:132410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.132410
Minnady M, Jayapal G, Poochi S, Nethaji P, Mathalaimuthu B (2022) Hepatoprotective effect of indigenous medicinal plants-a review. Indian J Pharm Sci 84:1116–1132
Mohammed HA, Khan RA, Abdel-Hafez AA, Abdel-Aziz M, Ahmed E, Enany S, Mahgoub S, Al-Rugaie O, Alsharidah M, Aly MS (2021) Phytochemical profiling, in vitro and in silico anti-microbial and anti-cancer activity evaluations and staph gyraseb and h-top-iiβ receptor-docking studies of major constituents of Zygophyllum coccineum L. aqueous-ethanolic extract and its subsequent fractions: an approach to validate traditional phytomedicinal knowledge. Molecules 26:577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030577
Pires DE, Blundell TL, Ascher DB (2015) Pkcsm: predicting small-molecule pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties using graph-based signatures. J Med Chem 58:4066–4072. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00104
Rowe HC, Ro D-K, Rieseberg LH (2012) Response of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) leaf surface defenses to exogenous methyl jasmonate. PLoS One 7:37191. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037191
Roy S, Mathew M (2018) Fluid flow modulates electrical activity in cardiac herg potassium channels. J Biol Chem 293:4289–4303. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037191
Sánchez-Moreiras A, Weiss O, Reigosa-Roger M (2003) Allelopathic evidence in the Poaceae. Bot Rev 69:300–319. https://doi.org/10.1663/0006-8101(2003)069[0300:AEITP]2.0.CO;2
Sanguinetti MC (2014) Herg1 channel agonists and cardiac arrhythmia. Curr Opin Pharmacol 15:22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2013.11.006
Scalbert A, Morand C, Manach C, Rémésy C (2002) Absorption and metabolism of polyphenols in the gut and impact on health. Biomed Pharmacother 56:276–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0753-3322(02)00205-6
Siddiqui MA, Ali Z, Chittiboyina AG, Khan IA (2018) Hepatoprotective effect of steroidal glycosides from Dioscorea villosa on hydrogen peroxide-induced hepatotoxicity in hepg2 cells. Front Pharmacol 9:797. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00797
Sonibare M, Ayoola I, Gueye B, Abberton M, D’souza R, Kuhnert N (2018) Leaves metabolomic profiling of Musa acuminata accessions using UPLC–QTOF–MS/MS and their antioxidant activity. J Food Meas Charact 12:1093–1106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-018-9725-4
Soreng RJ, Peterson PM, Romaschenko K, Davidse G, Zuloaga FO, Judziewicz EJ, Filgueiras TS, Davis JI, Morrone O (2015) A worldwide phylogenetic classification of the Poaceae (Gramineae). J Syst Evol 53:117–137. https://doi.org/10.1111/jse.12150
Su Y, Han FX, Chen J, Sridhar BM, Monts DL (2008) Phytoextraction and accumulation of mercury in three plant species: Indian mustard (Brassica juncea), beard grass (Polypogon monspeliensis), and Chinese brake fern (Pteris vittata). Int J Phytoremediation 10:547–560. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510802115091
Thirunavukkarasu P, Asha S, Ramanathan T, Balasubramanian T, Shanmogapriya R, Renugadevi G (2014) In vitro hepatoprotective activity of isolated fractions of Cressa cretica. Pharm Chem J 48:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-014-1061-3
Tian J, Wang X-Q, Tian Z (2022) Focusing on formononetin: recent perspectives for its neuroprotective potentials. Front Pharmacol 13:905898. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.905898
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AH and HA. Methodology: MH, MA, RE, and AI. Software: HA and TK. Validation: MH, MA, and RE. Formal analysis: MH, TK, and AI. Investigation: AA, YA, and TK. Resources: MH and AA. Data curation: MH, AAE, AI, and AH. Writing original draft: HA, MH, AAE, and RE. Writing, review, and editing: TK, MA, YA, AAE, SE, and AI. Supervision: HA and AA. Project administration: AH, HA, and AA-H. Funding acquisition: AA-H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abbass, H.S., Hegazy, M.M., kedra, T.A. et al. Polypogon monspeliensis Hepatoprotective Attributes: UHPLC/QTOF-MS/MS Metabolite Profiling and In Vitro and In Silico Studies. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-024-00554-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-024-00554-3