Abstract
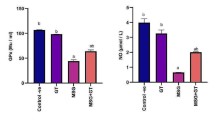
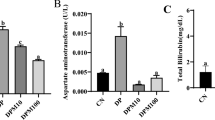
Propiconazole is a broadly used fungicide that leaves residues in food and water causing severe dangerous effects on humans and animals. The current investigation was performed to evaluate the propiconazole toxicity on the liver and kidney of male albino rats and to assess the protective role of carvacrol against these adverse effects. Sixty male Wistar albino rats were used in this experiment and were divided into four equal groups: control group, propiconazole group, carvacrol group, and propiconazole + carvacrol group. Rats were treated daily by oral gavage for 60 days with propiconazole (75 mg/kg) and/or carvacrol (50 mg/kg). The results demonstrated that exposure to propiconazole resulted in a significant elevation in serum biomarkers that indicate malfunction of the liver and kidney. Additionally, exposure to propiconazole resulted in oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation manifested by a significant reduction in glutathione content and catalase activity, and a significant increase in malondialdehyde content in the liver and kidney. These toxic effects were confirmed by histopathological studies and DNA laddering assay. Conversely, carvacrol reduced propiconazole-induced detrimental effects and improved the histopathological pictures of both liver and kidney tissues. Therefore, carvacrol can be used as a prophylactic natural compound against propiconazole-induced toxic effects in the liver and kidney.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JW, Wolf DC, George MH, Hester SD, Sun G, Thai SF, Delker DA, Moore T, Jones C, Nelson G, Roop BC, Leavitt S, Winkfield E, Ward WO, Nesnow S (2006) Toxicity profiles in mice treated with hepatotumorigenic and non-hepatotumorigenic triazole conazole fungicides: propiconazole triadimefon and myclobutanil. Toxicol Pathol 34:853–862. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230601047816
Alma MH, Mavi A, Yildirim A (2003) Screening chemical composition and in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the essential oils from Oreganum synaceum L growing in Turkey. Biol Pharm Bull 26:1725–1729. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.26.1725
Aristatile B, Numair AKS, Veeramani C, Pugalendi KV (2009) Antihyperlipidemic effect of carvacrol on D-galactosamine induced hepatotoxic rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 20:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp.2009.20.1.15
Azirak S, Rencuzogullari E (2008) The in vivo genotoxic effects of carvacrol and thymol in rat bone marrow cells. Environ Toxicol 23:728–735. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20380
Azouz RA, Hassanen EI (2020) Modulating effect of gum arabic on cisplatin-induced testicular damage in albino Wister rats. Rev Bras 30:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-020-00015-7
Azouz RA, Korany RMS (2020) Toxic impacts of amorphous silica nanoparticles on liver and kidney of male adult rats: an in vivo study. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02386-3
Baser KHC (2008) Biological and pharmacological activities of carvacrol and carvacrol bearing essential oils. Curr Pharm Des 14:3106–3120. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161208786404227
Ben Saad H, Kammoun I, Boudawara T, Zeghal KM, Hakim A, Amara IB (2017) Effects of selenium on tebuconazole-induced hepatotoxicity in adult rats. Res Rev Biosci 12:118
Bruno M, Moore T, Nesnow S, Ge Y (2009) Protein carbonyl formation in response to propiconazole-induced oxidative stress. J Proteome Res 8:2070–2078. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr801061r
Chen PJ, Moore T, Nesnow S (2008) Cytotoxic effects of propiconazole and its metabolites in mouse and human hepatoma cells and primary mouse hepatocytes. Toxicol in Vitro 22:1476–1483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2008.05.001
Devaraj VC, Krishna BG, Viswanatha GL (2011) Hepatoprotective activity of Hepax-A polyherbal formulation. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 1:142–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-1691(11)60013-0
Elhady MA, Khalaf AA, Kamel MM, Noshy PA (2019) Carvacrol ameliorates behavioral disturbances and DNA damage in the brain of rats exposed to propiconazole. NeuroToxicology 70:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2018.10.008
Guimarães AG, Oliveira GF, Melo MS, Cavalcanti SC, Antoniolli AR, Bonjardim LR, Silva FA, Santos JP, Rocha RF, Moreira JC, Araújo AA, Gelain DP, Quintans-Júnior LJ (2010) Bioassay-guided evaluation of antioxidant and antinociceptive activities of carvacrol. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 107:949–957. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2010.00609.x
Hamdi H, Othmène YB, Ammar O (2019) Oxidative stress genotoxicity biochemical and histopathological modifications induced by epoxiconazole in liver and kidney of Wistar rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:17535–17547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05022-3
Hassanen EI, Khalaf AA, Tohamy AF, Mohammed ER, Farroh KY (2019a) Toxicopathological and immunological studies on different concentrations of chitosan-coated silver nanoparticles in rats. Int J Nanomedicine 14:4723–4739. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S207644
Hassanen EI, Tohamy AF, Hassan AM, Ibrahim MA, Issa MY, Farroh KY (2019b) Pomegranate juice diminishes the mitochondrial-dependent cell death and NF-ĸB signaling pathway induced by copper oxide nanoparticles on the liver and kidneys of rats. Int J Nanomedicine 14:8905–8922. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S229461
Hassanen EI, Morsy EA, Hussien AM, Ibrahim MA, Farroh KY (2020) The effect of different concentrations of gold nanoparticles on growth performance toxicopathological and immunological parameters of broiler chickens. Biosci Rep 40:BSR20194296. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20194296
JMPR (2004) Propiconazole. Pesticide Residues in Food – Part II Toxicological Evaluations. Joint FAO/WHO Meeting on Pesticide Residues, Rome, Italy, pp. 281–323
Khalaf AA, Hassanen EI, Azouz RA (2019) Ameliorative effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles against dermal toxicity induced by lead oxide in rats. Int J Nanomedicine 14:7729–7741. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S220572
Khalaf AA, Hassanen EI, Ibrahim MA (2020) Rosmarinic acid attenuates chromium-induced hepatic and renal oxidative damage and DNA damage in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 34:e22579. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22579
Klaunig JE, Kamendulis LM, Hocevar BA (2010) Oxidative stress and oxidative damage in carcinogenesis. Toxicol Pathol 38:96–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.11.028
Landa P, Kokoska L, Pribylova M, Vanek T, Marsik P (2009) In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of carvacrol: ınhibitory effect on COX-2 catalyzed prostaglandin E (2) biosynthesis. Arch Pharm Res 32:75–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1120-6
Li ZH, Zlabek V, Grabic R, Li P, Randak T (2011) Biochemical responses in gills of rainbow trout exposed to propiconazole. Cent Eur J Biol 6:84–90. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-010-0105-2
Maalej A, Mahmoudi A, Bouallagui Z, Fki I, Marrekchi R, Sayadi S (2017) Olive phenolic compounds attenuate deltamethrin-induced liver and kidney toxicity through regulating oxidative stress inflammation and apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol 106:455–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.06.010
Morgan A, Galal MK, Ogaly HA, Ibrahim MA, Abd-Elsalam RM, Noshy P (2017) Tiron ameliorates oxidative stress and inflammation in titanium dioxide nanoparticles induced nephrotoxicity of male rats. Biomed Pharmacother 93:779–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.006
Mustafa SA, Karieb SS, Davies SJ, Jha AN (2015) Assessment of oxidative damage to DNA transcriptional expression of key genes lipid peroxidation and histopathological changes in carp Cyprinus carpio L following exposure to chronic hypoxic and subsequent recovery in normoxic conditions. Mutagenesis 3:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/geu048
Naziroglu M, Karaoglu A, Aksoy AO (2004) Selenium and higher dose vitamin E administration protects cisplatin induced oxidative damage to renal liver lens tissues in rats. Toxicology 195:221–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2003.10.012
Noshy PA, Elhady MA, Khalaf AA, Kamel MM, Hassanen EI (2018) Ameliorative effect of carvacrol against propiconazole-induced neurobehavioral toxicity in rats. NeuroToxicology 67:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2018.05.005
Ortiz PA, Bruno ME, Moore T, Nesnow S, Winnik W, Ge Y (2010) Proteomic analysis of propiconazole responses in mouse liver: comparison of genomic and proteomic profiles. Proteome Res 9:1268–1278. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr900755q
Satpute RM, Pawar PP, Puttewar S, Sawale SD, Ambhore PD (2017) Effect of resveratrol and tetracycline on the subacute paraquat toxicity in mice. Hum Exp Toxicol 36:1303–1314. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327116688070
Sharifi Rad M, Varoni EM, Iriti M, Martorell M, Setzer WN, del Mar CM, Salehi B, Soltani Nejad A, Rajabi S, Tajbakhsh M, Sharifi Rad J (2018) Carvacrol and human health: a comprehensive review. Phytother Res 32:1675–1687. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6103
Sivaranjani A, Sivagami G, Nalini N (2016) Chemopreventive effect of carvacrol on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine induced experimental colon carcinogenesis. J Cancer Res Ther 12:755–762. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1482.154925
Song X, Chen A, Liu Y, Wang XB, Zhou Y, Liu L, Zhang X, Wang L, Yang P (2013) CAR pretreatment attenuates myocardial oxidative stress and apoptosis following myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in mice. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 33:1624–1627
Sun G, Thai SF, Tully DB, Lambert GR, Goetz AK, Wolf DC, Dix DJ, Nesnow S (2005) Propiconazole-induced cytochrome P450 gene expression and enzymatic activities in rat and mouse liver. Toxicol Lett 155:277–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2004.10.006
Tsai ML, Lin CC, Lin WC, Yang CH (2011) Antimicrobial antioxidant and anti- inflammatory activities of essential oils from five selected herbs. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:1977–1983. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.110377
Ward WO, Delker DA, Hester SD, Thai SF, Wolf DC, Allen JW, Nesnow S (2006) Transcriptional profiles in liver from mice treated with hepatotumorigenic and nonhepatotumorigenic triazole conazole fungicides: propiconazole triadimefon and myclobutanil. Toxicol Pathol 34:863–878. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230601047832
Youdim KA, Joseph JA (2001) A possible emerging role of phytochemicals in improving age-related neurological dysfunction: a multiplicity of effects. Free Radic Biol Med 30:583–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(00)00510-4
Funding
This research work was financially supported by Cairo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AAK and MAE conceived the study and designed the experiment; EIH performed the pathological study. AAA performed the biochemical parameters; MAI and MKG performed the molecular assay. PAN performed the experimental design and carried out data analysis. RAA performed oxidative stress evaluations. All authors read, revised, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Disclosures
The authors declare that the experiments with animals were performed in compliance with international rules on the care and use of laboratory animals. The study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of the Cairo University (protocol approval number: CU-II-S-50-17).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalaf, A.A.A., Elhady, M.A., Hassanen, E.I. et al. Antioxidant Role of Carvacrol Against Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity Induced by Propiconazole in Rats. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 31, 67–74 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-021-00127-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-021-00127-8