Abstract
Background
Early-stage breast cancer is usually treated with breast-conserving surgery followed by adjuvant radiation therapy. Acute skin toxicity is a common radiation-induced side effect experienced by many patients. Recently, a combination of bisphosphonates (zoledronic acid) and statins (pravastatin), or ZOPRA, was shown to radio-protect normal tissues by enhancing DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) repair mechanism. However, there are no studies assessing the effect of ZOPRA on cancerous cells. The purpose of this study is to characterize the in vitro effect of the zoledronic acid (ZO), pravastatin (PRA), and ZOPRA treatment on the molecular and cellular radiosensitivity of breast cancer cell lines.
Materials
Two breast cancer cell lines, MDA MB 231 and MCF-7, were tested. Cells were treated with different concentrations of pravastatin (PRA), zoledronate (ZO), as well as their ZOPRA combination, before irradiation. Anti-γH2AX and anti-pATM immunofluorescence were performed to study DNA DSB repair kinetics. MTT assay was performed to assess cell proliferation and viability, and flow cytometry was performed to analyze the effect of the drugs on the cell cycle distribution. The clonogenic assay was used to assess cell survival.
Results
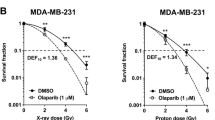
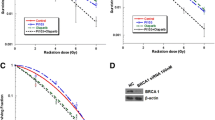
ZO, PRA, and ZOPRA treatments were shown to increase the residual number of γH2AX foci for both cell lines. ZOPRA treatment was also shown to reduce the activity of the ATM kinase in MCF-7. ZOPRA induced a significant decrease in cell survival for both cell lines.
Conclusions
Our findings show that pretreatment with ZOPRA can decrease the radioresistance of breast cancer cells at the molecular and cellular levels. The fact that ZOPRA was previously shown to radioprotect normal tissues, makes it a good candidate to become a therapeutic window-widening drug.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ATM:
-
Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated
- pATM:
-
Phosphorylated ATM
- DSB:
-
Double-strand breaks
- DAPI:
-
4’,6’Diamidino-2-Phenyl-indole
- Gy:
-
Gray (absorbed dose)
- γH2AX:
-
Phosphorylated histone H2AX
- IF:
-
Immunofluorescence
- MN:
-
Micronuclei
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- NHEJ:
-
Non-homologous end-joining
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PE:
-
Plating efficiency
- PRA:
-
Pravastatin
- RT:
-
Radiotherapy
- SF:
-
Surviving fraction
- ZO:
-
Zoledronic acid
- ZOPRA:
-
Zoledronic acid and pravastatin
References
Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J, Margolese RG, Deutsch M, Fisher ER, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(16):1233–41.
Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Mariani L, Greco M, Saccozzi R, Luini A, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized study comparing breast-conserving surgery with radical mastectomy for early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(16):1227–32.
Darby S, McGale P, Correa C, Taylor C, Arriagada R, Clarke M, et al. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378(9804):1707–16.
Bray FN, Simmons BJ, Wolfson AH, Nouri K. Acute and chronic cutaneous reactions to ionizing radiation therapy. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2016;6(2):185–206.
Singh M, Alavi A, Wong R, Akita S. Radiodermatitis: a review of our current understanding. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17(3):277–92.
Leventhal J, Young MR. Radiation dermatitis: recognition, prevention, and management. Oncology. 2017;31(12):885–7.
Bodgi L, Granzotto A, Devic C, Vogin G, Lesne A, Bottollier-Depois JF, et al. A single formula to describe radiation-induced protein relocalization: towards a mathematical definition of individual radiosensitivity. J Theor Biol. 2013;333:135–45.
Le Reun E, Bodgi L, Granzotto A, Sonzogni L, Ferlazzo ML, Al-Choboq J, et al. Quantitative correlations between radiosensitivity biomarkers show that the ATM protein kinase is strongly involved in the radiotoxicities observed after radiotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10434.
Goutham HV, Mumbrekar KD, Vadhiraja BM, Fernandes DJ, Sharan K, Kanive Parashiva G, et al. DNA double-strand break analysis by gamma-H2AX foci: a useful method for determining the overreactors to radiation-induced acute reactions among head-and-neck cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;84(5):e607–12.
Rothkamm K, Lobrich M. Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low x-ray doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(9):5057–62.
Bodgi L, Foray N. The nucleo-shuttling of the ATM protein as a basis for a novel theory of radiation response: resolution of the linear-quadratic model. Int J Radiat Biol. 2016;92(3):117–31.
Granzotto A, Benadjaoud MA, Vogin G, Devic C, Ferlazzo ML, Bodgi L, et al. Influence of nucleoshuttling of the ATM protein in the healthy tissues response to radiation therapy: toward a molecular classification of human radiosensitivity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016;94(3):450–60.
Maalouf M, Granzotto A, Devic C, Bodgi L, Ferlazzo M, Peaucelle C, et al. Influence of linear energy transfer on the nucleo-shuttling of the ATM protein: a novel biological interpretation relevant for particles and radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019;103(3):709–18.
Colin C, Devic C, Noël A, Rabilloud M, Zabot M-T, Pinet-Isaac S, et al. DNA double-strand breaks induced by mammographic screening procedures in human mammary epithelial cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 2011;87(11):1103–12.
Wang H, Mu X, He H, Zhang X-D. Cancer radiosensitizers. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018;39(1):24–48.
Ferlazzo ML, Sonzogni L, Granzotto A, Bodgi L, Lartin O, Devic C, et al. Mutations of the Huntington’s disease protein impact on the ATM-dependent signaling and repair pathways of the radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks: corrective effect of statins and bisphosphonates. Mol Neurobiol. 2014;49:1200–11.
Ferlazzo ML, Bach-Tobdji MKE, Djerad A, Sonzogni L, Devic C, Granzotto A, et al. Radiobiological characterization of tuberous sclerosis: a delay in the nucleo-shuttling of ATM may be responsible for radiosensitivity. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(6):4973–83.
Combemale P, Sonzogni L, Devic C, Bencokova Z, Ferlazzo ML, Granzotto A, et al. Individual response to radiation of individuals with neurofibromatosis Type I: Role of the ATM protein and influence of statins and bisphosphonates. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(1):556–73.
Al-Choboq J, Ferlazzo ML, Sonzogni L, Granzotto A, El-Nachef L, Maalouf M, et al. Usher syndrome belongs to the genetic diseases associated with radiosensitivity: influence of the ATM protein kinase. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1570.
Moulay Lakhdar I, Ferlazzo ML, Al Choboq J, Berthel E, Sonzogni L, Devic C, et al. Fibroblasts from retinoblastoma patients show radiosensitivity linked to abnormal localization of the ATM protein. Curr Eye Res. 2021;46(4):546–57.
Francis M, Ahmad A, Bodgi L, Azzam P, Youssef T, Abou Daher A, et al. SMPDL3b modulates radiation-induced DNA damage response in renal podocytes. FASEB J. 2022;36(10): e22545.
Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative G. Adjuvant bisphosphonate treatment in early breast cancer: meta-analyses of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet. 2015;386(10001):1353–1361.
Taylor F, Huffman MD, Macedo AF, Moore TH, Burke M, Davey SG, et al. (2013) Statins for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;1:4816.
Korte V, Gademann G, Gawish A, Ochel H-J. Modulation of radiosensitivity of DU145 prostate carcinoma cells by simvastatin. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023;149(8):4509–14.
d’Hose D, Mignion L, Hamelin L, Sonveaux P, Jordan BF, Gallez B. Statins alleviate tumor hypoxia in prostate cancer models by decreasing oxygen consumption: an opportunity for radiosensitization? Biomolecules. 2022;12(10):1418.
Nowakowska MK, Lei X, Thompson MT, Shaitelman SF, Wehner MR, Woodward WA, et al. Association of statin use with clinical outcomes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer. 2021;127(22):4142–50.
Zhao G, Ji Y, Ye Q, Ye X, Wo G, Chen X, et al. Effect of statins use on risk and prognosis of breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Anticancer Drugs. 2022;33(1):e507–18.
Varela I, Pereira S, Ugalde AP, Navarro CL, Suarez MF, Cau P, et al. Combined treatment with statins and aminobisphosphonates extends longevity in a mouse model of human premature aging. Nat Med. 2008;14(7):767–72.
Rahal OM, Woodward WA. Cholesterol and radiosensitivity. Curr Breast Cancer Rep. 2016;8(1):32–9.
Misra J, Mohanty ST, Madan S, Fernandes JA, Ebetino FH, Russell RGG, et al. Zoledronate attenuates accumulation of DNA damage in mesenchymal stem cells and protects their function. Stem Cells. 2016;34(3):756–67.
Soto DE, Daignault S, Sandler HM, Ray ME. No Effect of statins on biochemical outcomes after radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Urology. 2009;73(1):158–62.
Kim EH, Kim M-S, Lee K-H, Koh J-S, Jung W-G, Kong C-B. Zoledronic acid is an effective radiosensitizer in the treatment of osteosarcoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7(43):70869–80.
Alcaraz M, Olivares A, Achel DG, Alcaraz-Saura M. Effects of bisphosphonates in combination with ionizing radiation and antioxidants on the growth of prostate and melanoma cells lines. Anticancer Res. 2013;33(8):3217–24.
Kars MD, Iseri ÖD, Ural AU, Avcu F, Beyzadeoglu M, Dirican B, et al. Development of radioresistance in drug resistant human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Radiother Pract. 2009;8(4):207–13.
Collection ATC. MCF7 (ATCC® HTB-22™) ATCC; [Available from: https://www.atcc.org/products/all/htb-22.aspx#generalinformation
Collection ATC. MDA-MB-231 (ATCC® HTB-26™) [Available from: https://www.atcc.org/products/all/htb-26.aspx#
Njeh CF, Salmon HW, Schiller C. The impact of dose rate on the accuracy of step-and-shoot intensity-modulated radiation therapy quality assurance using varian 2300CD. J Med Phys. 2017;42(4):206–12.
Valentin J. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE), quality factor (Q), and radiation weighting factor (wR):ICRP Publication 92: Approved by the Commission in January 2003. Ann ICRP. 2003;33(4):1–121.
Liston DR, Davis M. Clinically relevant concentrations of anticancer drugs: a guide for nonclinical studies. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(14):3489.
Puck TT, Marcus PI. Action of x-rays on mammalian cells. J Exp Med. 1956;103(5):653–66.
Bodgi L, Bahmad HF, Araji T, Al Choboq J, Bou-Gharios J, Cheaito K, et al. Assessing radiosensitivity of bladder cancer in vitro: A 2D vs. 3D approach. Front Oncol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00153.
Rothkamm K, Kruger I, Thompson LH, Lobrich M. Pathways of DNA double-strand break repair during the mammalian cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(16):5706–15.
Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS, Bonner WM. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(10):5858–68.
Grote SJ, Joshi GP, Revell SH, Shaw CA. Observations of radiation-induced chromosome fragment loss in live mammalian cells in culture, and its effect on colony-forming ability. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1981;39(4):395–408.
Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature. 2003;421(6922):499–506.
Burma S, Chen BP, Murphy M, Kurimasa A, Chen DJ. ATM phosphorylates histone H2AX in response to DNA double-strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(45):42462–7.
Wasserman TH, Twentyman P. Use of a colorimetric microtiter (MTT) assay in determining the radiosensitivity of cells from murine solid tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1988;15(3):699–702.
Slavotinek A, McMillan TJ, Steel CM. Measurement of radiation survival using the MTT assay. Eur J Cancer. 1994;30(9):1376–82.
Foray N, Bourguignon M, Hamada N. Individual response to ionizing radiation. Mutat Res. 2016;770(Pt B):369–86.
Jiang H, Panda S, Gekara NO. Comet and micronucleus assays for analyzing DNA damage and genome integrity. Methods Enzymol. 2019;625:299–307.
ICRP. Prevention of accidental exposures to patients undergoing radiation therapy. A report of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. 2000. Report No.: 0146–6453 Contract No.: 3.
Elzahhar PA, Nematalla HA, Al-Koussa H, Abrahamian C, El-Yazbi AF, Bodgi L, et al. Inclusion of Nitrofurantoin into the Realm of Cancer Chemotherapy via Biology-Oriented Synthesis and Drug Repurposing. J Med Chem. 2023;66:4565–87.
Lesueur P, Chevalier F, Austry J-B, Waissi W, Burckel H, Noël G, et al. Poly-(ADP-ribose)-polymerase inhibitors as radiosensitizers: a systematic review of pre-clinical and clinical human studies. Oncotarget. 2017;8(40):69105–24.
Ortiz T, Burguillos MA, López-Lluch G, Navas P, Herrador M, González I, et al. Enhanced induction of apoptosis in a radio-resistant bladder tumor cell line by combined treatments with X-rays and wortmannin. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2008;47(4):445–52.
Brichkina A, Bulavin DV. Cancer suppression by systemic inactivation of p38MAPK. Oncotarget. 2017;8(9):14275–6.
Tu X, Kahila MM, Zhou Q, Yu J, Kalari KR, Wang L, et al. ATR inhibition is a promising radiosensitizing strategy for triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018;17(11):2462.
Overgaard J, Horsman MR. Modification of hypoxia induced radioresistance in tumors by the use of oxygen and sensitizers. Semin Radiat Oncol. 1996;6:10–21.
Azzi J, Waked A, Bou-Gharios J, Al Choboq J, Geara F, Bodgi L, et al. Radiosensitizing effect of curcumin on human bladder cancer cell lines: impact on DNA repair mechanisms. Nutr Cancer. 2022;74(6):2207–21.
Hatanaka T. Clinical pharmacokinetics of pravastatin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2000;39(6):397–412.
Le Reun E, Granzotto A, Pêtre A, Bodgi L, Beldjoudi G, Lacornerie T, et al. Influence of the hypersensitivity to low dose phenomenon on the tumor response to hypofractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(15):3979.
Bodgi L, Al-Choboq J, Araji T, Bou-Gharios J, Azzi J, Challita R, et al. Radiation treatment timing and dose delivery: effects on bladder cancer cells in 3D in vitro culture. Radiation. 2022;2(4):318–37.
George N, Joshi MB, Satyamoorthy K. DNA damage-induced senescence is associated with metabolomic reprogramming in breast cancer cells. Biochimie. 2023;216:71–82.
Pinar B, Henríquez-Hernández LA, Lara PC, Bordon E, Rodriguez-Gallego C, Lloret M, et al. Radiation induced apoptosis and initial DNA damage are inversely related in locally advanced breast cancer patients. Radiat Oncol. 2010;5:1–5.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all members of the Radiation Oncology department of AUBMC, Abou-Kheir’s Laboratory for their support and all members of the core facilities in the DTS Building for their help and support.
Funding
This research was supported by funding from the Medical Practice Plan of the American University of Beirut. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, LB, WA, ZA; data acquisition and methodology, LB, JBG, JA, RC, CF, KB, HK, FC; validation and data analysis, LB, JBG, JA, FG, WA, ZA; writing and original draft preparation, LB, JBG; review and editing: all the authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no Conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bodgi, L., Bou-Gharios, J., Azzi, J. et al. Effect of bisphosphonates and statins on the in vitro radiosensitivity of breast cancer cell lines. Pharmacol. Rep 76, 171–184 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-023-00560-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-023-00560-7