Abstract
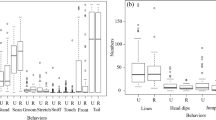
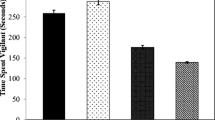
The Hyacinth Macaw (Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus) is a species considered vulnerable by the IUCN Red List, and many individuals are found in captivity in Brazil. In captive environments, due to the lack of stimuli, these animals demonstrate abnormal behaviors due to a high degree of inactivity. Among the strategies to minimize this problem, increase the natural behavior, and improve the well-being are the techniques of environmental enrichment of the enclosure. In order to investigate the effectiveness of these techniques for this species, we evaluated two distinct phases: the time before and the time during the implementation of enrichment, using an ethogram. The method employed was based on the sample session by time interval, totaling 20 h per individual, per phase. As an enrichment, natural objects (branches, vines, and leaves) were assembled into mobiles, containing pieces of the animal’s daily diet. The electivity index was applied to compare the use of different quadrants and the different locations in the enclosure. The results showed greater exploration of the enclosure, a reduction of abnormal behaviors, and a decrease of inactivity. The quadrants were more used by both couples during the environmental enrichment phase and the decrease in the use of wire mesh was offset by the increase in ground use. In view of the results found, we conclude that environmental enrichment demonstrated to be an important tool in the management of captive hyacinth macaws, providing a better quality of life.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azevedo CS, Caldeira JR, Faggioli ÂB, Cipreste CF (2016) Effects of different environmental enrichment items on the behavior of the endangered Lear’s Macaw (Anodorhynchus leari, Psittacidae) at Belo Horizonte Zoo, Brazil. Rev Bras Ornitol 24:204–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03544347
Brereton JE (2020) Current directions in animal enclosure use studies. J Zoo Aquarium Res 8:1–9. https://doi.org/10.19227/jzar.v8i1.330
Clyvia A, Faggioli AB, Cipreste CF (2015) Effects of environmental enrichment in a captive pair of Golden Parakeet (Guaruba guarouba, Psittacidae) with abnormal behaviors. Rev Bras Ornitol 23:309–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03544297
Coe JC (1985) Design and perception: making the zoo experience real. Zoo Biol 4:197–208. https://doi.org/10.1002/zoo.1430040211
de Almeida AC, Palme R, Moreira N (2018) How environmental enrichment affects behavioral and glucocorticoid responses in captive Blue-and-yellow Macaws (Ara ararauna). Appl Anim Behav Sci 201:125–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2017.12.019
Fernandez EJ, Tamborski MA, Pickens SR, Timberlake W (2009) Animal–visitor interactions in the modern zoo: conflicts and interventions. Appl Anim Behav Sci 120:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2009.06.002
Fernandez EJ, Kinley RC, Timberlake W (2019) Training penguins to interact with enrichment devices for lasting effects. Zoo Biol 38:481–489. https://doi.org/10.1002/zoo.21510
Garner JP, Meehan CL, Famula TR, Mench JA (2006) Genetic, environmental, and neighbor effects on the severity of stereotypies and feather picking in Orange-winged Amazon Parrots (Amazona amazonica): an epidemiological study. Appl Anim Behav Sci 96:153–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2005.09.009
Guedes NMR (2015) Projeto Arara Azul – Biologia, Manejo e Conservação. In: Inst. Arara Azul. http://www.institutoararaazul.org.br. Accessed 25 Feb 2020
ICMBio (2018) Livro vermelho da fauna brasileira ameaçada de extinção: Volume I, 1°. ICMBio/MMA, Brasília
IUCN/SSC (2014) Guidelines on the use of ex situ management for species conservation, version 2. Gland, Switzerland
Lumeij JT, Hommers CJ (2008) Foraging “enrichment” as treatment for pterotillomania. Appl Anim Behav Sci 111:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2007.05.015
Maia CM, Volpato GL, Santos EF (2012) A case study: the effect of visitors on two captive Pumas with respect to the time of the day. J Appl Anim Welf Sci 15:222–235. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888705.2012.683758
Martin P, Bateson P (2007) Measuring behaviour, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Mason GJ, Latham NR (2004) Can’t stop, won’t stop: is stereotypy a reliable animal welfare indicator? Anim Welf 13:S57–S69
Mellen J, MacPhee MS (2001) Philosophy of environmental enrichment: past, present, and future. Zoo Biol 20:211–226. https://doi.org/10.1002/zoo.1021
Mellor DJ, Hunt S, Gusset M (2015) Caring for wildlife: the world zoo and aquarium animal welfare strategy. WAZA Executive Office, Gland
Newberry RC (1995) Environmental enrichment: increasing the biological relevance of captive environments. Appl Anim Behav Sci 44:229–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1591(95)00616-Z
Nimon AJ, Dalziel FR (1992) Cross-species interaction and communication: a study method applied to captive Siamang (Hylobates syndactylus) and Long-billed Corella (Cacatua tenuirostris) contacts with humans. Appl Anim Behav Sci 33:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1591(05)80013-9
Pizzutto CS (2006) The importance of animal well-being for reproduction in captive. Annu Rev Biomed Sci 5. https://doi.org/10.5016/1806-8774.2003v5p39
Pizzutto CS, Scarpelli KC, Rossi AP, Chiozzotto EN, Leschonski C (2013) Bem-estar no cativeiro: um desafio a ser vencido. Rev Educ Contin em Med Veterinária e Zootec do CRMV-SP 11:6–17. https://doi.org/10.36440/recmvz.v11i2.16218
Reimer J, Maia CM, Santos EF (2016) Environmental enrichments for a group of captive macaws: low interaction does not mean low behavioral changes. J Appl Anim Welf Sci 19:385–395. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888705.2016.1175944
Ross SR, Schapiro SJ, Hau J, Lukas KE (2009) Space use as an indicator of enclosure appropriateness: a novel measure of captive animal welfare. Appl Anim Behav Sci 121:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2009.08.007
Shepherdson D (1994) The role of environmental enrichment in the captive breeding and reintroduction of endangered species. In: Olney PJ, Mace G, Feistner A (eds) Creative conservation: interactive management of wild and captive animals. Chapman & Hall, London, p 517
Shepherdson DJ, Mellen JD, Hutchins M (1999) Second nature: environmental enrichment for captive animals. Smithsonian Books, Washington
Shyne A (2006) Meta-analytic review of the effects of enrichment on stereotypic behavior in zoo mammals. Zoo Biol 25:317–337. https://doi.org/10.1002/zoo.20091
Telles LF, Malm C, Melo MM, Vilela DAR, Lago LA, Silva MX, Martins NRS (2015) Arrancamento de penas psicogênico em maritacas: haloperidol e enriquecimento ambiental. Cienc Rural 45:1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20140318
Vanderploeg HA, Scavia D (1979) Calculation and use of selectivity coefficients of feeding: zooplankton grazing. Ecol Model 7:135–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3800(79)90004-8
Young RJ (2003) Environmental enrichment for captive animals. Blackwell Science Ltd, Oxford
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the following institutions and persons: Mr. James Edward Brereton (University Centre Sparsholt) for helping us with the electivity index; Zooparque - Itatiba and all its employees for the support and conduct of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Research involving animals/ethics statement
All procedures for ethics in research using animals were followed (according to Brazilian legislation)—at the time of the experiment, there were no legal requirement for Ethics Council.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by: Eduardo Santos
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Checon, C.T., Rosenfield, D.A., Jorge-Neto, P.N. et al. Influence of environmental enrichment on the behavioral variables of caged Hyacinth Macaws (Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus). Ornithol. Res. 28, 125–132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43388-020-00017-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43388-020-00017-y