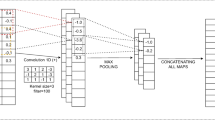
Abstract
Offensive Language detection in social media platforms has been an active field of research over the past years. In non-native English-speaking countries, social media users mostly use a code-mixed form of text in their posts/comments. This poses several challenges for offensive content identification tasks and considering the low resources available for the Tamil language, the task becomes much more challenging. The current study presents extensive experiments using multiple deep learning and transfers learning models to detect offensive content on YouTube. We propose a novel and flexible approach of selective translation and transliteration techniques to reap better results from fine-tuning and ensembling multilingual transformer networks like BERT, DistilBERT, and XLM-RoBERTa. The experimental results showed that ULMFiT is the best model for this task. The best performing models were ULMFiT and mBERT-BiLSTM for this Tamil code-mix dataset instead of more popular transfer learning models such as DistilBERT and XLM-RoBERTa and hybrid deep learning models. The proposed model ULMFiT and mBERT-BiLSTM yielded good results and are promising for effective offensive speech identification in low-resourced languages.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this experiment are available in DravidianLangTech—EACL 2021(https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/27654).
Code availability
All software used in the above article are available from the public data repository at GitHub (https://github.com/Chaarangan/ODL-Tamil-SN).
Notes
Tamil language, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tamil_language. Accessed 05 Oct 2021.
Natural Language Toolkit, https://www.nltk.org/. Accessed 10 June 2021.
Googletrans 3.0.0, https://pypi.org/project/googletrans/. Accessed 17 May 2021.
Ai4bharat-transliteration 0.5.0.3, https://pypi.org/project/ai4bharat-transliteration/. Accessed 17 May 2021.
GloVe: Global Vectors for Word Representation, https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/glove/. Accessed 15 May 2021.
DistilBERT, https://huggingface.co/transformers/model_doc/distilbert.html. Accessed 20 May 2021.
Fastai, https://docs.fast.ai/. Accessed 18 May 2021.
Hugging Face, https://github.com/huggingface/. Accessed 28 Apr 2021.
Glove, http://nlp.stanford.edu/data/glove.6B.zip. Accessed 15 May 2021.
BERT, https://github.com/google-research/bert. Accessed 28 April 2021.
DravidianLangTech-2021, https://dravidianlangtech.github.io/2021/index.html. Accessed 29 Apr 2021.
References
Chakravarthi BR, Priyadharshini R, Jose N, Kumar MA, Mandl T, Kumaresan PK, Ponnusamy RRLH, McCrae JP, Sherly E. Findings of the shared task on offensive language identification in Tamil, Malayalam, and Kannada. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 133–45. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.17. Accessed 15 May 2021.
Vigna FD, Cimino A, Dell’Orletta F, Petrocchi M, Tesconi M. Hate me, hate me not: hate speech detection on Facebook. In: ITASEC; 2017.
Chakravarthi BR, Muralidaran V, Priyadharshini R, McCrae JP. Corpus creation for sentiment analysis in code-mixed Tamil-English Text. In: Proceedings of the 1st joint workshop on spoken language technologies for Under-resourced languages (SLTU) and Collaboration and Computing for Under-Resourced Languages (CCURL). European Language Resources association, Marseille, France; 2020, p. 202–10. https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.sltu-1.28. Accessed 28 Apr 2021.
Suryawanshi S, Chakravarthi BR, Arcan M, Buitelaar P. Multimodal Meme Dataset (MultiOFF) for Identifying Offensive Content in Image and Text. In: Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying. European Language Resources Association (ELRA), Marseille, France; 2020, p. 32–41. https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.trac-1.6. Accessed 15 May 2021.
Jose N, Chakravarthi BR, Suryawanshi S, Sherly E, McCrae JP. A Survey of Current Datasets for Code-Switching Research. In: 2020 6th international conference on advanced computing and communication systems (ICACCS); 2020, p. 136–41.
Dave B, Bhat S, Majumder P. IRNLP_DAIICT@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021:Offensive Language identification in Dravidian Languages using TF-IDF Char N-grams and MuRIL. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021 , pp. 266–9. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.37. Accessed 10 May 2021.
Chakravarthi BR. HopeEDI: a multilingual hope speech detection dataset for equality, diversity, and inclusion. In: Proceedings of the third workshop on computational modeling of people’s opinions, personality, and emotion’s in social media. Association for Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain (Online); 2020, p. 41–53. https://aclanthology.org/2020.peoples-1.5. Accessed 11 May 2021.
Kumar R, Ojha AK, Lahiri B, Zampieri M, Malmasi S, Murdock V, Kadar D (editors): Proceedings of the second workshop on trolling, aggression and cyberbullying. European Language Resources Association (ELRA), Marseille, France; 2020. https://aclanthology.org/2020.trac-1.0. Accessed 25 Apr 2021.
Chakravarthi BR, Arcan M, McCrae JP. Improving wordnets for under-resourced languages using machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 9th Global Wordnet Conference. Global Wordnet Association, Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore; 2018, p. 77–86. https://aclanthology.org/2018.gwc-1.10. Accessed 29 Apr 2021.
Devlin J, Chang MW, Lee K, Toutanova K. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Proceedings of the 2019 conference of the North American chapter of the association for computational linguistics: human language technologies, volume 1 (long and short papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, Minnesota; 2019, p. 4171–86. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/N19-1423. https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/N19-1423. Accessed 15 Apr 2021.
Conneau A, Khandelwal K, Goyal N, Chaudhary V, Wenzek G, Guzmán F, Grave E, Ott M, Zettlemoyer L, Stoyanov V. Unsupervised Cross-lingual Representation Learning at Scale; 2019. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.02116
Dadvar M, Trieschnigg D, Ordelman R, de Jong F. Improving Cyberbullying Detection with User Context; 2013, p. 693–6 . https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-369735_62
Kalaivani A, Thenmozhi D. SSN_NLP_MLRG at SemEval-2020 Task 12: Offensive Language Identification in English, Danish, Greek Using BERT and Machine Learning Approach. In: Proceedings of the fourteenth workshop on semantic evaluation. International Committee for Computational Linguistics, Barcelona (online); 2020, p. 2161–70. https://aclanthology.org/2020.semeval-1.287. Accessed 15 Apr 2021.
Hande A, Priyadharshini R, Chakravarthi BR. KanCMD: Kannada CodeMixed Dataset for Sentiment Analysis and Offensive Language Detection. In: Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Computational Modeling of People’s Opinions, Personality, and Emotion’s in Social Media. Association for Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain (Online); 2020, p. 54–63. https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.peoples-1.6. Accessed 20 Apr 2021.
Aroyehun S.T., Gelbukh A. Aggression Detection in Social Media: Using Deep Neural Networks, Data Augmentation, and Pseudo Labeling. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying (TRAC-2018). Association for Computational Linguistics, Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA; 2018, p. 90–7. https://aclanthology.org/W18-4411. Accessed 16 Apr 2021.
Malmasi S, Zampieri M. Detecting Hate Speech in Social Media. In: Proceedings of the International Conference Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing, RANLP 2017. INCOMA Ltd., Varna, Bulgaria; 2017, p. 467–72. https://doi.org/10.26615/978-954-452-049-6_062
Pitenis Z, Zampieri M, Ranasinghe T. Offensive language identification in Greek. In: Proceedings of the 12th language resources and evaluation conference. European Language Resources Association, Marseille, France; 2020, p. 5113–9. https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.lrec-1.629. Accessed 18 Apr 2021.
Hettiarachchi H, Ranasinghe T. Emoji Powered Capsule Network to Detect Type and Target of Offensive Posts in Social Media. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing (RANLP 2019). INCOMA Ltd., Varna, Bulgaria; 2019, p. 474–80. https://doi.org/10.26615/978-954-452-056-4_056. https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/R19-1056. Accessed 17 Apr 2021.
Chakravarthi BR, Priyadharshini R, Muralidaran V, Suryawanshi S, Jose N, Sherly E, McCrae JP. Overview of the Track on Sentiment Analysis for Dravidian Languages in Code-Mixed Text. In: Forum for Information Retrieval Evaluation, FIRE 2020. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA; 2020, p. 21–4 . https://doi.org/10.1145/3441501.3441515.
Sanh V, Debut L, Chaumond J, Wolf T. DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter; 2019. arXiv e-prints arXiv:1910.01108
Vasantharajan C, Thayasivam U. Hypers@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: Offensive language identification in Dravidian code-mixed YouTube Comments and Posts. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Speech and Language Technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 195–202 . https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.26. Accessed 12 May 2021.
Ranasinghe T, Gupte S, Zampieri M, Nwogu I. WLV-RIT at HASOC-Dravidian-CodeMix-FIRE2020: Offensive Language Identification in Code-switched YouTube Comments. In: FIRE; 2020.
Arora G. Gauravarora@HASOC-Dravidian-CodeMix-FIRE2020: Pre-training ULMFiT on Synthetically Generated Code-Mixed Data for Hate Speech Detection. In: FIRE; 2020.
Howard J, Ruder S. Universal Language Model Fine-tuning for Text Classification; 2018. arXiv e-prints arXiv:1801.06146
Zampieri M, Malmasi S, Nakov P, Rosenthal S, Farra N, Kumar R. Predicting the Type and Target of Offensive Posts in Social Media. In: Proceedings of the 2019 conference of the North American chapter of the association for computational linguistics: human language technologies, Vol. 1 (long and short papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, Minnesota; 2019, pp. 1415–20. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/N19-1144. https://aclanthology.org/N19-1144. Accessed 08 May 2021.
Roark B, Wolf-Sonkin L, Kirov C, Mielke SJ, Johny C, Demirsahin I, Hall KB. Processing South Asian Languages Written in the Latin Script: the Dakshina Dataset. In: LREC; 2020.
Zhang Y, Jin R, Zhou ZH. Understanding bag-of-words model: a statistical framework. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. 2010;1:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-010-0001-0.
Rhanoui M, Mikram M, Yousfi S, Barzali S. A CNN-BiLSTM model for document-level sentiment analysis. Mach Learn Knowl Extract. 2019;1(3):832–47.
Lample G, Conneau A. Cross-lingual Language Model Pretraining. In: NeurIPS; 2019.
Liu Y, Ott M, Goyal N, Du J, Joshi M, Chen D, Levy O, Lewis M, Zettlemoyer L, Stoyanov V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach; 2019. arXiv e-prints arXiv:1907.11692.
Kudo T, Richardson J. SentencePiece: A simple and language independent subword tokenizer and detokenizer for Neural Text Processing. In: Proceedings of the 2018 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing: system demonstrations. Association for Computational Linguistics, Brussels, Belgium; 2018, p. 66–71. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D18-2012. https://aclanthology.org/D18-2012. Accessed 16 May 2021.
Kudo T. Subword Regularization: Improving Neural Network Translation Models with Multiple Subword Candidates. In: Proceedings of the 56th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (Vol. 1: Long Papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, Melbourne, Australia; 2018, pp. 66–75. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P18-1007. https://aclanthology.org/P18-1007. Accessed 18 May 2021.
Saha D, Paharia N, Chakraborty D, Saha P, Mukherjee A. Hate-Alert@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: Ensembling strategies for Transformer-based Offensive language Detection. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 270–6. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.38. Accessed 21 Jun 2021.
Kedia K, Nandy A. Indicnlp@kgp at DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: Offensive Language Identification in Dravidian Languages. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Speech and Language Technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 330–5. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.48. Accessed 16 May 2021.
Zhao Y, Tao X. ZYJ123@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: Offensive Language Identification based on XLM-RoBERTa with DPCNN. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Speech and Language Technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 216–221. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.29. Accessed 19 May 2021.
Jayanthi SM, Gupta A. SJ_AJ@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: Task-Adaptive Pre-Training of Multilingual BERT models for Offensive Language Identification. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Speech and Language Technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 307–12. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.44. Accessed 05 Jun 2021.
Sharif O, Hossain E, Hoque MM. NLP-CUET@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: Offensive Language Detection from Multilingual Code-Mixed Text using Transformers. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 255–61. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.35. Accessed 19 Jun 2021.
Li Z. Codewithzichao@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: Exploring Multimodal Transformers for Meme Classification in Tamil Language. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Speech and Language Technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 352–6. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.52. Accessed 20 May 2021.
Huang B, Bai Y. HUB@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: identify and classify offensive text in multilingual code mixing in social media. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 203–9. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.27. Accessed 20 May 2021.
Balouchzahi F, B K A, Shashirekha HL. MUCS@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021:COOLI-code-mixing offensive language identification. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 323–9. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.47. Accessed 02 May 2021.
Tula D, Potluri P, Ms S, Doddapaneni S, Sahu P, Sukumaran R, Patwa P. Bitions@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: ensemble of multilingual language models with pseudo labeling for offence detection in Dravidian Languages. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 291–9. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.42. Accessed 14 Jun 2021.
Ghanghor N, Krishnamurthy P, Thavareesan S, Priyadharshini R, Chakravarthi BR. IIITK@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: offensive language identification and meme classification in Tamil, Malayalam and Kannada. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 222–9. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.30. Accessed 19 Jun 2021.
Dowlagar S, Mamidi R. OFFLangOne@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: transformers with the class balanced loss for offensive language identification in Dravidian Code-Mixed text. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Speech and Language Technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 154–9. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.19. Accessed 13 Jun 2021.
Chen S, Kong B. cs@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: offensive language identification based on multilingual BERT model. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 230–5. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.31. Accessed 19 Jun 2021.
Bharathi B, Agnusimmaculate Silvia A. SSNCSE_NLP@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: offensive language identification on multilingual code mixing text. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 313–8. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.45. Accessed 25 May 2021.
Garain A, Mandal A, Naskar SK. JUNLP@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: offensive language identification in Dravidian Langauges. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 319–22. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.46. Accessed 13 June 2021.
Yasaswini K, Puranik K, Hande A, Priyadharshini R, Thavareesan S, Chakravarthi BR. IIITT@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: transfer learning for offensive language detection in Dravidian Languages. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 187–94. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.25. Accessed 13 June 2021.
Renjit S, Idicula SM. CUSATNLP@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: language agnostic classification of offensive content in Tweets. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 236–42. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.32. Accessed 14 June 2021.
Sreelakshmi K, Premjith B, Soman K. Amrita_CEN_NLP@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: Deep Learning-based Offensive Language Identification in Malayalam, Tamil and Kannada. In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Speech and Language Technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 249–54. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.34. Accessed 14 June 2021.
Andrew JJ. JudithJeyafreedaAndrew@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: offensive language detection for Dravidian Code-mixed YouTube comments. In: Proceedings of the first workshop on speech and language technologies for Dravidian Languages. Kyiv: Association for Computational Linguistics; 2021, p. 169–74. https://aclanthology.org/2021.dravidianlangtech-1.22. Accessed 14 June 2021.
Acknowledgements
We want to thank the DravidianLangTech—EACL 2021 organizers (https://dravidianlangtech.github.io/2021/html/organizers.html) for releasing the required dataset as publicly available. Also, we would like to express our thanks to Mr.Sanjeepan Sivapiran (https://www.linkedin.com/in/sanjeepan/) and Mr.Temcious Fernando (https://www.linkedin.com/in/temcious-fernando-2a69a0196/) for their helpful suggestions to improve and clarify this manuscript. We further thank the three anonymous reviewers for their insightful suggestions and feedback.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the topical collection “Machine Learning for Offensive and Highly Emotional Content on Social Media” guest edited by Bharathi Raja Asoka Chakravarthi, Anand Kumar M, Sandip Modha, Thomas Mandl and Prasenjit Majumder.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasantharajan, C., Thayasivam, U. Towards Offensive Language Identification for Tamil Code-Mixed YouTube Comments and Posts. SN COMPUT. SCI. 3, 94 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-021-00977-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-021-00977-y