Abstract
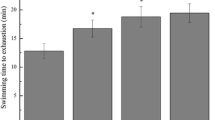
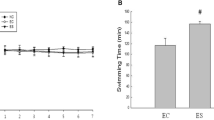
Oxidative damage and proinflammatory cytokines are involved in exhaustive exercise-induced fatigue. This study aimed to investigate the effects of bee venom, a natural toxin, on fatigue and tissue damage in rats that underwent forced swimming exercise. Rats were divided into four groups: control, swimming exercise (SE), bee venom (BV) and swimming exercise + bee venom (SE + BV). SE and SE + BV groups were subjected to forced swimming (load of 7% body weight) for 5 days. BV and SE + BV groups were injected with 1 mg/kg BV subcutaneously. Swimming time, blood lactate and TNF-α levels, MDA and GSH levels in liver and gastrocnemius muscle were evaluated. Swimming time was shorter in SE + BV group than SE group. There was no difference in lactate levels between SE and SE + BV groups. MDA and GSH levels were increased in SE, BV and SE + BV groups. TNF-α levels were increased in BV group compared to control and SE groups. Our study demonstrated that BV administration before exhaustive exercise in rats did not provide anti-fatigue effect. Additionally, BV did not show anti-inflammatory activity and had different effects on antioxidant capacity at tissue level. Further research might explore the effects of different doses and durations of BV on exhaustive exercise.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abd El-Haleim EA (2020) Molecular study on the potential protective effects of bee venom against fructose-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. Pharmacology 105(11–12):692–704
Açıkel Elmas M, Atay N, Bingöl Özakpınar Ö, Arbak S, Kolgazi M, Şener G, Ercan F (2020) Morphological evaluation of the effects of exercise on high-fat-diet-induced liver damage in rats. Turk J Gastroenterol 31(9):626–632
Ahmed O, Fahim H, Mahmoud A, Eman Ahmed EA (2017) Bee venom and hesperidin effectively mitigate complete freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis via immunomodulation and enhancement of antioxidant defense system. Arch Rheumatol 33(2):198–212
Akil M, Gurbuz U, Bicer M, Halifeoglu I, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc R (2015) Selenium prevents lipid peroxidation in liver and lung tissues of rats in acute swimming exercise. BratislLekListy 116(4):233–235. https://doi.org/10.4149/bll_2015_045 (PMID: 25773950)
Altinoz E, Ozmen T, Oner Z, Elbe H, Erdemli ME, Bag HG (2016) Saffron (its active constituent, crocin) supplementation attenuates lipid peroxidation and protects against tissue injury. BratislLekListy 117(7):381–387. https://doi.org/10.4149/bll_2016_075 (PMID: 27546539)
An HJ, Kim JY, Kim WH, Gwon MG, Gu HM, Jeon MJ, Han SM, Pak SC, Lee CK, Park IS, Park KK (2018) Therapeutic effects of beevenom and its major component, melittin, on atopic dermatitis in vivo and in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 175(23):4310–4324
Casuso RA, Aragon-Vela J, Huertas JR, Ruiz-Ariza A, Martínez-Lopez EJ (2018) Comparison of the inflammatory and stress response between sprint interval swimming and running. Scand J Med Sci Sports 28(4):1371–1378
Chang Q, Miao X, Ju X, Zhu L, Huang C, Huang T, Zuo X, Gao C (2013) Effects of pulse current on endurance exercise and its anti-fatigue properties in the hepatic tissue of trained rats. PLoS One 8(10):e75093
Chang CC, Chen CW, Owaga E, Lee WT, Liu TN, Hsieh RH (2020) Mangosteen concentrate drink supplementation promotes antioxidant status and lactate clearance in rats after exercise. Nutrients 12(5):1447
El-Aarag B, Magdy M, AlAjmi MF, Khalifa SAM, El-Seedi HR (2019) Melittin exerts beneficial effects on paraquat-induced lung injuries in mice by modifying oxidative stress and apoptosis. Molecules 24(8):1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081498.PMID:30995821;PMCID:PMC6514788
Gajski G, Garaj-Vrhovac V (2011) Bee venom induced cytogenetic damage and decreased cell viability in human white blood cells after treatment in vitro: a multi-biomarker approach. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 32(2):201–211
Gajski G, Garaj-Vrhovac V (2013) Melittin: a lytic peptide with anticancer properties. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36(2):697–705
Gajski G, Domijan AM, Garaj-Vrhovac V (2012) Alterations of GSH and MDA levels and their association with bee venom-induced DNA damage in human peripheral blood leukocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen 53(6):469–477. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.21708 (Epub 2012 Jun 25 PMID: 22730252)
Gajski G, Domijan AM, Žegura B, Štern A, Gerić M, Novak Jovanović I, Vrhovac I, Madunić J, Breljak D, Filipič M, Garaj-Vrhovac V (2016) Melittin induced cytogenetic damage, oxidative stress and changes in gene expression in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Toxicon 110:56–67
Garaj-Vrhovac V, Gajski G (2009) Evaluation of the cytogenetic status of human lymphocytes after exposure to a high concentration of bee venom in vitro. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol 60(1):27–34
Gu H, Kim WH, An HJ, Kim JY, Gwon MG, Han SM, Leem J, Park KK (2018) Therapeutic effects of bee venom on experimental atopic dermatitis. Mol Med Rep 18(4):3711–3718
Hanafi MY, Zaher ELM, El-Adely SEM, Sakr A, Ghobashi AHM, Hemly MH, Kazem AH, Kamel MA (2018) The therapeutic effects of bee venom on some metabolic and antioxidant parameters associated with HFD-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats. ExpTher Med 15(6):5091–5099
Hellner M, Winter D, von Georgi R, Münstedt K (2008) Apitherapy: usage and experience in german beekeepers. Evid Based Compl Alternat Med 5(4):475–479
Kocyigit A, Guler EM, Kaleli S (2019) Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative properties of honey bee venom on Freund’s Complete Adjuvant-induced arthritis model in rats. Toxicon 161:4–11
Koshinaka K, Honda A, Masuda H, Sato A (2020) Effect of quercetin treatment on mitochondrial biogenesis and exercise-induced amp-activated protein kinase activation in rat skeletal muscle. Nutrients 12(3):729
Li TG, Shui L, Ge DY, Pu R, Bai SM, Lu J, Chen YS (2019) Moxibustion reduces inflammatory response in the hippocampus of a chronic exercise-induced fatigue rat. Front IntegrNeurosci 20(13):48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2019.00048.PMID:31616260;PMCID:PMC6763602
Lima FD, Stamm DN, Della-Pace ID, Dobrachinski F, de Carvalho NR, Royes LFF, Soares FA, Rocha JB, González-Gallego J, Bresciani G (2013) Swimming training induces liver mitochondrial adaptations to oxidative stress in rats submitted to repeated exhaustive swimming bouts. PLoS One 8(2):e55668. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055668
Lin TC, Wang SH, Huang CC, Lai YC, Song TY, Tsai MS (2018) Anti-fatigue, antioxidation and anti-inflammatory effects of eucalyptus oil aromatherapy in swimming-exercised rats. Chin J Physiol 61(5):257–265
Liu L, Wu X, Zhang B, Yang W, Li D, Dong Y, Yin Y, Chen Q (2017) Protective effects of tea polyphenols on exhaustive exercise-induced fatigue, inflammation and tissue damage. Food Nutr Res 61(1):1333390
Meligi NM, Ismail SA, Tawfik NS (2020) Protective effects of honey and beevenom against lipopolysaccharide and carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatoxicity and lipid peroxidation in rats. Toxicol Res (Camb) 9(5):693–705
Oršolić N (2012) Bee venom in cancer therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31(1–2):173–194
Pala R, Genc E, Tuzcu M, Orhan C, Sahin N, Er B, Cinar V, Sahin K (2018) L-Carnitine supplementation increases expression of PPAR-γ and glucose transporters in skeletal muscle of chronically and acutely exercised rats. Cell Mol Biol 64(1):1–6
Shin IS, Kim DH, Jang EY, Kim HY, Yoo HS (2019) Anti-fatigue properties of cultivated wild ginseng distilled extract and its active component panaxydol in rats. J Pharm 22(2):68–74
Shui L, Yi RN, Wu YJ, Bai SM, Si Q, Bo AG, Wuyun GR, Si LG, Chen YS, Lu J (2020) Effects of mongolian warm acupuncture on iNOS/NO and inflammatory cytokines in the hippocampus of chronic fatigue rats. Front IntegrNeurosci 31(13):78. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2019.00078.PMID:32082125;PMCID:PMC7006054
Son DJ, Lee JW, Lee YH, Song HS, Lee CK, Hong JT (2007) Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis, pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its constituent compounds. Pharmacol Ther 115(2):246–270
Steckling FM, Lima FD, Farinha JB, Rosa PC, Royes LFF, Cuevas MJ, Bresciani G, Soares FA, González-Gallego J, Barcelos RP (2020) Diclofenac attenuates inflammation through TLR4 pathway and improves exercise performance after exhaustive swimming. Scand J Med Sci Sports 30(2):264–271
Tekeoğlu İ, Akdoğan M, Çelik İ (2020) Investigation of anti-inflammatory effects of bee venom in experimentally induced adjuvant arthritis. Reumatologia 58(5):265–271
Xu J, Li Y (2012) Effects of salidroside on exhaustive exercise-induced oxidative stress in rats. Mol Med Rep 6(5):1195–1198. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2012.1060 (Epub 2012 Sep 3 PMID: 22948446)
Yang DK, Lee SJ, Adam GO, Kim SJ (2020) Aralia continentalis kitagawa extract attenuates the fatigue induced by exhaustive exercise through inhibition of oxidative stress. Antioxidants (Basel) 9(5):379
Yoon SY, Roh DH, Kwon YB, Kim HW, Seo HS, Han HJ, Lee HJ, Beitz AJ, Lee JH (2009) Acupoint stimulation with diluted bee venom (apipuncture) potentiates the analgesic effect of intrathecal clonidine in the rodent formalin test and in a neuropathic pain model. J Pain 10(3):253–263
Zhang S, Liu Y, Ye Y, Wang XR, Lin LT, Xiao LY, Zhou P, Shi GX, Liu CZ (2018) Bee venom therapy: potential mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Toxicon 148:64–73
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS and MK designed the study. AS, BD and BA performed the in vivo study. MK, BD and BA performed the biochemical analysis. IA and OA analyzed the data. MK, IA and OA wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines provided by the Experimental Animal Laboratory and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Dokuz Eylul University Medical Faculty, Turkey (approval number: 43/2020). All experimental procedures were appropriate to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of National Institutes of Health (USA).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senturk, A., Dalkiran, B., Acikgoz, B. et al. The effects of bee venom on liver and skeletal muscle in exhaustive swimming rats. BIOLOGIA FUTURA 73, 237–244 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42977-022-00115-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42977-022-00115-6