Abstract
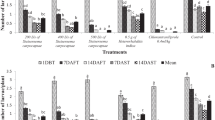
Fall armyworm (FAW), Spodoptera frugiperda, invaded India in 2018. Since then, this pest was considered as one of the serious threats to maize growers. A handful of management strategies have been developed to manage this pest. One such strategy is the application of sand mixed insecticides to leaf whorls. The present study evaluates the effect of different concentrations of sand mixed chlorantraniliprole applied to the maize whorl on the FAW reproductive biology. The sand mixed chlorantraniliprole at 0.4 ml/kg was significantly effective in inducing higher mortality, lower foliar consumption, lower pupal weight, fecundity and hatchability compared to the recommended foliar spray at 0.4 ml/L. Up to 14 days post-treatment, chlorantraniliprole mixed with sand (0.4 ml/kg) and foliar spray (0.4 ml/L) were equally effective in altering FAW fitness, whereas chlorantraniliprole mixed with sand (0.4 ml/kg) was continue to perform significantly better with a prolonged effect up to 30 days. Therefore, the whorl application of sand-mixed chlorantraniliprole at a dosage of 0.4 ml/kg can be used as an alternative delivery method of insecticide directly to the whorl instead of recommended and commonly practiced foliar spray.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams A, Gore J, Catchot A, Musser F, Cook D, Krishnan N, Irby T (2016) Residual and systemic efficacy of chlorantraniliprole and flubendiamide against corn earworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in soybean. J Econ Entomol 109:2411–2417
Babendreier D, Koku Agboyi L, Beseh P, Osae M, Nboyine J, Ofori SE, Frimpong JO, Attuquaye Clottey V, Kenis M (2020) The efficacy of alternative, environmentally friendly plant protection measures for control of fall armyworm, S frugiperda in maize. InSects 11:240–246
Cameron RA, Williams CJ, Portillo HE, Marcon PC, Teixeira LA (2015) Systemic application of chlorantraniliprole to cabbage transplants for control of foliar-feeding lepidopteran pests. Crop Prot 67:13–19
Cordova D, Benner EA, Sacher MD, Rauh JJ, Sopa JS, Lahm GP, Selby TP, Stevenson TM, Flexner L, Gutteridge S, Rhoades DF (2006) Anthranilic diamides: a new class of insecticides with a novel mode of action, ryanodine receptor activation. Pesticide Biochem Physiol 84:196–214
Deshmukh S, Pavithra HB, Kalleshwaraswamy CM, Shivanna BK, Maruthi MS, Mota-Sanchez D (2020) Field efficacy of insecticides for management of invasive fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith)(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on maize in India. Florida Entomol 103:221–227
Divya J, Kalleshwaraswamy CM, Deshmukh S, Ambarish S, Sunil C (2021a) Evaluation of whorl application of insecticides mixed with sand against fall army worm S. frugiperda in Maize. Indian J Entomol 1:617–621
Divya J, Kalleshwaraswamy CM, Mallikarjuna HB, Deshmukh S (2021b) Does recently invaded fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda displace native lepidopteran pests of maize in India? Curr Sci 120:1358–1367
Goergen G, Kumar PL, Sankung SB, Togola A, Tamo M (2016) First report of outbreaks of the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae), a new alien invasive pest in West and Central Africa. PLoS ONE 11:165–170
Guo L, Desneux N, Sonoda S, Liang P, Han P, Gao XW (2013) Sublethal and transgenerational effects of chlorantraniliprole on biological traits of the diamondback moth, Plutella Xylostella. Crop Prot 48:29–34
Han WS, Zhang SF, Shen FY, Liu M, Ren CC, Gao XW (2012) Residual toxicity and sublethal effects of chlorantraniliprole on P. xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Pest Manag Sci 68:1184–1190
Huang L, Lu M, Han G, Du Y, Wang J (2016) Sublethal effects of chlorantraniliprole on development, reproduction and vitellogenin gene (CsVg) expression in the rice stem borer, Chilo suppressalis. Pest Manag Sci 72:2280–2286
Kalleshwaraswamy CM, Ambarish S, Onkarappa S, Deshmukh SS, Sunil C (2022a) Whorl application of soil mixed chlorantraniliprole 18.5 SC is effective against invasive fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda J.E. Smith (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in maize. J Ent Res 46:738–745
Kalleshwaraswamy CM, Divya J, Mallikarjuna HB, Deshmukh SS, Sunil C (2023) Cannibalistic nature and time of habitat occupancy of invasive maize fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda are the key factors for competitive displacement of native stem borer, Sesamia inferens in India. Curr Sci 124:348–354
Kalleshwaraswamy CM, Kannan M, Prakash N (2022b) Silicon as a natural plant guard against insect pests. In: Etesami H (ed) Silicon and nano-silicon in environmental stress management and crop quality Improvement: Progress and prospects. Academic Press, pp 219–227
Kambrekar DN (2020) New ready mix formulation of chlorantraniliprole plus lambda cyhalothrin with translaminar action against insect pests of soybean. India J Plant Prot 47:3–4
Lanka SK, Ottea JA, Davis JA, Hernandez AB, Stout MJ (2013) Systemic effects of thiamethoxam and chlorantraniliprole seed treatments on adult Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in rice. Pest Manag Sci 69:250–256
Navik O, Shylesha AN, Patil J, Venkatesan T, Lalitha Y, Ashika TR (2021) Damage, distribution and natural enemies of invasive fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. smith) under rainfed maize in Karnataka, India. Crop Prot 143:1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2021.105536
Olivi B (2016) Impact of simulated corn earworm damage on field corn yield and the influence of chlorantraniliprole and flubendiamide on fall armyworm and agronomic characteristics of field corn. M. Sc. (Agri.) thesis, Mississippi State University. Mississippi (USA), pp 1–14
Pes MP, Melo AA, Stacke RS, Zanella R, Perini CR, Silva FM, Carus Guedes JV (2020) Translocation of chlorantraniliprole and cyantraniliprole applied to corn as seed treatment and foliar spraying to control S. frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). PLoS ONE 1:222–231
Pitre HN (1986) Chemical control of the fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): an update. Florida Entomol 1:570–580
Sharanabasappa, Kalleshwara swamy CM, Asokan R, Swamy HM, Maruthi MS, Pavithra HB, Hegde K, Navi S, Prabhu ST, Goergen G (2018) First report of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), an alien invasive pest on maize in India. Pest Manag Hort Ecosyst 24:23–29
Sharma S, Tiwari S, Thapa RB, Pokhrel S, Neupane S (2022) Research article laboratory bioassay of fall armyworm, (Spodoptera frugiperda) larva using various insecticides. J Agric for Environ 5:130–135
Teixeira LA, Gut LJ, Wise JC, Isaacs R (2009) Lethal and sublethal effects of chlorantraniliprole on three species of Rhagoletis fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae). Pest Manag Sci 65:137–143
Zhang RM, Dong JF, Chen JH, Ji QE, Cui JJ (2013) The sublethal effects of chlorantraniliprole on H. armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Integr Agric 12:457–466
Zhang Q, Liu Y, Wyckhuys KA, Liang H, Desneux N, Lu Y (2021) Lethal and sublethal effects of chlorantraniliprole on H. armigera adults enhance the potential for use in attract and kill control strategies. Entomol Gen 41:111–120
Acknowledgements
All authors have read and approved the manuscript
Funding
The work was partially funded by Staff research Project by the Director of Research, KSNUAHS, Shivamogga.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Ankica Kondic-Spika.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Meghana, A., Kalleshwaraswamy, C.M., Deshmukh, S.S. et al. Effect of whorl application of sand mixed chlorantraniliprole 18.5 SC on the reproductive biology of invasive fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in maize. CEREAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 52, 683–690 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-023-00402-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-023-00402-5