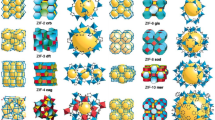
Abstract
Co-based metal–organic framework (MOF), a kind of porous crystal material composed of Co ions and organic linkers, is a common type of MOF. It not only has the intrinsic properties of MOF, such as structural diversity, functional adjustability, and high surface area, but more importantly, it contains Co metal species, which are considered by many reports to be active catalytic centers for many reactions. Meanwhile, metal catalysts always received wide and sustained attention. The combination of the two types of catalysts can enhance the catalytic performance and achieve the “1 + 1 > 2” effect. In this review, we mainly overview the synthesis methods of Co-based MOF-derived metal catalysts from nano- to atom- level and their applications in the catalysis field in recent years and put forward our own views and prospects for this research direction.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author.
References
Wang Q, Astruc D. State of the art and prospects in metal-organic framework (MOF)-based and MOF-derived nanocatalysis. Chem Rev. 2020;120(2):1438.
Bavykina A, Kolobov N, Khan IS, Bau JA, Ramirez A, Gascon J. Metal-organic frameworks in heterogeneous catalysis: recent progress, new trends, and future perspectives. Chem Rev. 2020;120(16):8468.
Wei YS, Zhang M, Zou R, Xu Q. Metal-organic framework-based catalysts with single metal sites. Chem Rev. 2020;120(21):12089.
Hou C-C, Wang H-F, Li C, Xu Q. From metal–organic frameworks to single/dual-atom and cluster metal catalysts for energy applications. Energy Environ Sci. 2020;13(6):1658.
Jiao L, Wang Y, Jiang H-L, Xu Q. Metal-organic frameworks as platforms for catalytic applications. Adv Mater. 2018;30(37):1703663.
Meng G, Sun J, Tao L, Ji K, Wang P, Wang Y, Sun X, Cui T, Du S, Chen J, Wang D, Li Y. Ru1Con single-atom alloy for enhancing Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. ACS Catal. 2021;11(3):1886.
Chen W, Filot IAW, Pestman R, Hensen EJM. Mechanism of Cobalt-Catalyzed CO Hydrogenation: 2. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. ACS Catal. 2017;7(12):8061.
Okoye-Chine CG, Moyo M, Hildebrandt D. The effect of hydrophobicity on SiO2–supported Co catalysts in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Fuel. 2021;296: 120667.
Huang Z, Hao L, Ma X, Zhang S, Zhang R, Yue K, Wang Y. A facile reaction strategy for the synthesis of MOF-based pine-needle-like nanocluster hierarchical structure for efficient overall water splitting. Inorg Chem. 2021;60(6):4047.
Abdelkader-Fernández VK, Fernandes DM, Balula SS, Cunha-Silva L, Freire C. Oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalytic improvement in POM@ZIF nanocomposites: a bidirectional synergistic effect. ACS Appl Energy Mater. 2020;3(3):2925.
Wen H, Zhang S, Yu T, Yi Z, Guo R. ZIF-67-based catalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. Nanoscale. 2021;13(28):12058.
Wang XX, Cullen DA, Pan Y-T, Hwang S, Wang M, Feng Z, Wang J, Engelhard MH, Zhang H, He Y, Shao Y, Su D, More KL, Spendelow JS, Wu G. Nitrogen-coordinated single cobalt atom catalysts for oxygen reduction in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Adv Mater. 2018;30(11):1706758.
Peng H, Liu F, Liu X, Liao S, You C, Tian X, Nan H, Luo F, Song H, Fu Z, Huang P. Effect of transition metals on the structure and performance of the doped carbon catalysts derived from polyaniline and melamine for ORR application. ACS Catal. 2014;4(10):3797.
Chen Y, Gao R, Ji S, Li H, Tang K, Jiang P, Hu H, Zhang Z, Hao H, Qu Q, Liang X, Chen W, Dong J, Wang D, Li Y. Atomic-level modulation of electronic density at cobalt single-atom sites derived from metal-organic frameworks: enhanced oxygen reduction performance. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60(6):3212.
Osmieri L, Monteverde Videla AHA, Ocón P, Specchia S. Kinetics of oxygen electroreduction on Me–N–C (Me = Fe Co, Cu) catalysts in acidic medium: insights on the effect of the transition metal. J Phys Chem C. 2017;121(33):17796.
Xu H, Cheng D, Cao D, Zeng XC. A universal principle for a rational design of single-atom electrocatalysts. Nat Catal. 2018;1(5):339.
Usman M, Humayun M, Garba MD, Ullah L, Zeb Z, Helal A, Suliman MH, Alfaifi BY, Iqbal N, Abdinejad M, Tahir AA, Ullah H. Electrochemical reduction of CO2: a review of cobalt based catalysts for carbon dioxide conversion to fuels. Nanomaterials. 2021;11(8):2029.
Song X, Zhang H, Yang Y, Zhang B, Zuo M, Cao X, Sun J, Lin C, Li X, Jiang Z. Bifunctional nitrogen and cobalt codoped hollow carbon for electrochemical syngas production. Adv Sci. 2018;5(7):1800177.
Geng Z, Cao Y, Chen W, Kong X, Liu Y, Yao T, Lin Y. Regulating the coordination environment of Co single atoms for achieving efficient electrocatalytic activity in CO2 reduction. Appl Catal B. 2019;240:234.
Lou Y, Xu J, Zhang Y, Pan C, Dong Y, Zhu Y. Metal-support interaction for heterogeneous catalysis: from nanoparticles to single atoms. Mater Today Nano. 2020;12: 100093.
James TE, Hemmingson SL, Campbell CT. Energy of supported metal catalysts: from single atoms to large metal nanoparticles. ACS Catal. 2015;5(10):5673.
Wang H, Lu J. A review on particle size effect in metal-catalyzed heterogeneous reactions. Chin J Chem. 2020;38(11):1422.
Liu L, Corma A. Metal catalysts for heterogeneous catalysis: from single atoms to nanoclusters and nanoparticles. Chem Rev. 2018;118(10):4981.
Zhang L, Zhou M, Wang A, Zhang T. Selective hydrogenation over supported metal catalysts: from nanoparticles to single atoms. Chem Rev. 2020;120(2):683.
Pitzalis E, Psaro R, Evangelisti C. From metal vapor to supported single atoms, clusters and nanoparticles: recent advances to heterogeneous catalysts. Inorg Chim Acta. 2022;533: 120782.
Han X, Ling X, Wang Y, Ma T, Zhong C, Hu W, Deng Y. Generation of nanoparticle, atomic-cluster, and single-atom cobalt catalysts from zeolitic imidazole frameworks by spatial isolation and their use in zinc-air batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58(16):5359.
Kou Z, Zang W, Ma Y, Pan Z, Mu S, Gao X, Tang B, Xiong M, Zhao X, Cheetham AK, Zheng L, Wang J. Cage-confinement pyrolysis route to size-controlled molybdenum-based oxygen electrode catalysts: from isolated atoms to clusters and nanoparticles. Nano Energy. 2020;67: 104288.
Habib NR, Asedegbega-Nieto E, Taddesse AM, Diaz I. Non-noble MNP@MOF materials: synthesis and applications in heterogeneous catalysis. Dalton Trans. 2021;50(30):10340.
Luo L, Jin R. Atomically precise metal nanoclusters meet metal-organic frameworks. iScience. 2021;24(10):103206.
Buceta D, Piñeiro Y, Vázquez-Vázquez C, Rivas J, López-Quintela MA. Metallic clusters: theoretical background, properties and synthesis in microemulsions. Catalysts. 2014;4(4):356.
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC. The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B. 2003;107(3):668.
Schauermann S, Hoffmann J, Johánek V, Hartmann J, Libuda J, Freund H-J. Catalytic activity and poisoning of specific sites on supported metal nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2002;41(14):2532.
Janssens TVW, Clausen BS, Hvolbæk B, Falsig H, Christensen CH, Bligaard T, Nørskov JK. Insights into the reactivity of supported Au nanoparticles: combining theory and experiments. Top Catal. 2007;44(1):15.
Wu J, Li P, Pan Y-T, Warren S, Yin X, Yang H. Surface lattice-engineered bimetallic nanoparticles and their catalytic properties. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41(24):8066.
Taylor KJ, Pettiette-Hall CL, Cheshnovsky O, Smalley RE. Ultraviolet photoelectron spectra of coinage metal clusters. J Chem Phys. 1992;96(4):3319.
Boronat M, Leyva-Pérez A, Corma A. Theoretical and experimental insights into the origin of the catalytic activity of subnanometric gold clusters: attempts to predict reactivity with clusters and nanoparticles of gold. Acc Chem Res. 2014;47(3):834.
Fernández EM, Soler JM, Garzón IL, Balbás LC. Trends in the structure and bonding of noble metal clusters. Phys Rev B. 2004;70(16): 165403.
Zhang Q, Guan J. Single-atom catalysts for electrocatalytic applications. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(31):2000768.
Kou Z, Zang W, Wang P, Li X, Wang J. Single atom catalysts: a surface heterocompound perspective. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020;5(5):757.
Xi J, Jung HS, Xu Y, Xiao F, Bae JW, Wang S. Single-atom catalysts: synthesis strategies, catalytic applications, and performance regulation of single-atom catalysts. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(12):2170081.
Zhang X, Sun X, Xu D, Tao X, Dai P, Guo Q, Liu X. Synthesis of MOF-derived Co@C composites and application for efficient hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Appl Surf Sci. 2019;469:764.
Zhou L, Meng J, Li P, Tao Z, Mai L, Chen J. Ultrasmall cobalt nanoparticles supported on nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanowires for hydrogen evolution from ammonia borane. Mater Horiz. 2017;4(2):268.
Zacho SL, Mielby J, Kegnæs S. Hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane over ZIF-67 derived Co nanoparticle catalysts. Catal Sci Technol. 2018;8(18):4741.
Chen S, Ling L-L, Jiang S-F, Jiang H. Selective hydrogenation of nitroarenes under mild conditions by the optimization of active sites in a well defined Co@NC catalyst. Green Chem. 2020;22(17):5730.
Sun X, Olivos-Suarez AI, Oar-Arteta L, Rozhko E, Osadchii D, Bavykina A, Kapteijn F, Gascon J. Metal-organic framework mediated cobalt/nitrogen-doped carbon hybrids as efficient and chemoselective catalysts for the hydrogenation of nitroarenes. ChemCatChem. 2017;9(10):1854.
Chen M, Xiong R, Cui X, Wang Q, Liu X. SiO2-encompassed Co@N-Doped porous carbon assemblies as recyclable catalysts for efficient hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Langmuir. 2019;35(3):671.
Zhang C, Guo X, Yuan Q, Zhang R, Chang Q, Li K, Xiao B, Liu S, Ma C, Liu X, Xu Y, Wen X, Yang Y, Li Y. Ethyne-reducing metal-organic frameworks to control fabrications of core/shell nanoparticles as catalysts. ACS Catal. 2018;8(8):7120.
Chen H, Shen K, Mao Q, Chen J, Li Y. Nanoreactor of MOF-derived yolk-shell Co@C–N: precisely controllable structure and enhanced catalytic activity. ACS Catal. 2018;8(2):1417.
Chen Z, Wu R, Liu Y, Ha Y, Guo Y, Sun D, Liu M, Fang F. Ultrafine Co nanoparticles encapsulated in carbon-nanotubes-grafted graphene sheets as advanced electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv Mater. 2018;30(30):1802011.
Wang R, Yan T, Han L, Chen G, Li H, Zhang J, Shi L, Zhang D. Tuning the dimensions and structures of nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials derived from sacrificial g-C3N4/metal–organic frameworks for enhanced electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. J Mater Chem A. 2018;6(14):5752.
Guo H, Feng Q, Zhu J, Xu J, Li Q, Liu S, Xu K, Zhang C, Liu T. Cobalt nanoparticle-embedded nitrogen-doped carbon/carbon nanotube frameworks derived from a metal–organic framework for tri-functional ORR, OER and HER electrocatalysis. J Mater Chem A. 2019;7(8):3664.
Tong Y, Xue G, Wang H, Liu M, Wang J, Hao C, Zhang X, Wang D, Shi X, Liu W, Li G, Tang Z. Interfacial coupling between noble metal nanoparticles and metal–organic frameworks for enhanced catalytic activity. Nanoscale. 2018;10(35):16425.
Yu H, Jing Y, Du C-F, Wang J. Tuning the reversible chemisorption of hydroxyl ions to promote the electrocatalysis on ultrathin metal-organic framework nanosheets. J Energy Chem. 2022;65:71.
Ding S, Zhang C, Liu Y, Jiang H, Xing W, Chen R. Pd nanoparticles supported on N-doped porous carbons derived from ZIF-67: enhanced catalytic performance in phenol hydrogenation. J Ind Eng Chem. 2017;46:258.
Zhou A, Guo R-M, Zhou J, Dou Y, Chen Y, Li J-R. Pd@ZIF-67 derived recyclable Pd-Based catalysts with hierarchical pores for high-performance heck reaction. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2018;6(2):2103.
Zhang W, Wu W, Long Y, Wang F, Ma J. Co-Ag alloy protected by nitrogen doped carbon as highly efficient and chemoselective catalysts for the hydrogenation of halogenated nitrobenzenes. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;522:217.
Jiang P, Chen J, Wang C, Yang K, Gong S, Liu S, Lin Z, Li M, Xia G, Yang Y, Su J, Chen Q. Tuning the activity of carbon for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution via an iridium-cobalt alloy core encapsulated in nitrogen-doped carbon cages. Adv Mater. 2018;30(9):1705324.
Li D, Zong Z, Tang Z, Liu Z, Chen S, Tian Y, Wang X. Total water splitting catalyzed by Co@Ir core-shell nanoparticles encapsulated in nitrogen-doped porous carbon derived from metal-organic frameworks. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2018;6(4):5105.
Chen L-N, Li H-Q, Yan M-W, Yuan C-F, Zhan W-W, Jiang Y-Q, Xie Z-X, Kuang Q, Zheng L-S. Ternary alloys encapsulated within different mofs via a self-sacrificing template process: a potential platform for the investigation of size-selective catalytic performances. Small. 2017;13(33):1700683.
Xiao Z, Xu F. A two-dimensional zeolitic imidazolate framework loaded with an acrylate-substituted oxoiron cluster as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. New J Chem. 2022;46(23):11095.
Li X-H, He P, Wang T, Zhang X-W, Chen W-L, Li Y-G. Keggin-type polyoxometalate-based ZIF-67 for enhanced photocatalytic nitrogen fixation. Chemsuschem. 2020;13(10):2769.
Li L, Fang Z-B, Deng W, Yi J-D, Wang R, Liu T-F. Precise construction of stable bimetallic metal–organic frameworks with single-site Ti(IV) incorporation in nodes for efficient photocatalytic oxygen evolution. CCS Chem. 2022;4(8):2782.
Xiang W, Zhang Y, Lin H, Liu C-J. Nanoparticle/metal–organic framework composites for catalytic applications: current status and perspective. Molecules. 2017;22(12):2103.
Zheng F, Fan Y, Chen W. Homogeneous distribution of Pt16(C4O4SH5)26 clusters in ZIF-67 for efficient hydrogen generation and oxygen reduction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(32):38170.
Fang Y, Xiao Z, Li J, Lollar C, Liu L, Lian X, Yuan S, Banerjee S, Zhang P, Zhou H-C. Formation of a highly reactive cobalt nanocluster crystal within a highly negatively charged porous coordination cage. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2018;57(19):5283.
Gao L, Chen S, Cai R, Zhao Q, Zhao X, Yang D. DUT-58 (Co) derived synthesis of co clusters as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalyst for zinc-air battery. Global Chall. 2018;2(1):1700086.
Li H, Zhang M, Zhou W, Duan J, Jin W. Ultrathin 2D catalysts with N-coordinated single Co atom outside Co cluster for highly efficient Zn-air battery. Chem Eng J. 2021;421: 129719.
Zou Q, Xu F, Ma J, Zhang H, Wang Y. Carboxylate-assisted ZIF-derived Co nanoclusters anchoring hierarchically porous carbon as high-efficient zinc-air batteries cathode catalysts. J Alloys Compd. 2022;923: 166393.
Zang W, Sumboja A, Ma Y, Zhang H, Wu Y, Wu S, Wu H, Liu Z, Guan C, Wang J, Pennycook SJ. Single Co atoms anchored in porous N-doped carbon for efficient zinc−air battery cathodes. ACS Catal. 2018;8(10):8961.
Wang X, Chen Z, Zhao X, Yao T, Chen W, You R, Zhao C, Wu G, Wang J, Huang W, Yang J, Hong X, Wei S, Wu Y, Li Y. Regulation of coordination number over single co sites: triggering the efficient electroreduction of CO2. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2018;57(7):1944.
Li X, Jiao Y, Cui Y, Dai C, Ren P, Song C, Ma X. Synergistic catalysis of the synthesis of ammonia with Co-based catalysts and plasma: from nanoparticles to a single atom. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(44):52498.
Wan J, Zhao Z, Shang H, Peng B, Chen W, Pei J, Zheng L, Dong J, Cao R, Sarangi R, Jiang Z, Zhou D, Zhuang Z, Zhang J, Wang D, Li Y. In situ phosphatizing of triphenylphosphine encapsulated within metal-organic frameworks to design atomic Co1–P1N3 interfacial structure for promoting catalytic performance. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142(18):8431.
Yuan S, Zhang J, Hu L, Li J, Li S, Gao Y, Zhang Q, Gu L, Yang W, Feng X, Wang B. Decarboxylation-induced defects in MOF-derived single cobalt atom@carbon electrocatalysts for efficient oxygen reduction. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60(40):21685.
Sun X, Olivos-Suarez AI, Osadchii D, Romero MJV, Kapteijn F, Gascon J. Single cobalt sites in mesoporous N-doped carbon matrix for selective catalytic hydrogenation of nitroarenes. J Catal. 2018;357:20.
Sun X, Sun S, Gu S, Liang Z, Zhang J, Yang Y, Deng Z, Wei P, Peng J, Xu Y, Fang C, Li Q, Han J, Jiang Z, Huang Y. High-performance single atom bifunctional oxygen catalysts derived from ZIF-67 superstructures. Nano Energy. 2019;61:245.
Wang X, Li P, Li Z, Chen W, Zhou H, Zhao Y, Wang X, Zheng L, Dong J, Lin Y, Zheng X, Yan W, Yang J, Yang Z, Qu Y, Yuan T, Wu Y, Li Y. 2D MOF induced accessible and exclusive Co single sites for an efficient O-silylation of alcohols with silanes. Chem Commun. 2019;55(46):6563.
Dilpazir S, He H, Li Z, Wang M, Lu P, Liu R, Xie Z, Gao D, Zhang G. Cobalt single atoms immobilized N-doped carbon nanotubes for enhanced bifunctional catalysis toward oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions. ACS Appl Energy Mater. 2018;1(7):3283.
He Y, Hwang S, Cullen DA, Uddin MA, Langhorst L, Li B, Karakalos S, Kropf AJ, Wegener EC, Sokolowski J, Chen M, Myers D, Su D, More KL, Wang G, Litster S, Wu G. Highly active atomically dispersed CoN4 fuel cell cathode catalysts derived from surfactant-assisted MOFs: carbon-shell confinement strategy. Energy Environ Sci. 2019;12(1):250.
Zhou L, Zhou P, Zhang Y, Liu B, Gao P, Guo S. 3D star-like atypical hybrid MOF derived single-atom catalyst boosts oxygen reduction catalysis. J Energy Chem. 2021;55:355.
Yang H, Lin Q, Wu Y, Li G, Hu Q, Chai X, Ren X, Zhang Q, Liu J, He C. Highly efficient utilization of single atoms via constructing 3D and free-standing electrodes for CO2 reduction with ultrahigh current density. Nano Energy. 2020;70: 104454.
Shao S, Yang Y, Sun K, Yang S, Li A, Yang F, Luo X, Hao S, Ke Y. Electron-rich ruthenium single-atom alloy for aqueous levulinic acid hydrogenation. ACS Catal. 2021;11(19):12146.
Zhao R, Liang Z, Gao S, Yang C, Zhu B, Zhao J, Qu C, Zou R, Xu Q. Puffing up energetic metal-organic frameworks to large carbon networks with hierarchical porosity and atomically dispersed metal sites. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58(7):1975.
Rong C, Shen X, Wang Y, Thomsen L, Zhao T, Li Y, Lu X, Amal R, Zhao C. Electronic structure engineering of single-atom Ru sites via Co–N4 sites for bifunctional pH-universal water splitting. Adv Mater. 2022;34(21):2110103.
Xiao M, Zhu J, Li S, Li G, Liu W, Deng Y-P, Bai Z, Ma L, Feng M, Wu T, Su D, Lu J, Yu A, Chen Z. 3d-orbital occupancy regulated Ir-Co atomic pair toward superior bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis. ACS Catal. 2021;11(14):8837.
Yang J, Zeng D, Li J, Dong L, Ong W-J, He Y. A highly efficient Fenton-like catalyst based on isolated diatomic Fe-Co anchored on N-doped porous carbon. Chem Eng J. 2021;404: 126376.
Wang J, Huang Z, Liu W, Chang C, Tang H, Li Z, Chen W, Jia C, Yao T, Wei S, Wu Y, Li Y. Design of N-coordinated dual-metal sites: a stable and active Pt-free catalyst for acidic oxygen reduction reaction. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139(48):17281.
Zhang D, Chen W, Li Z, Chen Y, Zheng L, Gong Y, Li Q, Shen R, Han Y, Cheong W-C, Gu L, Li Y. Isolated Fe and Co dual active sites on nitrogen-doped carbon for a highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Chem Commun. 2018;54(34):4274.
Wang J, Liu W, Luo G, Li Z, Zhao C, Zhang H, Zhu M, Xu Q, Wang X, Zhao C, Qu Y, Yang Z, Yao T, Li Y, Lin Y, Wu Y, Li Y. Synergistic effect of well-defined dual sites boosting the oxygen reduction reaction. Energy Environ Sci. 2018;11(12):3375.
Wei Y-S, Sun L, Wang M, Hong J, Zou L, Liu H, Wang Y, Zhang M, Liu Z, Li Y, Horike S, Suenaga K, Xu Q. Fabricating dual-atom iron catalysts for efficient oxygen evolution reaction: a heteroatom modulator approach. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;59(37):16013.
Hu B, Huang A, Zhang X, Chen Z, Tu R, Zhu W, Zhuang Z, Chen C, Peng Q, Li Y. Atomic Co/Ni dual sites with N/P-coordination as bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst for rechargeable zinc-air batteries. Nano Res. 2021;14(10):3482.
Luo Y, Zhang J, Chen J, Chen Y, Zhang C, Luo Y, Wang G, Wang R. Bi-functional electrocatalysis through synergetic coupling strategy of atomically dispersed Fe and Co active sites anchored on 3D nitrogen-doped carbon sheets for Zn-air battery. J Catal. 2021;397:223.
Wang Y, Wan X, Liu J, Li W, Li Y, Guo X, Liu X, Shang J, Shui J. Catalysis stability enhancement of Fe/Co dual-atom site via phosphorus coordination for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Nano Res. 2022;15(4):3082.
Zhang L, Fischer JMTA, Jia Y, Yan X, Xu W, Wang X, Chen J, Yang D, Liu H, Zhuang L, Hankel M, Searles DJ, Huang K, Feng S, Brown CL, Yao X. Coordination of atomic Co–Pt coupling species at carbon defects as active sites for oxygen reduction reaction. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(34):10757.
Liu M, Xu Q, Miao Q, Yang S, Wu P, Liu G, He J, Yu C, Zeng G. Atomic Co–N4 and Co nanoparticles confined in COF@ZIF-67 derived core–shell carbon frameworks: bifunctional non-precious metal catalysts toward the ORR and HER. J Mater Chem A. 2022;10(1):228.
Yang X, Wang Y, Wang X, Mei B, Luo E, Li Y, Meng Q, Jin Z, Jiang Z, Liu C, Ge J, Xing W. CO-tolerant PEMFC anodes enabled by synergistic catalysis between iridium single-atom sites and nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60(50):26177.
Shen Q, Jin H, Li P, Yu X, Zheng L, Song W, Cao C. Breaking the activity limitation of iridium single-atom catalyst in hydrogenation of quinoline with synergistic nanoparticles catalysis. Nano Res. 2022;15(6):5024.
Zheng B, Xu J, Song J, Wu H, Mei X, Zhang K, Han W, Wu W, He M, Han B. Nanoparticles and single atoms of cobalt synergistically enabled low-temperature reductive amination of carbonyl compounds. Chem Sci. 2022;13(31):9047.
Ma Z, Liu S, Tang N, Song T, Motokura K, Shen Z, Yang Y. Coexistence of Fe nanoclusters boosting fe single atoms to generate singlet oxygen for efficient aerobic oxidation of primary amines to imines. ACS Catal. 2022;12(9):5595.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Natural Science research project of Universities in Anhui Province (KJ2021ZD0001) and the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (2208085MB20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, YX., Zhou, YT. & Zhu, MZ. Co-based MOF derived metal catalysts: from nano-level to atom-level. Tungsten 5, 201–216 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-022-00197-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-022-00197-8