Abstract
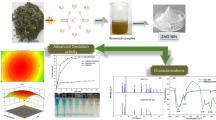
The reduction of azo dyes to less toxic and more easily biodegradable amine derivatives is an effective strategy for the treatment of industrial wastewater. The present work aimed to study the reduction reaction of azo dye Congo red (CR) catalyzed by nanoparticles (NPs) of chromium oxides (Cr2O3NPs) immobilized on bentonite in the presence of NaBH4. Cr(III) ions were intercalated using ion exchange reactions to obtain Cr-bentonite, and then the immobilized chromium cations were treated using NaBH4 leading to the formation of Cr2O3NPs-bentonite. The physicochemical properties of the samples were investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS), UV–Visible diffuse reflectance (UV–Vis DR), and Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy techniques. The results showed the formation of various chromium species, in which the most dominant were chromium oxide nanoparticles, on the bentonite surface with an average particle size between 20 and 35 nm. Line-scan analysis showed a reactive catalytic surface due to the excellent distribution of Cr on the bentonite surfaces. The best-performing catalyst, Cr2O3NPs-bentonite, displayed significant catalytic activity compared to the bentonite and Cr-bentonite materials, with a full reduction time of 630 s and a rate constant, kapp, equal to 0.034 s–1. The resulting products (benzidine and sodium 3, 4-diaminonaphthalene-1-sulfonate) from the catalytic reduction exhibited low toxicity compared to the CR dye; these products are easy to use in chemical synthesis. All results collected from this work indicated that this low-cost catalyst can be exploited to eliminate other dyes from the environment.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data and materials for this study are available herein.
References
Abdelkrim, S., Mokhtar, A., Djelad, A., Bennabi, F., Souna, A., Bengueddach, A., & Sassi, M. (2020). Chitosan/ag-bentonite nanocomposites: Preparation, characterization, swelling and biological properties. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 30, 831–840.
Abdelkrim, S., Mokhtar, A., Djelad, A., Hachemaoui, M., Boukoussa, B., & Sassi, M. (2022). Insights into catalytic reduction of dyes catalyzed by nanocomposite beads alginate@ Fe3O4: Experimental and DFT study on the mechanism of reduction. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 650, 129595.
Ahmad, Z., Shamim, A., Mahmood, S., Mahmood, T., & Khan, F. U. (2018). Biological synthesis and characterization of chromium (III) oxide nanoparticles. Engineering and Applied Science Letters, 1, 23–29.
Alexander, J. A., Ahmad Zaini, M. A., Surajudeen, A., Aliyu, E.-N.U., & Omeiza, A. U. (2019). Surface modification of low-cost bentonite adsorbents—a review. Particulate Science and Technology, 37, 538–549.
Almontasser, A. & Parveen, A. Preparation and characterization of chromium oxide nanoparticles. Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, 2020, AIP Publishing LLC, Pp. 020010.
Andrades, M. S., Rodríguez-Cruz, M. S., Sánchez-Martín, M. J., & Sánchez-Camazano, M. (2004). Effect of the modification of natural clay minerals with hexadecylpyridinium cation on the adsorption–desorption of fungicides. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 84, 133–141.
Ansari Mojarad, A., Tamjidi, S., & Esmaeili, H. (2020). Clay/starch/Fe3O4 nanocomposite as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of methyl violet dye from aqueous media. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 102, 1–22.
Arbaoui, F., & Boucherit, M. N. (2014). Comparison of two algerian bentonites: Physico-chemical and retention capacity study. Applied Clay Science, 91, 6–11.
Aroke, U., Abdulkarim, A., & Ogubunka, R. (2013). Fourier-transform infrared characterization of kaolin, granite, bentonite and barite. ATBU Journal of Environmental Technology, 6, 42–53.
Asli, B., Abdelkrim, S., Zahraoui, M., Mokhtar, A., Hachemaoui, M., Bennabi, F., Ahmed, A. B., Sardi, A., & Boukoussa, B. (2022). Catalytic reduction and antibacterial activity of MCM-41 modified by silver nanoparticles. Silicon, 14, 12587–12598.
Avila, M. C., Lick, I. D., Comelli, N. A., & Ruiz, M. L. (2021). Adsorption of an anionic dye from aqueous solution on a treated clay. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 15, 100688.
Bakr, E. A., El-Attar, H. G., & Salem, M. A. (2019). Colloidal ag@ pd core–shell nanoparticles showing fast catalytic eradication of dyes from water and excellent antimicrobial behavior. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 45, 1509–1526.
Benali, F., Boukoussa, B., Ismail, I., Hachemaoui, M., Iqbal, J., Taha, I., Cherifi, Z., & Mokhtar, A. (2021). One pot preparation of CeO2@ alginate composite beads for the catalytic reduction of mb dye: Effect of cerium percentage. Surfaces and Interfaces, 26, 101306.
Benmaati, A., Boukoussa, B., Hadjadj Aoul, R., Hachemaoui, M., Kerbadou, R. M., Habib Zahmani, H., & Hacini, S. (2022). Insights into catalytic reduction of organic pollutants catalyzed by nanoparticles supported on zeolite clinoptilolite. Silicon, 14, 8831–8843.
Carretero, M. I. (2002). Clay minerals and their beneficial effects upon human health. A Review. Applied Clay Science, 21, 155–163.
Carretero, M. I., Gomes, C., & Tateo, F. (2006). Clays and human health. Developments in Clay Science, 1, 717–741.
Chen, M., Liu, P., Wang, C., Ren, W., & Diao, G. (2014). Fast catalytic reduction of an azo dye by recoverable and reusable Fe3O4@ pani@ au magnetic composites. New Journal of Chemistry, 38, 4566–4573.
Cheng, M., Song, W., Ma, W., Chen, C., Zhao, J., Lin, J., & Zhu, H. (2008). Catalytic activity of iron species in layered clays for photodegradation of organic dyes under visible irradiation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 77, 355–363.
Cheng, Y., Zhang, X., Xie, W., Chen, D. & Li, G. (2013) The adsorptive ability of Ti-pillared montmorillonite for lead (II) cations. Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Materials for Renewable Energy and Environment, pp. 577–580.
De León, M. A., Castiglioni, J., Bussi, J., & Sergio, M. (2008). Catalytic activity of an iron-pillared montmorillonitic clay mineral in heterogeneous photo-Fenton process. Catalysis Today, 133, 600–605.
Gomes, Cd. S. F., & Silva, J. B. P. (2007). Minerals and clay minerals in medical geology. Applied Clay Science, 36, 4–21.
Hachemaoui, M., Boukoussa, B., Ismail, I., Mokhtar, A., Taha, I., Iqbal, J., Hacini, S., Bengueddach, A., & Hamacha, R. (2021a). CuNPs-loaded amines-functionalized-SBA-15 as effective catalysts for catalytic reduction of cationic and anionic dyes. Colloids and Surfaces a: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 623, 126729.
Hachemaoui, M., Mokhtar, A., Ismail, I., Mohamedi, M. W., Iqbal, J., Taha, I., Bennabi, F., Zaoui, F., Bengueddach, A., & Hamacha, R. (2021b). M (M: Cu Co, Cr or Fe) nanoparticles-loaded metal-organic framework mil-101 (Cr) material by sonication process: Catalytic activity and antibacterial properties. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 323, 111244.
Hayati-Ashtiani, M. (2011). Characterization of nano-porous bentonite (montmorillonite) particles using FTIR and BET-BJH analyses. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 28, 71–76.
Hosseini, F., Hosseini, F., Jafari, S. M., & Taheri, A. (2018). Bentonite nanoclay-based drug-delivery systems for treating melanoma. Clay Minerals, 53, 53–63.
Hudson, M. (1984) Journal of environmental science and health. Part c: Environmental carcinogenesis reviews: Edited by joseph g. Arcos, mary f. Argus and yin-tak woo. Price: Volume 1, number 1, 1983 (2 issues), institutional rate $31.50, individual rate $15.75. Issn: 0736-3001. Food Chemistry, 15, 67.
Ikhtiyarova, G., Özcan, A. S., Gök, Ö., & Özcan, A. (2012). Characterization of natural and organobentonite by XRD, SEM, FT-IR, and thermal analysis techniques and its adsorption behaviour in aqueous solutions. Clay Minerals, 47, 31–44.
Imanipoor, J., Mohammadi, M., & Dinari, M. (2021). Evaluating the performance of l-methionine modified montmorillonite k10 and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane functionalized magnesium phyllosilicate organoclays for adsorptive removal of azithromycin from water. Separation and Purification Technology, 275, 119256.
Jana, D., & De, G. (2012). Controlled and stepwise generation of Cu2O, Cu2O@Cu and Cu nanoparticles inside the transparent alumina films and their catalytic activity. RSC Advances, 2, 9606–9613.
Jlassi, K., Krupa, I., & Chehimi, M.M. (2017) Overview: Clay preparation, properties, modification. Chapter 1, pp. 1–28 In K. Jlassi, M.M. Chehimi, and S. Thomas (eds.). Clay-Polymer Nanocomposites, Elsevier, https://urldefense.com/v3/__https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-46153-5.00001-X
Joseph, A., Vellayan, K., González, B., Vicente, M. A., & Gil, A. (2019). Effective degradation of methylene blue in aqueous solution using pd-supported Cu-doped Ti-pillared montmorillonite catalyst. Applied Clay Science, 168, 7–10.
Kaur, N., & Kishore, D. (2012). Montmorillonite: An efficient, heterogeneous and green catalyst for organic synthesis. Journal of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Research, 4, 991–1015.
Khan, S. A., Shahid, S., Hanif, S., Almoallim, H. S., Alharbi, S. A., & Sellami, H. (2021). Green synthesis of chromium oxide nanoparticles for antibacterial, antioxidant anticancer, and biocompatibility activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22, 502.
Korichi, S., Elias, A., & Mefti, A. (2009). Characterization of smectite after acid activation with microwave irradiation. Applied Clay Science, 42, 432–438.
Krishnan, S.K., Subbiah, K., Kalivel, P. & Subramanian, K. (2021) Degradation of azo dye red me4bl treated with immobilised bimetallic zero-valent iron nanoparticles doped with palladium. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.2007381
Li, H., Wu, P., Dang, Z., Zhu, N., Li, P., & Wu, J. (2011). Synthesis, characterization, and visible-light photo-fenton catalytic activity of hydroxy Fe/Al-intercalated montmorillonite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 59, 466–477.
Liang, S.-T., Zhang, H.-L., Luo, M.-T., Luo, K.-J., Li, P., Xu, H.-B., & Zhang, Y. (2014). Colour performance investigation of a Cr2O3 green pigment prepared via the thermal decomposition of CrOOH. Ceramics International, 40, 4367–4373.
Liang, S.-T., Zhang, H.-L., Luo, M.-T., Liu, H.-X., Bai, Y.-L., Xu, H.-B., & Zhang, Y. (2015). Preparation of Cr2O3-based pigments with high NIR reflectance via thermal decomposition of CrOOH. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 25, 2646–2647.
Madejová, J., & Komadel, P. (2001). Baseline studies of The Clay Minerals Society source clays: Infrared methods. Clays and Clay Minerals, 49, 410–432.
Madhav, S., Ahamad, A., Singh, P., & Mishra, P. K. (2018). A review of textile industry: Wet processing, environmental impacts, and effluent treatment methods. Environmental Quality Management, 27, 31–41.
Madi, C., Tabbal, M., Christidis, T., Isber, S., Nsouli, B. & Zahraman, K. Microstructural characterization of chromium oxide thin films grown by remote plasma assisted pulsed laser deposition. Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2007, IOP Publishing, Pp. 128.
Marquardt, D. W. (1963). An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 11, 431–441.
Mekki, A., Hachemaoui, M., Mokhtar, A., Issam, I., Bennabi, F., Iqbal, J., Rahmani, K., Bengueddach, A., & Boukoussa, B. (2022). Catalytic behavior and antibacterial/antifungal activities of new mnps/zeolite@ alginate composite beads. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 198, 37–45.
Mokhtar, A., Bennabi, F., Abdelkrim, S., Sardi, A., Boukoussa, B., Souna, A., Bengueddach, A., & Sassi, M. (2020). Evaluation of intercalated layered materials as an antimicrobial and drug delivery system: A comparative study. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry, 96, 353–364.
Naseem, K., Farooqi, Z. H., Begum, R., & Irfan, A. (2018). Removal of congo red dye from aqueous medium by its catalytic reduction using sodium borohydride in the presence of various inorganic nano-catalysts: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 187, 296–307.
Ngah, W. W., Teong, L., Toh, R., & Hanafiah, M. (2012). Utilization of chitosan–zeolite composite in the removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution: Adsorption, desorption and fixed bed column studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 209, 46–53.
Park, J.-H., Shin, H.-J., Kim, M. H., Kim, J.-S., Kang, N., Lee, J.-Y., Kim, K.-T., Lee, J. I., & Kim, D.-D. (2016). Application of montmorillonite in bentonite as a pharmaceutical excipient in drug delivery systems. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation, 46, 363–375.
Patterson, A. (1939). The scherrer formula for x-ray particle size determination. Physical Review, 56, 978.
Petrović, R., Lazarević, S., Janković-Častvan, I., Matić, T., Milivojević, M., Milošević, D., & Veljović, Đ. (2023). Removal of trivalent chromium from aqueous solutions by natural clays: Valorization of saturated adsorbents as raw materials in ceramic manufacturing. Applied Clay Science, 231, 106747.
Singh, B. K., Lee, S., & Na, K. (2020). An overview on metal-related catalysts: Metal oxides, nanoporous metals and supported metal nanoparticles on metal organic frameworks and zeolites. Rare Metals, 39, 751–766.
Teğin, İ. & Saka, C. (2021) Chemical and thermal activation of clay sample for improvement adsorption capacity of methylene blue. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2021.1928105
Tharmaraj, V., Vandarkuzhali, S. A. A., Karthikeyan, G., & Pachamuthu, M. (2022). Efficient and recyclable AuNPs@ aminoclay nanocomposite catalyst for the reduction of organic dyes. Surfaces and Interfaces, 32, 102052.
Vakili, M., Deng, S., Cagnetta, G., Wang, W., Meng, P., Liu, D., & Yu, G. (2019). Regeneration of chitosan-based adsorbents used in heavy metal adsorption: A review. Separation and Purification Technology, 224, 373–387.
Varadavenkatesan, T., Selvaraj, R., & Vinayagam, R. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using thunbergia grandiflora flower extract and its catalytic action in reduction of congo red dye. Materials Today: Proceedings, 23, 39–42.
Zhang, Q., Gao, S., & Yu, J. (2022). Metal sites in zeolites: Synthesis, characterization, and catalysis. Chemical Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00315
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through a research project number RGP.2/226/43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Associate Editor: Jun Kawamata
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zahraoui, M., Mokhtar, A., Medjhouda, Z.A.K. et al. Catalytic Reduction of Congo Red to Low-Toxicity Forms Using a Low-Cost Catalyst Based on Modified Bentonite Material. Clays Clay Miner. 71, 74–90 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42860-023-00226-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42860-023-00226-8