Abstract
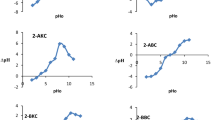
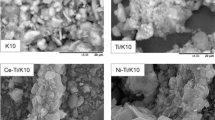
Because they are so widespread, the use of saponites is significant in many industries. The modification of saponite-rich clay minerals is known to improve their existing characteristics and may provide new functional properties. The objective of the present paper was to characterize the effects of adding nanosized graphene-like molybdenum (Mo) and tungsten (W) sulfides on the textural and surface characteristics of composites based on native saponite and saponite pre-modified with nanoscale magnetite. The textural characteristics were investigated by the nitrogen adsorption-desorption method and scanning electron microscopy. The total acidity, Hammett Brönsted centers, and Quasi-Equilibrium Thermo Desorption (QE-TD) Lewis centers were characteristics used to probe the acid-base properties of the modified composites. In all cases, modification proved to have a significant effect on both the surface and textural properties of the clay matrix. Modification of the native saponite by graphene-like Mo and W sulfides resulted in a decrease in the specific surface area, except a slight increase in the surface area of the magnetite-containing saponite was observed. Analysis of the acid-base characteristics of native and magnetite-modified saponite (MMS) indicated the ability of modified MoS2 and WS2 additives to alter the acid-base state of the surface. The addition of graphene-like Mo and W sulfides increased the total acidity of native and MMS, with MoS2 modification being more promising because, in almost all the samples, saponite composite materials increased the number of both Brönsted and Lewis active centers compared with WS2, which was determined by the corresponding methods. The acid-base characteristics of the saponite-containing samples, which were studied in an aqueous medium by various methods, are in good correlation with each other, and are consistent with the sorption activity of cationic and anionic dyes.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Borisenko, V. E., Krivosheeva, A. V., & Shaposhnikov, V. L. (2016). Band structure and optical properties of molybdenum and tungsten dichalcogenides. Bulletin of the Foundation for Fundamental Research, 3, 41–48 [in Russian].
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H., & Teller, E. (1938). Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 60, 309–319.
Carretero, M. I., & Pozo, M. (2009). Clay and non-clay minerals in the pharmaceutical industry: Part I. Excipients and medical applications. Applied Clay Science, 46, 73–80.
Chanturiya, V., Minenko, V., Suvorova, O., Pletneva, V., & Makarov, D. (2017). Electrochemical modification of saponite for manufacture of ceramic building materials. Applied Clay Science, 135, 199–205.
Choy, J. H., Choi, S. J., Oh, J. M., & Park, M. (2007). Clay minerals and layered double hydroxides for novel biological applications. Applied Clay Science, 36, 122–132.
Dai, Q. L., Yan, B., Liang, Y., & Xu, B. Q. (2017). Water effects on the acidic property of typical solid acid catalysts by 3,3-dimethylbut-1-ene isomerization and 2-propanol dehydration reactions. Catalysis Today, 295, 110–118.
Donauerová, A., Bujdák, J., Smolinská, M., & Bujdáková, H. (2015). Photophysical and antibacterial properties of complex systems based on smectite, a cationic surfactant and methylene blue. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 151, 135–141.
Dontsova, T. A., Kulikov, L. M., & Astrelin, I. M. (2017). Adsorption photocatalytic properties of micronic and graphene (2D) nanoparticles of molybdenum dichalcogenides. Journal of Water Chemistry and Technology, 39, 132–137.
Dontsova, T. A., Yanushevskaya, E. I., Nahirniak, S. V., Makarchuk, O. V., Ivanets, A. I., Roshchina, M. Y., Kutuzova, A. S., & Kulikov, L. M. (2018). Directional control of the structural adsorption properties of clays by magnetite modification. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2018, 6573016.
Fatimaha, I., Nurillahia, R., Sahronia, I., & Muraza, O. (2019). TiO2-pillared saponite and photosensitization using a ruthenium complex for photocatalytic enhancement of the photodegradation of bromophenol blue. Applied Clay Science, 183, 105302.
Gregg, S. J. & Sing, K. S. W. (1982). Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity. Second Printing. London and New York: Academic Press, 303 pp.
Hammett, L. P., & Deyrup, A. J. (1932). A series of simple basic indicators. I. The acidity functions of mixtures of sulfuric acids with water. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 54, 2721–2739.
Hover, V. C., Walter, L. M., Peacor, D. R., & Martini, A. M. (1999). Mg-smectite authigenesis in a marine evaporative environment, Salina Ometepec, Baja California. Clays and Clay Minerals, 47, 252–268.
Hu, K. H., Hu, X. G., Xu, Y. F., & Pan, X. Z. (2010). The effect of morphology and size on the photocatalytic properties of MoS2. Reaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis, 100, 153–163.
Kumaresan, S., Radheshyam, R. P., Bhavesh, D. K., & Hari, C. B. (2019). Synthesis of saponite based nanocomposites to improve the controlled oral drug release of model drug quinine hydrochloride dihydrate. Pharmaceuticals, 12, 105.
López-Galindo, A., Viseras, C., & Cerezo, P. (2007). Compositional, technical and safety specifications of clays to be used as pharmaceutical and cosmetic products. Applied Clay Science, 36, 51–63.
Makarchuk, O., Dontsova, T. & Krymets, G. (2017a). Magnetic mineral nanocomposite sorbents for removal of surfactants. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 7th International Conference on Nanomaterials: Applications & Properties (NAP-2017): 2017-January, 02MFPM02.
Makarchuk, O., Dontsova, T., Perekos, A., Skoblik, A., & Svystunov, Y. (2017c). Magnetic mineral nanocomposite sorbents for wastewater treatment. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2017, 8579598.
Makarchuk, O., Dontsova, T., & Perekos, A. (2017b). Magnetic nanocomposite sorbents on mineral base. Springer Proceedings in Physics, 195, 705–719.
Murray, H. H. (1999). Applied clay mineralogy today and tomorrow. Clay Minerals, 34, 39–49.
Mykhailenko, N., Makarchuk, O., Dontsova, T., Gorobets, S., & Astrelin, I. (2015). Purification of aqueous media by magnetically operated saponite sorbents. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4, 13–20.
Nityashree, N., Price, C. A. H., Pastor-Perez, L., Manohara1, G. V., Garcia, S., Maroto-Valer, M. M., & Reina, T. R. (2020). Carbon stabilised saponite supported transition metal-alloy catalysts for chemical CO2 utilisation via reverse water-gas shift reaction. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 261, 118241.
Petra, L., Billik, P., Melichová, Z., & Komadel, P. (2017). Mechanochemically activated saponite as materials for Cu2+ and Ni2+ removal from aqueous solutions. Applied Clay Science, 143, 22–28.
Polyakov, V. E., & Tarasevich, Y. I. (2012). Ion exchange equilibria involving uncharged cations on saponite. Journal of Water Chemistry and Technology, 34, 18–27.
Puziy, A. M., Poddubnaya, O. I., Kochkin, Y. N., Vlasenko, N. V., & Tsyba, M. M. (2010). Acid properties of phosphoric acid activated carbons and their catalytic behavior in ETBE synthesis. Carbon, 48, 706–713.
Qiao, X. Q., Hu, F. C., Tian, F. Y., Hou, D. F., & Li, D. S. (2016). Equilibrium and kinetic studies on MB adsorption by ultrathin 2D MoS2 nanosheets. RSC Advances, 6, 11631–11636.
Rodriguez, V. M. A., Suarez, B. M., Lopez, G. J. D., & Bañares, M. M. A. (1994). Acid Activation of a Ferrous Saponite (Griffithite): Physico-Chemical Characterization and Surface Area of the Products Obtained. Clays and Clay Minerals, 42, 724–730.
Samara, E., Matsi, T., Zdragas, A., & Barbayiannis, N. (2019). Use of clay minerals for sewage sludge stabilization and a preliminary assessment of the treated sludge's fertilization capacity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 35387–35398.
Shao, H., & Pinnavaia, T. J. (2010). Synthesis and properties of nanoparticle forms saponite clay, cancrinite zeolite and phase mixtures thereof. Microporous Mesoporous Materials, 133, 10–17.
Sokol, H., Sprynskyy, M., Ganzyuk, A., Raks, V., & Buszewski, B. (2019). Structural, mineral and elemental composition features of iron-rich saponite clay from Tashkiv deposit (Ukraine). Colloids Interfaces, 3, 10.
Sprynskyya, M., Sokolb, H., Rafińskaa, K., Brzozowskaa, W., Railean-Plugarua, V., Pomastowskic, P., & Buszewskia, B. (2019). Preparation of AgNPs/saponite nanocomposites without reduction agents and study of its antibacterial activity. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 180, 457–465.
Szabo´, T., Mitea, R., Leeman, H., Premachandra, G. S., Johnston, C. T., Szekeres, M., De’ka’ny, I., & Schoonheydt, R. A. (2008). Adsorption of protamine and papain proteins on saponiteю. Clays and Clay Minerals, 56, 494–504.
Tanabe, K., Misono, M., Hattori, H., & Ono, Y. (1990). Solid Acids and Bases. Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, 51, 364.
Tangaraj, V., Janot, J. M., Jaber, M., Bechelany, M., & Balme, S. (2017). Adsorption and photophysical properties of fluorescent dyes over montmorillonite and saponite modified by surfactant. Chemosphere, Elsevier, 184, 1355–1361.
Tarasevich, J. I., Poljakov, V. E., Ivanova, Z. G., & Trifonova, M. Y. (2011). Composition, structure and thermal stability of exchangeable cations hydrates of saponite. Journal of Water Chemistry and Technology, 33, 381–391.
Treiman, A. H., Morris, R. V., Agresti, D. G., Graff, T. G., Achilles, C. N., Rampe, E. B., Bristow, T. F., Ming, D. W., Blake, D. F., Vaniman, D. T., Bish, D. L., Chipera, S. J., Morrison, S. M., & Downs, R. T. (2014). Ferrian saponite from the Santa Monica Mountains (California, U.S.A., Earth): Characterization as an analog for clay minerals on Mars with application to Yellowknife Bay in Gale Crater. American Mineralogist, 99, 2234–2250.
Vasilyeva, I. G., Asanov, I. P., & Kulikov, L. M. (2015). Experiments and consideration about surface nonstoichiometry of few-layer MoS2 prepared by chemical vapor deposition. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 119, 23259–23267.
Villarroel-Rocha, J., Barrera, D., & Sapag, K. (2014). Introducing a self-consistent test and the corresponding modification in the Barrett, Joyner and Halenda method for pore-size determination. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 200, 68–78.
Vlasenko, N. V., Kochkin, Y. N., Telbiz, G. M., Shvets, A. V., & Strizhak, P. E. (2019a). Insight into the active sites nature of zeolite H-BEA for liquid phase etherification of isobutylene with ethanol. RSC Advances, 9, 35957–35968.
Vlasenko, N. V., Kyriienko, P. I., Valihura, K. V., Yanushevska, O. I., Soloviev, S. O., & Strizhak, P. E. (2019b). Effect of Modifying Additives on the Catalytic Properties of Zirconia in the process of Ethanol Conversion to 1-Butanol. Theoretical and Experimental Chemistry, 55, 40–46.
Vogels, R. J. M. J., Kloprogge, J. T., & Geus, J. W. (2005). Synthesis and characterization of saponite clays. American Mineralogist, 90, 931–944.
Zhoua, C. H., Zhoua, Q., Wua, Q. Q., Petitd, S., Jianga, X. C., Xiaa, S. T., Lib, C. S., & Yua, W. H. (2019). Modification, hybridization and applications of saponite: An overview. Applied Clay Science, 168, 136–154.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Svitlana Nahirniak for her support in conducting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
(Received 16 October 2019; revised 24 Jun 2020; AE: Peter Ryan)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanushevska, O.I., Dontsova, T.A., Aleksyk, A.I. et al. SURFACE AND STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES OF CLAY MATERIALS BASED ON NATURAL SAPONITE. Clays Clay Miner. 68, 465–475 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42860-020-00088-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42860-020-00088-4