Abstract
Purpose
In previous studies, the stability and maturity of forced aerated composts were examined from the physicochemical analysis inside the reactors. The objective of this study is to check the maturity and effects of forced aerated composts after its addition to soil and plants.
Methods
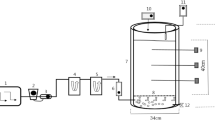
The composts were prepared from fresh chicken manure and sawdust in cylindrical reactors and aerated at 0.75, 0.50, and 0.25 L min−1 kg−1 organic matter (OM) for 1 month. Afterward, it was mixed with soil and coded as treatment T1 (0.75 L min−1 kg−1 OM aeration rate + soil), T2 (0.50 L min−1 kg−1 OM aeration rate + soil), T3 (0.25 L min−1 kg−1 OM aeration rate + soil), and CS (only soil), respectively. The soil properties (pH, electrical conductivity (EC), organic matter content (OM), loss of organic matter content, bulk density (BD), water holding(WH)) and plant growth (shoot length (cm), leaves’ area (cm2), fresh and dry weight (g)) were checked for 4 months.
Results
The results showed a significant increase (at P < 0.05) in soil properties in T1, T2, and T3 as compared with CS. Among treatments T1, T2, and T3, the maximum pH (7.20 ± 0.07), OM degradation (77.06%), loss of organic matter (6.32 ± 0.42%), and WH (32.17 ± 0.32%) were observed in T3. Additionally, the lowest EC (1.15 ± 0.02 mS/cm) and BD (1.06 ± 0.02%) were observed in T3. Further a significant increased difference (at P < 0.05) in shoot length (21.40 ± 1.01 cm), leaves’ area (293.20 ± 16.33 cm2), fresh weight (88.22 ± 7.30 g), and dry weight (12.10 ± 0.91 g) of the plant were observed in T3.
Conclusion
The poultry manure compost’s aerated rate (0.25 L min−1 kg−1 OM) in T3 was observed to be more mature and stable as compared with T1 and T2.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, H. K., Richard, T. L., & Choi, H. L. (2007). Mass and thermal balance during composting of a poultry manure-wood shavings mixture at different aeration rates. Process Biochemistry, 42(2), 215–223. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201000537.
Aizat, M., Roslan, M. A., Sulaiman, A. N. W., & Karam, S. D. (2014). The relationship between soil pH and selected soil properties in 48 years logged-over forest. International Journal of Environmental Sciences, 4(6), 1129–1140. https://doi.org/10.6088/ijes.2014040600004.
Arancon, N. Q., Edwards, C. A., Bierman, P., Welch, C., & Metzger, J. D. (2004). Influences of vermicomposts on field strawberries: 1. Effects on growth and yields. Bioresource Technology, 93(2), 145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2003.10.014.
Arslan, E. I., Unlu, A., & Topal, M. (2011). Determination of the effect of aeration rate on composting of vegetable-fruit wastes. Clean: Soil, Air, Water, 39(11), 1014–1021. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201000537.
Arthur, E., Cornelis, W., & Razzaghi, F. (2012). Compost amendment to sandy soil affects soil properties and greenhouse tomato productivity. Compost Science and Utilization, 20(4), 215–221. https://doi.org/10.1080/1065657X.2012.10737051.
Aslam, D. N., Horwath, W., & VanderGheynst, J. S. (2008). Comparison of several maturity indicators for estimating phytotoxicity in compost-amended soil. Waste Management, 28(11), 2070–2076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2007.08.026.
Azeez, J. O., & Van Averbeke, W. (2010). Nitrogen mineralization potential of three animal manures applied on a sandy clay loam soil. Bioresource Technology, 101(14), 5645–5651. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2012.653022.
Azeez, J. O., & Van Averbeke, W. (2012). Dynamics of soil pH and electrical conductivity with the application of three animal manures. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 43(6), 865–874. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2012.653022.
Basak, J. K., Qasim, W., Okyere, F. G., Khan, F., Lee, J., Park, J., & Kim, H. T. (2019). Regression analysis to estimate morphology parameters of pepper plant in a controlled greenhouse system. Biosystems Engineering, 44(2), 57–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-019-00014-0.
Bohara, H., Dodla, S., Wang, J. J., Darapuneni, M., Acharya, B. S., Magdi, S., & Pavuluri, K. (2019). Influence of poultry litter and biochar on soil water dynamics and nutrient leaching from a very fine sandy loam soil. Soil and Tillage Research, 189(9), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.01.001.
Bolan, N. S., Szoci, A. A., Chuasavathi, T., Seshadri, B., Rothrock, M. J., & Panneerselvam, P. (2010). Uses and management of poultry litter. World's Poultry Science Journal, 66(4), 673–698. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0043933910000656.
Bruckner M.Z. (2012). Water and soil characterization- pH and electrical conductivity, microbial life educational resources. Montana State University Bozeman, https://serc.carleton.edu/microbelife/research_methods/environ_sampling/pH_EC.html
Cho, Y. Y., Oh, S., Oh, M. M., & Son, J. E. (2007). Estimation of individual leaf area, fresh weight, and dry weight of hydroponically grown cucumbers (Cucumis sativus L.) using leaf length, width, and SPAD value. Scientia Horticulturae, 111(4), 330–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2006.12.028.
Choi, K. Y., Paek, K. Y., & Lee, Y. B. (2000). Effect of air temperature on tipburn incidence of butterhead and leaf lettuce in a plant factory. In C. Kubota & C. Chun (Eds.), Transplant production in the 21st century (pp. 166–171). Dordrecht: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-9371-7_27.
Choi, S., Hinkle, A. F. (2018). Korea - republic of poultry and products annual. Global agriculture information Network. https://apps.fas.usda.gov/newgainapi/api/report/downloadreportbyfilename?filename=Poultry%20and%20Products%20Annual_Seoul_Korea%20-%20Republic%20of_9-4-2018.pdf. Accessed 15 Feb 2020.
Dalorima, T., Khandaker, M. M., Zakaria, A. J., & Hasbullah, M. (2018). Impact of organic fertilizations in improving BRIS soil conditions and growth of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 24(1), 112–118.
Gao, M., Li, B., Yu, A., Liang, F., Yang, L., & Sun, Y. (2010). The effect of aeration rate on forced-aeration composting of chicken manure and sawdust. Bioresource Technology, 101(6), 1899–1903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.027.
Guo, R., Li, G., Jiang, T., Schuchardt, F., Chen, T., Zhao, Y., & Shen, Y. (2012). Effect of aeration rate, C/N ratio and moisture content on the stability and maturity of compost. Bioresource Technology, 112, 171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.02.099.
Karhu, K., Mattila, T., Bergstrom, I., & Regina, K. (2011). Biochar addition to agricultural soil increased CH4 uptake and water holding capacity-results from a short-term pilot field study. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 140(1–2), 309–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2010.12.005.
Khalid, S., Qureshi, K. M., Hafiz, I. A., Khan, K. S., & Qureshi, U. S. (2013). Effect of organic amendments on vegetative growth, fruit and yield quality of strawberry. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Resources, 26(2), 104–112.
Kulcu, R., & Yaldiz, O. (2004). Determination of aeration rate and kinetics of composting some agricultural wastes. Bioresource Technology, 93(1), 49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2003.10.007.
Microsoft Office (2010). Seattle: Microsoft Corporation Inc.
Ogendo, R. O., Isutsa, D. K., & Singunga, D. O. (2008). Interaction of farm yard manure and plant population density effects on soil characteristics and productivity of mulched strawberry in a tropical climate. African Journal of Horticulture Science., 1(1), 100–115.
Paredes, C., Bernal, M. P., Cegarra, J., & Roig, A. (2002). Bio-degradation of olive mill wastewater sludge by its co-composting with agricultural wastes. Bioresource Technology, 85(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00078-0.
Partanen, P., Hultman, J., Paulin, L., Auvinen, P., & Romantschuk, M. (2010). Bacterial diversity at different stages of the composting process. BMC Microbiology, 10(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-10-94.
Perie, C., & Ouimet, R. (2008). Organic carbon, organic matter and bulk density relationships in boreal forest soils. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 88(3), 315–325. https://doi.org/10.4141/CJSS06008.
Phonsuwan, M., Lee, M. H., Moon, B. E., Choi, M. K., Keawjumpa, N., & Kim, H. T. (2016). Comparison on different qualities of compost on possible efficiencies of nutrient accumulation, heavy metal absorption and growth by chrysanthemum. International Conference on Sustainable Energy, Environment and Information Engineering, DEStech Transactions on Environment, Energy and Earth Sciences. Bangkok, Thailand. 23–27.
Preusch, P. L. (2003). Nitrogen and phosphorus availability and weed suppression from composted poultry litter applied as a mulch in a peach orchard. HortSciences, 38(6), 1108–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2003.12.005.
Qasim, W., Moon, B. E., Okyere, F. G., Khan, F., Nafees, M., & Kim, H. T. (2019). Influence of aeration rate and reactor shape on the composting of poultry manure and sawdust. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 69(5), 633–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.02.099.
Qasim, W., Moon, B. E., Phonsuwan, M., Jo, J. S., Lee, M. H., Nafees, M., & Kim, H. T. (2018). Effects of an aluminum sulfate and ferric chloride blend on poultry litter characteristics in vitro. Journal of Applied Poultry Resources, 27(1), 92–102. https://doi.org/10.3382/japr/pfx046.
Rasapoor, M., Nasrabadi, T., Kamali, M., & Hoveidi, H. (2009). The effects of aeration rate on generated compost quality, using aerated static pile method. Waste Management, 29(2), 570–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.04.012.
Robinson, M. D., & Al Busaidi, B. (2009). An assessment of the rangeland vegetation on the Saiq plateau, Jebel Akhdar, Oman. International Journal of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 35(4), 313–320.
Scotti, R., Pane, C., Spaccini, R., Palese, A. M., Piccolo, A., Celano, G., & Zaccardelli, M. (2016). On-farm compost: A useful tool to improve soil quality under intensive farming systems. Applied Soil Ecology, 107, 13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.05.004.
Sheng, J., Adeli, A., Brooks, J. P., McLaughlin, M. R., & Read, J. (2014). Effects of bedding materials in applied poultry litter and immobilizing agents on runoff water, soil properties, and bermuda grass growth. Journal of Environmental Quality, 43, 290–296. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2012.0070.
Wang, X., Lu, S., Gao, C., Xu, X., Wei, Y., Bai, X., Feng, C., Gao, N., Liu, M., & Wu, L. (2014). Biomass-based multifunctional fertilizer system featuring controlled-release nutrient, water-retention and amelioration of soil. RSC Advances, 4(35), 18382–18390. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra00207e.
Wong, J., Li, S., & Wong, M. H. (1995). Coal fly ash as a composting material for sewage sludge: effects on microbial activities. Environmental Technology, 16(6), 527–537. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593331608616294.
Wu, J., Zhao, Y., Yu, H., Wei, D., Yang, T., Wei, Z., Lu, Q., & Zhang, X. (2019). Effects of aeration rates on the structural changes in humic substance during co-composting of digestates and chicken manure. Science of the Total Environment, 658, 510–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.198.
Funding
This research was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture and Forestry (IPET) through Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs Research Center Support Program, funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (Project No. 717001-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, F., Basak, J.K., Jaihuni, M. et al. Forced Aerated Poultry Compost Effects on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Lettuce Plant Growth. J. Biosyst. Eng. 45, 104–116 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-020-00050-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-020-00050-1