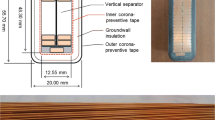
Abstract
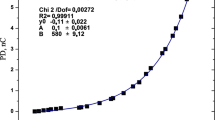
Although the AC current and dissipation factor in phases A, B, and C were good, the magnitude of partial discharge (PD) was measured to be 191,525 pC, 11,430 pC, and 10,809 pC for phases A, B, and C, respectively, at the phase voltage of 11.5 kV, in the insulation diagnostic test of a steam turbine generator (374 MVA, 20 kV) stator winding. Root cause analysis and maintenance work were performed over the 2nd–4th tests since the magnitude of the PD of the generator was determined to be defective in phase A. It was found that the largest discharge pulse was generated in Turbine End (TE) 54 on the endwinding side of the generator in phase A. The groundwall insulation of TE 54 on the endwinding side of the generator was removed in the 2nd test and the PD magnitude that was measured after separating the temperature signal line from the copper bar was 177,649 pC, which was not significantly different from the 191,525 pC in the 1st test. Therefore, the magnitude of the PD decreased significantly to 6057 pC after connecting the temperature signal line to the copper bar. The PD magnitude was 6121 pC as a result of recovering the removed main insulation material in the 3rd test, and the PD magnitude was good at 8123 pC as a result of recovering the groundwall insulation and finally finishing the external paintwork in the 4th test.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim H-D (2002) Analysis of insulation aging mechanism in generator stator windings. J KIEEME 15(2):119–126
Morin R, Bartnikas R, Menard P (2000) A three-phase multi-stress accelerated electrical aging test facility for stator bars. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 15(2):149–156
Griffith G, Tucker S, Milsom J, Stone G (2000) Problems with modern air-cooled generator stator winding insulation. IEEE Electr Insul Mag 16(6):6–10
McDermid W, Bromley JC (1999) Experience with directional couplers for partial discharge measurements on rotating machines in operation. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 14(2):175–184
Kim B-H, Kim H-D (2006) Properties of on-line partial discharge in hydrogenerator stator windings. Trans Korean Inst Electr Eng C 55(4):172–177
Stone GC, Warren V (2006) Objective methods to interpret partial-discharge data on rotating-machine stator windings. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 42(1):195–200
Lee S-H, Kong T-S, Kim H-D (2020) Analysis of insulation diagnosis for generator-motor stator winding in pumped storage power plant. J Electr Eng Technol 15(3):1269–1280
Yoshida H, Umemoto K (1986) Insulation diagnosis for rotating machine insulation. IEEE Trans Electr Insul 6:1021–1025
Ju Y et al (2009) Development of off-line diagnosis and life assessment technology for generator (1st stage report). Ministry of Knowledge Economy , South Korea
Hudon C, Belec M (2005) Partial discharge signal interpretation for generator diagnostics. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 12(2):297–319
Kim HD, Ju YH (2002) Comparison of off-line and on-line partial discharge for large motors. In Conference record of the the 2002 IEEE international symposium on electrical insulation (Cat. No. 02CH37316), pp. 27–30. IEEE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HC., Kim, HD. Insulation Diagnosis Characteristics According to the Stator Winding Maintenance Procedure of a 20 kV Class Steam Turbine Generator. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 16, 3307–3312 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-021-00868-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-021-00868-5