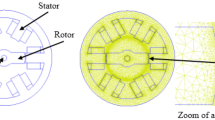
Abstract
The switched reluctance motor (SRM) is of great interest in industrial applications due to its highly appreciated performances and especially for its open loop operating capacity. However, its model is highly nonlinear when taking into account magnetics saturation effects. In this paper, in order to increase the zones of acceleration of the SRM, a new shape of rotor is proposed in order to push the limits of operation towards the high frequencies. The finite element method (FEM) through the FEMM field calculation software was used in order to take into account the geometric structure and saturation phenomena of the magnetic circuit of the machine. Using some tools of chaos, the results obtained have been compared with other SRM structures such as conventional and attack-teeth structures. It appeared that the proposed hollow-teeth structure shows a good dynamic performance in open loop and allows a perfectly periodic dynamic response at high control frequencies. Indeed, the presence of small teeth on the rotor teeth increases the acceleration zones of the machine, which allows it to operate at high frequencies.
Graphic abstract
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller TJE (1993) Switched reluctance motors and their control . Magna Physics Publishing and Clarendon Press, Hillsboro
Krishnan R (2001) Switched reluctance motor drives: modeling, simulation, analysis, design and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Prabhu V, Rajini V, Balaji M (2015) A comparative study of operating angle optimization of switched reluctance motor with robust speed controller using PSO and GA. J Electr Eng Technol 10(2):551–559
Xu YZ, Zhong R, Chen L, Lu SL (2012) Analytical method to optimize turn-on angle and turn-off angle for switched reluctance motor drives. IET Electr Power Appl 6(9):593–603
Mirzaeian B, Moallem M, Tahani V, Lucas C (2002) Multi-objective optimization method based on a genetic algorithm for switched reluctance motor design. IEEE Trans Magn 38(3):1524–1527
El-kharashi E (2007) A rotor consisting of two iron cylinders for switched reluctance motors. J Electr Eng 1(2):377–384
Bagard P (1996) Outils coupants, conditions de coupe et stratégies en Usinage à Grande Vitesse des Outillages et formes complexes : Piont de départ de la chaîne CFAO. Journées de l'usinage. http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?title=Outils%20coupants%2C%20conditions%20de%20coupe%20et%20strat%C3%A9gies%20en%20Usinage%20%C3%A0%20Grande%20Vitesse%20des%20Outillages%20et%20formes%20complexes%3A%20Point%20de%20d%C3%A9part%20de%20la%20cha%C3%AEne. Accessed 12 Oct 2020
Defretin AL, Levaillant G (2002) Usinage à grande vitesse. Technique de l'ingénieur, traité génie mécanique. https://scholar.google.fr/scholar?hl=fr&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Defretin%2C+A.+L.+and+Levaillant%2C+G&btnG=. Accessed 12 Oct 2020
Fayard H (1999) Procédés à réluctance variable pour la conversion d'énergie électromécanique directe: application à l’usinage à grande vitesse. Thèse de Doctorat de l’Université de METZ
Bagard P, Palleau M (1995) On gagne à les usiner à grande vitesse. Cetim-Inf 142:39–43
Vives-Fos R (1993) Etude d'électrobroches à réluctance variable pour l'usinage à grande vitesse. Thèse de Doctorat, Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers
Kenmoe FED, Takorabet N, Meibody FT, Sargos MF (2010) Nonlinear finite element-circuit model of a hybrid stepping motor. COMPEL Int J Comput Math Electr Electron Eng 29(4):957–963
Libing J, Jia C, Tong B (2019) Analytical method for magnetic field and electromagnetic performances in switched reluctance machines. J Electr Eng Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-019-00167-0
Maruthachalam S, Palaniswamy N (2011) Determination of flux linkage characteristics and inductance of submersible switched reluctance motor using software tools. J Comput Sci 7(2):179–187
Vaithilingam M (2012) Zare, aris and marhaban, “computation of electromagnetic torque in a double rotor switched reluctance motor using flux tube method.” Energies 5:4008–4026
Ohyama K, Naguib M, Nashed K, Aso K, Fujii H, Uehara H (2006) Design using finite element analysis of a switched eeluctance motor for electric vehicle. J Power Electron 6:163–171
Parreira B, Rafael S, Pires AJ, Costa Branco PJ (2005) Obtaining the magnetic characteristics of an 8/6 switched reluctance machine : from FEM analysis to the experimental tests. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 52(6):1635–1643
Labiod L, Bahri M, Srairi K, Mahdad B, Benchouia MT, Benbouzid MEH (2014) Static and dynamic analysis of non-linear magnetic characteristics in switched reluctance motors based on circuit-coupled time stepping finite element method. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-014-0294-6,Sept
Costa Branco PJ (2007) Influence of magnetic nonlinearities on simulation accuracy of switched reluctance motor models IEEE power engineering society general meeting. pp.1 7
Ghousia SF, Kar N (2007) Performance analysis of an 8/6 switched reluctance machine using finite-element method. IEEE power engineering society general meeting
Jebarani ES, Suresh Kumar KS, Jayakumar J (2016) Torque modeling of switchedreluctance motor using LSSVM-DE. COMPEL Int J Comput Math Electr Electron Eng Neurocomput 211(26):117–128
Castro De MR, Robert B, Goeldel C (2008) Bifurcations and chaotic dynamics in a linear switched reluctance motor. In IEEE 2008 13th international power electronics and motion control conference, Poznan Poland. Doi: 10.1109/EPEPEMC.2008.4635581
De Castro MR, Robert B, Goeldel C (2009) Strange attractor and fractal dimension in a linear switched reluctance motor. In: 2009 6th international multi-conference on systems, signals and devices, SSD 2009, Djerba, Tunisia
Pera MC, Robert B, Goeldel C (1999) Quasiperiodicity and chaos in a step motor. Proceedings of the 8th EPE conference, Lausanne, Suisse
Pera MC, Robert B, Goeldel C (2000) Nonlinear dynamics in electromechanical systems-application to a hybrid stepping motor. Electromotion 7:31–42
Reiss J, Alin F, Sandler M, Robert B (2002) A detailed analysis of the nonlinear dynamics of the electric step motor. In: IEEE 2002 IEEE international conference on industrial technology, 2002. IEEE ICIT '02., Bangkok, Thaïland. DOI: 10.1109/ICIT.2002.1189321
Robert B, Alin F, Goeldel C (2001) Aperiodic and chaotic dynamics in hybrid step motor—new experimental results. In: IEEEISIE 2001. IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics proceedings (Cat. No.01TH8570), Pusan, South Korea, pp. 2136–2141. DOI: 10.1109/ISIE.2001.932047
Ujera Sudha R, Ragavi V, Chandrasegar T (2017) Analyzing correlation coefficient using software metrics. IEEE international conference on trends in electronics and informatics (ICEI). DOI: 10.1109/ICOEI.2017.8300894
Zhong L (2002) Bifurcations and chaos in a permanent-magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans Circ Syst 49(3):383–387. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-est.2017.0090
Asakura T (2000) Chaos detection in velocity control of induction motor and its control by using neural network. In: IEEEWCC 2000—ICSP 2000. 2000 5th international conference on signal processing proceedings. 16th World computer congress 2000, Beijing, China, pp.1633–1638. DOI: 10.1109/ICOSP.2000.893414
Gao Y, Chau KT (2003) Design of permanent magnets to avoid chaos in PM synchronous machines. IEEE Trans Magn 39(5):2995–2997
Gourragui I, Léonard F, Vivalda JC, Abba G (2006) Rotor shape design of switched reluctance motor. XVII international conference on electrical machines, Chania, Crete Island, Greece
Labiod C, Bahri M, Srairi K, Mahdad B, Benchouia MT, Benbouzid MEH (2015) Speed control of 8/6 switched reluctance motor with torque ripple reduction taking into account magnetic saturation effects. Energy Procedia 74:112–121
Asgar M, Afjei E (2009) A new class of resonant discharge drive topology for switched reluctance motor. Iran J Electr Electron Eng 5(4):261–269
Xu A-D, Zhao X, He K, Cao Y (2018) Torque-ripple reduction of SRM using optimized voltage vector in DTC. IET Electr Syst Transp 8(1):35–43
Gottwald GA, Melbourne I (2004) A new test for chaos in deterministic systems. Proc R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 460(2042):603–611
Gottwald GA, Melbourne I (2009) On the Implementation of the 0–1 Test for Chaos. SIAM J Appl Dyn Syst 8(1):129–145
Armand Eyebe Fouda JS, Samrat Sabat L, Yves Effa J (2013) A modified 0–1 test for chaos detection in oversampled time series observations. Int J Bifurc Chaos. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127414500631
Zhang H, Baoquan K, Yaru Q, Yinxi J, Hailin Z (2014) Research on a switched reluctance motor with auxiliary rotor teeth. In: 7th international conference on electrical machines and systems (ICEMS), Oct. 22–25, 2014, Hangzhou, China
Antoine JF, Sauvey C, Visa C, Abba G (2003) Optimisation de la forme d'un rotor de MRV 6/2 pour I'UGV. In: Electrotechnique du futur, EF'03 (Supelec, Ed.). pp. 24, 1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guidkaya, G., Fankem, E.D.K. & Effa, J.Y. A New Rotor Shape Design of 6/2 Switched Reluctance Motor: Comparative Analysis of its Chaotic Behavior with Other Structures. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 16, 309–320 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-020-00574-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-020-00574-8