Abstract
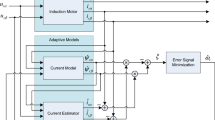
In this paper we present a new improved sensorless vector control of induction motor based on an improved adaptive Luenberger observer. The proposed observer is designed to estimate both speed and motor parameters from measured stator currents, stator voltages and estimated rotor fluxes. The proposed sensorless drive has for purpose to compensate at the same time both stator resistance and rotor time constant inverse variation, which change during operation. Indeed, in the proposed adaptive Luenberger observer, a Fuzzy Logic Controller will be adopted as an adaptation mechanism. The proposed observer stability is proved by the Lyapunov’s theorem and its feasibility is verified by series of experimental tests. The relevant results and the effectiveness of the improved system are clearly shown through obtained experimental results with an induction motor of 1 kW driven by dSPACE system.






























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelwanis MI, El-Sehiemy RA (2019) A fuzzy-based controller of a modified six-phase induction motor driving a pumping system. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Electr Eng 43:153–165
Agrebi Zorgani Y, Koubaa Y, Boussak M (2016) MRAS state estimator for speed sensorless ISFOC induction motor drives with Luenberger load torque estimation. ISA Trans 61:308–317
Alonge F, Cangemi T, D’Ippolito F, Fagiolini A, Sferlazza A (2015) Convergence analysis of extended kalman filter for sensorless control of induction motor. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62:2341–2352
Ameid T, Menacer A, Talhaoui H, Harzellia I (2017) Rotor resistance estimation using Extended Kalman filter and spectral analysis for rotor bar fault diagnosis of sensorless vector control induction motor. Measurement 111:243–259
Banarezaei S, Shalchian M (2019) Design of a model-based fuzzy-pid controller with self-tuning scalingfactor for idle speed control of automotive engine. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Electr Eng 43:13–31
Cirrincione M, Pucci M, Vitale G (2012) Power converters and AC electrical drives with linear neural networks. CRC Press, Florida, pp 531–603
Cirrincione M, Accetta A, Pucci M, Vitale G (2013) MRAS speed observer for high-performance linear induction motor drives based on linear neural networks. IEEE Trans Power Electr 28:123–134
Derdiyok A, Güven MK, Rehman H, Inanc N, Xu L (2002) Design and implementation of a new sliding-mode observer for speed-sensorless control of induction machine. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 49:1177–1182
Gacho J, Žalman M (2010) IM based speed servodrive with luenberger observer. J Electr Eng 61:149–156
Gadoue SM, Giaouris D, Finch J (2010) MRAS sensorless vector control of an induction motor using new sliding-mode and fuzzy-logic adaptation mechanisms. IEEE Trans Energy Conver 25:394–402
Habibullah M, Lu DDC (2015) A speed-sensorless FS-PTC of Induction motors using extended kalman filters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62:6765–6778
Hadj Saïd S, Mimouni M, M’Sahli F, Farza M (2011) High gain observer based on-line rotor and stator resistances estimation for IMs. Simul Model Pract Th 19:1518–1529
Hazzab A, Bousserhane IK, Zerbo M, Sicard P (2006) Real time implementation of fuzzy gain scheduling of pi controller for induction motor machine control. Neural Process Lett 24:203–215
Hinkkanen M, Leppanen VM, Luomi J (2005) Flux observer enhanced with low-frequency signal injection allowing sensorless zero-frequency operation of induction motors. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 41:52–59
Inanc N (2007) A robust sliding mode flux and speed observer for speed sensorless control of an indirect field oriented induction motor drives. Electr Pow Syst Res 77:1681–1688
Jouili M, Agrebi Y, Koubaa Y, Boussak M (2015) A Luenberger state observer for simultaneous estimation of speed and stator resistance in sensorless IRFOC induction motor drives. In: IEEE 16th international conference on sciences and techniques of automatic control and computer engineering (STA), pp 898–904. https://doi.org/10.1109/STA.2015.7505225
Jouili M, Jarray K, Koubaa Y, Boussak M (2012) Luenberger state observer for speed sensorless ISFOC induction motor drives. Electr Pow Syst Res 89:139–147
Kubota H, Matsuse K, Nakmo T (1993) DSP-based speed adaptive flux observer of induction motor. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 29:344–348
Kubota H, Matsuse K (1994) Speed sensorless field-oriented control of induction motor with rotor resistance adaptation. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 30:1219–1224
Lokriti A, Salhi I, Doubabi S, Zidani Y (2013) Induction motor speed drive improvement using fuzzy IP-self-tuning controller. A real time implementation. ISA Trans 52:406–417
Luenberger DG (1971) An introduction to observers. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 16:596–602
Maes J, Melkebeek JA (2000) Speed-sensorless direct torque control of induction motors using an adaptive flux observer. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 36:778–785
Maiti S, Verma V, Chakraborty C, Hori Y (2012) An adaptive speed sensorless induction motor drive with artificial neural network for stability enhancement. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 8:757–766
Pacas Mario (2011) Sensorless drives in industrial applications”. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 5(2):16–23
Zaky MS, Metwaly MK, Azazi HZ, Deraz SA (2018) A new adaptive SMO for speed estimation of sensorless induction motor drives at zero and very low frequencies. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(9):6901–6911
Mohand Ouhrouche, Rachid Errouissi, Andrzej M. Trzynadlowski, Kambiz Arab Tehrani, Ammar Benzaioua (2016) A Novel Predictive Direct Torque Controller for Induction Motor Drives" IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, Vol : 63, Issue: 8
Moutchou M, Abbou A, Mahmoudi H (2015) MRAS-based sensorless speed backstepping control for induction machine, using a flux sliding mode observer. Turk J Electr Eng Co 23:187–200
Mihai C (2016) Design and implementation of a highly robust sensorless sliding mode observer for the flux magnitude of the induction motor. IEEE Trans Energy Conv 31(2):649–657
Naik NV, Panda A, Singh SP (2016) A three-level fuzzy-2 DTC of induction motor drive using SVPWM. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(3):1467–1479
Qu Z, Hinkkanen M, Harnefors L (2014) Gain scheduling of a full-order observer for sensorless induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 50:3834–3845
Rafa S, Larabi A, Barazane L, Manceur M, Essounbouli N, Hamzaoui A (2014) Implementation of a new fuzzy vector control of induction motor. ISA Trans 53:744–754
Ramesh T, Panda AK, Shiva Kumar S (2015) Type-2 fuzzy logic control based MRAS speed estimator for speed sensorless direct torque and flux control of an induction motor drive. ISA Trans 57:262–275
Rayyam M, Zazi M, Barradi Y (2018) A new metaheuristic unscented Kalman filter for state vector estimation of the induction motor based on Ant Lion optimizer. COMPEL Int J Comput Math Electr Electron Eng 37:1054–1068
Samadi M, Rakhtala SM (2019) Reducing cost and size in photovoltaic systems using three-level boost converter based on fuzzy logic controller. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Electr Eng 43:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40998-018-0145-6
Smith AN, Gadoue SM, Finch JW (2016) Improved rotor flux estimation at low speeds for torque mras-based sensorless induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Energy Conver 31:270–282
Vasić V, Vukosavic S, Levi E (2003) A stator resistance estimation scheme for speed sensorless rotor flux oriented induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Energy Conver 18:476–483
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 28:338–353
Zbede YB, Gadoue SM, Atkinson DJ (2016) Model Predictive MRAS Estimator for Sensorless Induction Motor Drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63:3511–3521
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boulghasoul, Z., Kandoussi, Z., Elbacha, A. et al. Fuzzy Improvement on Luenberger Observer Based Induction Motor Parameters Estimation for High Performances Sensorless Drive. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 15, 2179–2197 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-020-00495-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-020-00495-6