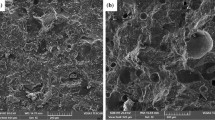
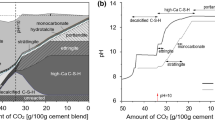
Abstract
The concrete industry confronts a pressing global challenge of resource depletion and a significant environmental impact linked to greenhouse gas emissions and water usage. Despite numerous studies on using waste materials as a partial cement substitute for concrete production, an efficient and sustainable conversion mechanism has not yet been investigated. This work studies the sugarcane bagasse ash synthesized from microwave pyrolysis (M-SCBA) and the cogeneration system (C-SCBA) as cement replacement materials and their effect on the concrete’s mechanical and permeability properties. The 10% C-SCBA concrete reached the highest compressive strength, achieving 11% higher performance than the Control sample. Partial replacement with 10% of M-SCBA in cement mortar produced a 14% higher relative strength index than the ashes generated by the cogeneration system (10% C-SCBA). Significant changes were observed in the concrete’s resistance to chloride-ion penetration when the cement was replaced by 30% M-SCBA, achieving 23% higher chloride ion resistance than the conventional cement concrete.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Agrela F, Alaejos P, Thomas C, Rueda J, Silva RV, Moreno-Juez J, Sanjuán MA, de Brito J, Sánchez de Rojas MI (2021) 26 — Normative review and necessary advances to promote the use of recycled aggregates and by-products in cement-based materials. In: de Brito J, Thomas C, Medina C, Agrela F (eds) Waste and Byproducts in Cement-Based Materials. Woodhead Publishing, pp 735–776.https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820549-5.00001-2
Allende S, Brodie G, Jacob MV (2022) Energy recovery from sugarcane bagasse under varying microwave-assisted pyrolysis conditions. Bioresource Technol Rep 20:101283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2022.101283
Allende S, Brodie G, Jacob MV (2023a) Breakdown of biomass for energy applications using microwave pyrolysis: a technological review. Environ Res 226:115619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115619
Allende S, Brodie G, Jacob MV (2023b) Energy recovery from pumpkin peel using microwave-assisted pyrolysis. Energies 16(18):6438
Barisso T (2021) Application of biochar as beneficial additive in concrete (master's Thesis). University of Nebraska-Lincoln
Brickler CA, Wu YD, Li SM, Anandhi A, Chen G (2021) Comparing physicochemical properties and sorption behaviors of pyrolysis-derived and microwave-mediated biochar. Sustain-Basel 13(4) 2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13042359
Bun P, Cyr M, Laniesse P, Bun KN, Idir R (2022) Concrete made of 100% recycled materials — feasibility study. Resour Conserv Recycl 180:106199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106199
Chen H-J, Shih N-H, Wu C-H, Lin S-K (2019) Effects of the loss on ignition of fly ash on the properties of high-volume fly ash concrete. Sustain-Basel 11(9):2704
Chen H, Chow CL, Laua D (2022) Developing green and sustainable concrete in integrating with different urban wastes. J Clean Prod 368:133057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133057
Choi S, Pyo S (2020) Fresh and hardened properties of Portland cement-slag concrete activated using the by-product of the liquid crystal display manufacturing process. Materials 13(19):4354
Chu H-y, Jiang J-y, Sun W, Zhang M (2017) Effects of graphene sulfonate nanosheets on mechanical and thermal properties of sacrificial concrete during high temperature exposure. Cem Concr Compos 82:252–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2017.06.007
Dixit A, Gupta S, Pang SD, Kua HW (2019) Waste valorisation using biochar for cement replacement and internal curing in ultra-high performance concrete. J Clean Prod 238:117876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117876
Fodah AEM, Ghosal MK, Behera D (2022) Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of agricultural residues: current scenario, challenges, and future direction. Int J Environ Sci Technol 19(3):2195–2220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03099-9
Foong SY, Liew RK, Yek PNY, Lam SS (2020) Production of biochar for potential catalytic and energy applications via microwave vacuum pyrolysis conversion of cassava stem. Mater Sci Energy Technol 3:728–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2020.08.002
Gautam R, Shyam S, Reddy BR, Govindaraju K, Vinu R (2019) Microwave-assisted pyrolysis and analytical fast pyrolysis of macroalgae: product analysis and effect of heating mechanism. Sustain Energy Fuel 3(11):3009–3020. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SE00162J
Grafmüller J, Böhm A, Zhuang Y, Spahr S, Müller P, Otto TN, Bucheli TD, Leifeld J, Giger R, Tobler M, Schmidt H-P, Dahmen N, Hagemann N (2022) Wood Ash as an Additive in Biomass Pyrolysis: Effects on Biochar Yield, Properties, and Agricultural Performance. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 10 (8):2720–2729. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c07694
Gupta S, Kua HW, Pang SD (2018) Biochar-mortar composite: manufacturing, evaluation of physical properties and economic viability. Constr Build Mater 167:874–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.02.104
Gupta S, Krishnan P, Kashani A, Kua HW (2020a) Application of biochar from coconut and wood waste to reduce shrinkage and improve physical properties of silica fume-cement mortar. Constr Build Mater 262:120688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120688
Gupta S, Kua HW, Pang SD (2020b) Effect of biochar on mechanical and permeability properties of concrete exposed to elevated temperature. Constr Build Mater 234:117338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117338
Hadiya V, Popat K, Vyas S, Varjani S, Vithanage M, Kumar Gupta V, Núñez Delgado A, Zhou Y, Loke Show P, Bilal M, Zhang Z, Sillanpää M, Sabyasachi Mohanty S, Patel Z (2022) Biochar production with amelioration of microwave-assisted pyrolysis: current scenario, drawbacks and perspectives. Bioresource Technol 355:127303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127303
Hamada HM, Jokhio GA, Yahaya FM, Humada AM, Gul Y (2018) The present state of the use of palm oil fuel ash (POFA) in concrete. Constr Build Mater 175:26–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.227
Haque MI, Khan RI, Ashraf W, Pendse H (2021) Production of sustainable, low-permeable and self-sensing cementitious composites using biochar. Sustain Mater Technol 28:e00279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2021.e00279
Ippolito JA, Cui L, Kammann C, Wrage-Mönnig N, Estavillo JM, Fuertes-Mendizabal T, Cayuela ML, Sigua G, Novak J, Spokas K, Borchard N (2020) Feedstock choice, pyrolysis temperature and type influence biochar characteristics: a comprehensive meta-data analysis review. Biochar 2(4):421–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-020-00067-x
Jittin V, Minnu SN, Bahurudeen A (2021) Potential of sugarcane bagasse ash as supplementary cementitious material and comparison with currently used rice husk ash. Construc Build Mater 273:121679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121679
Kathirvel P, Anik GA, Kaliyaperumal SRM (2019) Effect of partial replacement of cement with Prosopis juliflora ash on the strength and microstructural characteristics of cement concrete. Construct Build Mater 225:273–282
Kazmi SMS, Munir MJ, Wu Y-F (2021) Application of waste tire rubber and recycled aggregates in concrete products: a new compression casting approach. Resour Conserv Recycl 167:105353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105353
Khalid A, Khushnood RA, Ali Memon S (2022) Pyrolysis as an alternate to open burning of crop residue and scrap tires: greenhouse emissions assessment and mechanical performance investigation in concrete. J Clean Prod 365:132688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132688
Kim T, Olek J (2012) Effects of sample preparation and interpretation of thermogravimetric curves on calcium hydroxide in hydrated pastes and mortars. Trans Res Rec 2290(1):10–18. https://doi.org/10.3141/2290-02
Lam SS, Wan Mahari WA, Ok YS, Peng W, Chong CT, Ma NL, Chase HA, Liew Z, Yusup S, Kwon EE, Tsang DCW (2019) Microwave vacuum pyrolysis of waste plastic and used cooking oil for simultaneous waste reduction and sustainable energy conversion: recovery of cleaner liquid fuel and techno-economic analysis. Renew Sustain Energ Rev 115:109359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109359
Leng L, Xiong Q, Yang L, Li H, Zhou Y, Zhang W, Jiang S, Li H, Huang H (2021) An overview on engineering the surface area and porosity of biochar. Sci Total Environ 763(144204):144204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144204
Li X, Peng B, Liu Q, Zhang H (2022) Microwave pyrolysis coupled with conventional pre-pyrolysis of the stalk for syngas and biochar. Bioresour Technol 348:126745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126745
Mensah RA, Shanmugam V, Narayanan S, Razavi SMJ, Ulfberg A, Blanksvärd T, Sayahi F, Simonsson P, Reinke B, Försth M, Sas G, Sas D, Das O (2021) Biochar-added cementitious materials—a review on mechanical, thermal, and environmental properties. Sustainability 13(16):9336
Miller SA, Cunningham PR, Harvey JT (2019) Rice-based ash in concrete: a review of past work and potentialenvironmental sustainability. Resourc Conserv Recycl 146:416–430
Mo L, Fang J, Huang B, Wang A, Deng M (2019) Combined effects of biochar and MgO expansive additive on the autogenous shrinkage, internal relative humidity and compressive strength of cement pastes. Construct Build Mater 229:116877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116877
Mullane J (2022) Average electricity costs per kWh. Canstar Blu. https://www.canstarblue.com.au/electricity/electricity-costs-kwh/
Narasimha Reddy P, Ahmed Naqash J (2019) Experimental study on TGA, XRD and SEM analysis of concrete with ultra-fine slag (technical note). Int J Eng 32(5):679–684
Nguyen H, Moghadam MJ, Moayedi H (2019) Agricultural wastes preparation, management, and applications in civil engineering: a review. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:1039–1051
Nhuchhen DR, Afzal MT, Dreise T, Salema AA (2018) Characteristics of biochar and bio-oil produced from wood pellets pyrolysis using a bench scale fixed bed, microwave reactor. Biomass Bioenerg 119:293–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.09.035
Rerkpiboon A, Tangchirapat W, Jaturapitakkul C (2015) Strength, chloride resistance, and expansion of concretes containing ground bagasse ash. Construct Build Mater 101:983–989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.10.140
Reed EY, Chadwick DR, Hill PW, Jones DL (2017) Critical comparison of the impact of biochar and wood ash on soil organic matter cycling and grassland productivity. Soil Biol Biochem 110:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.03.012
Sasanipour H, Aslani F, Taherinezhad J (2021) Chloride ion permeability improvement of recycled aggregate concrete using pretreated recycled aggregates by silica fume slurry. Construct Build Mater 270:121498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121498
Tait MW, Cheung WM (2016) A comparative cradle-to-gate life cycle assessment of three concrete mix designs. Int J Life Cycle Assess 21(6):847–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-016-1045-5
Tantawy MA (2017) Effect of high temperatures on the microstructure of cement paste. J Mater Sci Chem Eng 5:33–48. https://doi.org/10.4236/msce.2017.511004
Tchamo Leussa CC, Libessart L, Djelal C, NjiomouDjangang C, Elimbi A (2020) Pozzolanic activity of kaolins containing aluminum hydroxide. Sci Rep 10(1):13230. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70146-3
Teixeira ER, Camões A, Branco FG, Aguiar JB, Fangueiro R (2019) Recycling of biomass and coal fly ash as cement replacement materialand its effect on hydration and carbonation of concrete. Waste Manag 94:39–48
Tomczyk A, Sokolowska Z, Boguta P (2020) Biochar physicochemical properties: pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev Environ Sci Bio 19(1):191–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09523-3
Torres de Sande V, Sadique M, Bras A, Pineda P (2022) Activated sugarcane bagasse ash as efficient admixture in cement-based mortars: mechanical and durability improvements. J Build Eng 59:105082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2022.105082
Toscano Miranda N, Lopes Motta I, Maciel Filho R, Wolf Maciel MR (2021) Sugarcane bagasse pyrolysis: a review of operating conditions and products properties. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 149:111394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111394
Wang W, Wang M, Huang J, Li X, Cai L, Shi SQ, Cui Y, Chen L, Ni Y (2020) High efficiency pyrolysis of used cigarette filters for ester-rich bio-oil through microwave-assisted heating. J Clean Prod 257:120596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120596
Wang X, Li C, Chen M, Wang J (2021) Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of seaweed biomass for aromatics-containing bio-oil production. E3S Web Conf 261:02045
Waqasa M, Aburiazaiza AS, Minadad R, Rehan M, Barakat MA, Nizami AS (2018) Development of biochar as fuel and catalyst in energy recovery technologies. J Clean Prod 188:477–488
Wijitkosum S, Jiwnok P (2019) Elemental composition of biochar obtained from agricultural waste for soil amendment and carbon sequestration. Appl Sci 9(19):3980
Yang X, Wang X-Y (2021) Hydration-strength-durability-workability of biochar-cement binary blends. J Build Eng 42:103064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103064
Zhang Y, Zhou C, Deng Z, Li X, Liu Y, Qu J, Li X, Wang L, Dai J, Fu J, Zhang C, Yu M, Yu H (2022) Influence of corn straw on distribution and migration of nitrogen and heavy metals during microwave-assisted pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge. Sci Total Environ 815:152303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152303
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Paul Trayner, Wilmar Sugar Townsville, Australia for supplying the sugarcane bagasse. The authors acknowledge the support of Kalvin Wurzinger, Liam H. Dent, and Dyllan James Abood for preparing the concrete samples and obtaining some of the experimental data presented in this work.
Funding
S. Allende received James Cook University Postgraduate Research Scholarship and Cooperative Research Centre for Developing Northern Australia top-up scholarship (Australian Government’s Cooperative Research Centre Program, CRCP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. A. performed the methodology, formal analysis, writing of original draft, and visualization. R. T. completed the data validation, writing — review and editing, and supervision. M. V. J. was a major contributor in the conceptualization, writing — review and editing, supervision, and project administration. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Allende, S., Tuladhar, R. & Jacob, M.V. Sugarcane Bagasse-Derived Carbon for Partial Replacement of Cementitious Material in Concrete. Mater Circ Econ 6, 3 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42824-023-00096-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42824-023-00096-4