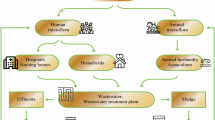
Abstract
The present study was designed to identify different bacterial pathogens in hospital wastewater samples and to determine their antibiotic resistant pattern against commonly used antibiotics. A total of 200 hospital wastewater samples were collected and analyzed accordingly. Of the 200 samples, only 60 yielded confirmed bacterial growth, while the remaining 140 samples showed negative results. Among 60 positive samples, a total of 7 different bacterial pathogens were isolated that included Staphylococcus aureus 16 (26.66%), Escherichia coli 14 (23.33%), P. aeruginosa 10 (16.66%), S. epidermidis 8 (13.33%), Enterobacter spp 7 (11.66%), S. pyogene 3 (5%) and Shigella 2 (3.33%). The antibiotic resistance pattern was checked by disc diffusion assay. All pathogens showed prominent susceptibility to Vancomycin, Cefixime, Tazobactam, and Doxycyline followed by other antibiotics, while pathogens showed noticeable resistance against Gentamycin, Amoxicillin, Tazobactam, and Tetracycline followed by other commonly used antibiotics. However, the S. pyogenes was the only pathogen that showed 100% resistance to Gentamycin, Tetracycline and levofloxacin, followed by Shigella which showed 100% resistance to Gentamycin and Tetracycline each. In particular, S. aureus was the most common pathogen isolated among other pathogens. The antibiotics to which bacterial pathogens showed high resistance were Gentamycin, Tetracycline, and Levofloxacin followed by other used antibiotics, while antibiotics of choice to which pathogens were prominently susceptible were Vancomycin, Cefixime, Tazobactam, and Doxycycline followed other used antibiotics. Hence, it was revealed from the present study that hospital wastewater communities are highly burdened by these antibiotic resistant bacteria and these are continuously disseminating to the outer environment which could pose an alarming situation to public health. Therefore, proper management protocols should need to be adopted to reduce the risk of exposure to such pathogens.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Khawaja T, Kirveskari J, Johansson S, Väisänen J, Djupsjöbacka A, Nevalainen A, Kantele A (2017) Patients hospitalized abroad as importers of multiresistant bacteria—a cross-sectional study. Clin Microbiol Infect 23(9):673-e1
Abdel-Raouf N, Al-Homaidan AA, Ibraheem IBM (2012) Microalgae and wastewater treatment. Saudi J Biol Sci 19(3):257–275
Amine AEK (2013) Extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing bacteria in waste water alexandria, Egypt. Int J Biosci Biochem Bioinformat 3(6):605
Ikram A, Hussain Shah SI, Naseem S, Absar SF, Ullah S, Ambreen T (2010) Status of hospital infection control measures at seven major tertiary care hospitals of northern Punjab. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 20(4):266–70
Khan HA, Baig FK, Mehboob R (2017) Nosocomial infections: epidemiology, prevention, control and surveillance. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 7(5):478–482
Beyene H, Redaie G (2011) Assessment of waste stabilization ponds for the treatment of hospital wastewater: the case of Hawassa university referral hospital. World Appl Sci J 15(1):142–150
Stalder T, Barraud O, Jové T, Casellas M, Gaschet M, Dagot C, Ploy MC (2014) Quantitative and qualitative impact of hospital effluent on dissemination of the integron pool. ISME J 8(4):768–777
Keen PL, Patrick DM (2013) Tracking change: a look at the ecological footprint of antibiotics and antimicrobial resistance. Antibiotics 2(2):191–205
Nunez L, Moretton J (2007) Disinfectant-resistant bacteria in Buenos Aires city hospital wastewater. Braz J Microbiol 38:644–648
Pandey A, Afsheen AF, Tiwari SK (2011) Isolation and characterization of multi drug resistance cultures from waste water. J Pharm Biomed Sci 13(7)
Diwan V, Tamhankar AJ, Khandal RK, Sen S, Aggarwal M, Marothi Y, Stålsby-Lundborg C (2010) Antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant bacteria in waters associated with a hospital in Ujjain, India. BMC Public Health 10(1):1–8
Anitha J, Jayraaj IA (2012) Isolation and identification of bacteria in biomedical wastes (BMW). Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4(5):386–388
Makky EA, Ibrahim MM, El-Gamal MS (2013) Presence of antibiotic resistant bacteria along the pharmaceuticals production line. Procedia Eng 53:715–721
Osthoff M, McGuinness SL, Wagen AZ, Eisen DP (2015) Urinary tract infections due to extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Gram-negative bacteria: identification of risk factors and outcome predictors in an Australian tertiary referral hospital. Int J Infect Dis 34:79–83
Ilyas H, Ilyas S, Ahmad SR, Nawaz MCH (2017) Waste generation rate and composition analysis of solid waste in Gujranwala City Pakistan. Int J Waste Resour 7(3):97
Crawford MA, Timme R, Lomonaco S, Lascols C, Fisher DJ, Sharma SK, Hughes MA (2016) Genome sequences of multidrug-resistant, colistin-susceptible and-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates from Pakistan. Genome Announc 4(6):e01419-16
Sharma P, Mathur N, Singh A, Sogani M, Bhatnagar P, Atri R, Pareek S (2015) Monitoring hospital wastewaters for their probable genotoxicity and mutagenicity. Environ Monit Assess 187(1):1–9
Sethi S, Sharma D, Mehta SD, Singh B, Smriti M, Kumar B, Sharma M (2006) Emergence of ciprofloxacin resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae in north India. Indian J Med Res 123(5):707–10
Delgado DYC, Barrigas ZPT, Astutillo SGO, Jaramillo APA, Ausili A (2016) Detection and molecular characterization of β-lactamase genes in clinical isolates of Gram-negative bacteria in Southern Ecuador. Braz J Infect Dis 20(6):627–630
Cheesbrough, M. (2006). District laboratory practice in tropical countries, part 2. Cambridge university press
CLSI, E. (2011). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; seventeenth informational supplement CLSI document M100-S17. Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087–1898 USA, 2007.
Asfaw T, Negash L, Kahsay A, Weldu Y (2017) Antibiotic resistant bacteria from treated and untreated hospital wastewater at Ayder Referral Hospital, Mekelle, North Ethiopia. Adv Microbiol 7(12):871–886
Danchaivijitr S, Wongchanapai W, Assanasen S, Jintanothaitavorn D (2005) Microbial and heavy metal contamination of treated hospital wastewater in Thailand. J Med Assoc Thai 88(10):S59-64
Fekadu S, Merid Y, Beyene H, Teshome W, Gebre-Selassie S (2015) Assessment of antibiotic-and disinfectant-resistant bacteria in hospital wastewater, south Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. J Infect Dev Ctries 9(02):149–156
Chitnis V, Chitnis D, Patil S (2000) Hospital effluent: a source of multiple drug-resistant bacteria. Curr Sci 989–991
Salem IB, Ouardani I, Hassine M, Aouni M (2011) Bacteriological and physico-chemical assessment of wastewater in different region of Tunisia: impact on human health. BMC Res Notes 4(1):1–11
Adieze IE, Nnadi C, Braide W, Azubuike C, Nduka I (2015) Antibiotic resistance pattern of bacterial isolates of liquid wastes and waste dump soils of hospitals in Owerri, Nigeria. Nigerian J Microbiol 29:3002–3011
Katouli M, Thompson JM, Gündoğdu A, Stratton HM (2012) Antibiotic resistant bacteria in hospital wastewaters and sewage treatment plants. In Sci Forum Stakeholder Engage 13:225–229
Iweriebor BC, Gaqavu S, Obi LC, Nwodo UU, Okoh AI (2015) Antibiotic susceptibilities of Enterococcus species isolated from hospital and domestic wastewater effluents in Alice, Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12(4):4231–4246
Blanch AR, Caplin JL, Iversen A, Kühn I, Manero A, Taylor HD, Vilanova X (2003) Comparison of enterococcal populations related to urban and hospital wastewater in various climatic and geographic European regions. J Appl Microbiol 94(6):994–1002
Servais P, Passerat J (2009) Antimicrobial resistance of fecal bacteria in waters of the Seine river watershed (France). Sci Total Environ 408(2):365–372
El-Lathy AM, El-Taweel GE, El-Sonosy MW, Samhan FA, Moussa TA (2009) Determination of pathogenic bacteria in wastewater using conventional and PCR techniques. Environmental Biotechnology 5:73–80
Quan PL, Sauzade M, Brouzes E (2018) dPCR: a technology review. Sensors 18(4):1271
Dhar BC, Lee NY (2018) Lab-on-a-chip technology for environmental monitoring of microorganisms. BioChip J 12(3):173–183
Efaq AN, Nagao H, NikNorulaini NA et al (2015) Survival of opportunistic fungi in clinical wastes. In 4th International Conference on Environmental Research and Technology (ICERT 2015) on 27–29
Okojokwu OJ, Inabo HI, Yakubu SE (2014) Parasitological profile of raw wastewater and the efficacy of biosand filter in reduction of parasite ova and cysts. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 18(1):5–9
Meo MI, Haydar S, Nadeem O, Hussain G, Rashid H (2014) Characterization of hospital wastewater, risk waste generation and management practices in Lahore. Proc Pakistan Acad Sci 51(4):317–9
Anwar O, Malik N, Asim M (2013) Evaluation of hospital waste management in public and private sector hospitals of Faisalabad City, Pakistan. Acad J Interdiscip Stud 2(2):161–161
Acknowledgements
We would like to thanks Sadia Qayyum (Department of Microbiology, Hazara University Mansehra, Pakistan) for his generous suggestion and help in revision of the final draft manuscript
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS helped in conceptualization, methodology, data processing and writing - original draft manuscript. IU, MAK and Matiullah helped in data collection. KA and TH performed formal analysis. AHM helped in writing, critical review, editing and submission of the draft manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final version of the draft manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahzad, A., Mian, A.H., Ul haq, I. et al. The Emergence of Different Bacterial Pathogens in Hospital Wastewater Samples and their Antibiotic Resistance Pattern. Mater Circ Econ 3, 28 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42824-021-00046-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42824-021-00046-y