Abstract
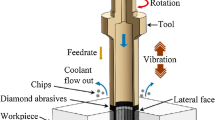
Carbon fiber and its composites are increasingly used in many fields including defence, military, and allied industries. Also, surface quality is given due importance, as mating parts are used in machineries for their functioning. In this work, the turning process is considered for Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) composites by varying three important cutting variables: cutting speed, feed, and depth of cut. Correspondingly, the surface roughness is measured after the completion of turning operation. As well, a prediction model is created using different fuzzy logic membership function and Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm (LMA) in artificial intelligence. Later, the surface roughness values from the developed models are compared against the experimental values for its correlation and effectiveness in using different membership functions of fuzzy logic and ANN. Thus, the experimental results are analyzed using the effect graphs and it is presented in detail.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li L, Sun L, Dai Z, Xiong Z, Huang B, Zhang Y (2019) Experimental investigation on mechanical properties and failure mechanisms of polymer composite-metal hybrid materials processed by direct injection-molding adhesion method. J Mater Process Tech 263:385–395
Singh AP, Sharma M, Singh I (2013) A review of modeling and control during drilling of fiber reinforced plastic composites. Composites B 47:118–125
Cenna AA, Mathew P (2002) Analysis and prediction of laser cutting parameters of fiber reinforced plastics (FRP) composite materials. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42:105–113
Krishnamoorthy A, Rajendra Boopathy S, Palanikumar K, Paulo Davim J (2012) Application of grey fuzzy logic for the optimization of drilling parameters for CFRP composites with multiple performance characteristics. Measurement 45:1286–1296
Wang Y, Thomas Hahn H (2007) AFM characterization of the interfacial properties of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites subjected to hygro thermal treatments. Compos Sci Technol 67:92–101
MeltemAltinKarataş HG (2018) A review on machinability of carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) and glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) composite materials. Defence Technol 14:318–326
Denis CD, R, Troulis M, Partridge I.K., (2006) Delamination of Z-pinned carbon fiber reinforced laminates. Compos Sci Technol 66:855–861
Santiuste C, Soldani X, Muguelez MH (2010) Machining FEM model of long fiber composites for aeronautical components. Compos Struct 92:691–698
Wan Aizan Wan Abdul Rahman (2008) Lee Tin Sin, Abdul Razak Rahmat, Injection moulding simulation analysis of natural fiber composite window frame. J Mater Process Technol 197:22–30
Hu NS, Zhang LC (2004) Some observations in grinding unidirectional carbon fiber-reinforced plastics. J Mater Process Technol 152:333–338
Rusinek R (2010) Cutting process of composite materials: an experimental study. Int J Non-Linear Mech 45:458–462
Palanikumar K (2011) Experimental investigation and optimisation in drilling of GFRP composites. Measurement 44:2138–2148
Palanikumar K, Rubio JC, Abrao AM, Correia AE, Davim JP (2008) Influence of drill point angle in high speed drilling of glass fiber reinforced plastics. J Compos Mater 42(24):2585–2597
Nalbant M, Gokkaya H, Toktas I, Sur G (2009) The experimental investigation of the effects of uncoated, PVD- and CVD- coated cemented carbide inserts and cutting parameters on surface roughness in CNC turning and its prediction using Artificial neural networks. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 25:211–223
Oktem H, Erzurumlu T, Kurtaran H (2005) Application of response surface methodology in the optimization of cutting conditions for surface roughness. J Mater Process Technol 170:11–16
Sarma PMMS, Karunamoorthy L, Palanikumar K (2008) Surface roughness parameters evaluation in machining GFRP composites by PCD tool using digital image processing. J Reinf Plast Compos 28(13):1567–1585
Everstine GC, Rogers TG (1971) A theory of machining of fiber-reinforced materials. J Composite Materials 5:94
Bhatnagar N, Naik NK, Ramakrishnan N (1993) Experimental investigations of drilling on CFRP composites. Mater Manuf Processes 8(6):683–701
Ahmad JS, Urban N, Cheraghi H (2012) Machining damage in edge trimming of CFRP. Mater Manuf Processes 27(7):802–808
Karkalos NE, Galanis NI, Markopoulos AP (2016) Surface roughness prediction for the milling of Ti–6Al–4V ELI alloy with the use of statistical and soft computing techniques. Measurement 90:25–35
Palanikumar K, Latha B, Senthilkumar VS, Davim JP (2013) Application of artificial neural network for the prediction of surface roughness in drilling GFRP composites. Mater Sci Forum 766:21–36
Rajasekaran T, Palanikumar K, Vinayagam BK (2011) Application of fuzzy logic for modeling surface roughness in turning CFRP using CBN tool. Prod Eng Res Devel 5:191–199
Rajasekaran T, Palanikumar K, Vinayagam BK (2011) Experimental investigation and analysis in turning of CFRP composites. J Compos Mater 46(7):809–821
Rajasekaran T, Palanikumar K, Vinayagam BK (2012) Turning CFRP composites with ceramic tool for surface roughness analysis. Procedia Eng 38:2922–2929
Sakuma K, Seto M (1983) Tool wear in cutting glass-fibre-reinforced-plastics (the relation between fibre orientation and tool wear). Bull JSME 26(2018):1420–1427
Bhatnagar N, Ramakrishnan NK, Komanduri R (1995) On the machining of fibre reinforced plastic (FRP) composite laminates. Int Jl Mach Tools Manufact 35(5):701–716
Palanikumar K, Mata F, Davim JP (2008) Analysis of surface roughness parameters in turning of FRP tubes by PCD tool. J Mater Process Technol 204:469–474
Tsao PL, Liu YG (2002) Study on PCD machining. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42:331–334
Yen J, Langari R (2006) Fuzzy Logic intelligence, Control, and Information. Ltd, New Delhi, Dorling Kindersley (India) Pvt
Latha B, Senthilkumar VS (2010) Application of artificial intelligence for the prediction of delamination in drilling GFRP composites. Int J Prec Technol 1(3/4):314–330
Kaviarasan V, Venkatesan R, Natarajan E (2019) Prediction of surface quality and optimization of process parameters in drilling of Delrin using neural network. Progr Rubber Plast Recycl Technol. 35(3):149–169. https://doi.org/10.1177/1477760619855078
Natarajan E, Kaviarasan V, Lim WH, TiangSSand Tan TT (2018) Enhanced multi-objective teaching-learning-based optimization for machining of Delrin. IEEE Access 6:51528–51546. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2869040
Natarajan E, Kaviarasan V, Lim WH, Tiang SS, Parasuraman S, Elango S (2020) Non-dominated sorting modified teaching learning -based optimization for multi-objective machining of polytetrafluoroethylene, (PTFE). J Intell Manuf 31:911–935
Latha B, Senthilkumar VS (2009) Analysis of thrust force in drilling glass fiber-reinforced plastic composites using fuzzy logic. Mater Manuf Processes 24(4):509–516
Jain AM, Haron H, Sharif S (2010) Prediction of surface roughness in the end milling machining using Artificial Neural Network. Expert Syst Appl 37:1755–1768
Davim JP, Mata F (2007) New machinability study of glass fiber reinforced plastics using polycrystalline diamond and cemented carbide (K15) tools. Mater Des 28:1050–1054
Ferreira JR, Coppini NL, Miranda GWA (1999) Machining optimization in carbon fiber reinforced composite materials. J Mater Process Technol 92–93:135–140
Palanikumar K, Paulo DJ (2007) Mathematical model to predict tool wear on the machining of glass fibre reinforced plastic composites. Mater Des 28:2008–2014
Santhanakrishnan G, Krishnamurthy R, Malhotra SK (1992) Investigation into the machining of carbon fibre reinforced plastics with cemented carbides. J Mater Process Technol 30:263–275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajasekaran, T., Palanikumar, K. & Latha, B. Investigation and analysis of surface roughness in machining carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites using artificial intelligence techniques. Carbon Lett. 32, 615–627 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-021-00298-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-021-00298-3