Abstract
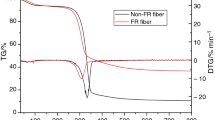
After flame-retardant treatment by the two different agents, the thermal behaviors of Lyocell fibers are discussed. In this research, H3PO4 and NaCl reduced the degradation rate and increased the char yield of the Lyocell fibers, and also increased the limiting oxygen index with the char yield increased. After treatment, the integral procedure decomposition temperature and the activation energy of Lyocell fibers are significantly increased by various concentration factors. These phenomena were indicated by the dehydration, rearrangement, formation of carbonyl groups, the evolution of carbon monoxide and dioxide, and carbonaceous residue formation. These effects were indicating the slow pathway of flame retardancy for the Lyocell fibers and are attributed to the two different flame-retardant agent treatments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim HG, Bai BC, In SJ, Lee YS (2016) Effects of an inorganic ammonium salt treatment on the flame-retardant performance of lyocell fibers. Carbon Lett 17(1):74–78
Lee JY, Kim JM, Cho DH, Park JK (2009) Fiber loading effect on the interlaminar mechanical and thermal properities of novel Lyocell, poly(butylene succinate) biocomposites. J Adhes Interf 10:106–112
Kim JG, Lee YS, In SJ (2018) Improved flame retardant performance of cellulose fibers following fluorine gas treatment. Carbon Lett 28:66–71
Loubinoux D, Chaunis S (1987) An experimental approach to spinning new cellulose fibers with N-methylmorpholine-oxide as a solvent. Text Res J 57:61–65
Woodings CR (1995) The development of advanced cellulosic fibers. Int J Biol Macromol 17:305–309
Peng S, Shao H, Hu X (2003) Lyocell fibers as the precursor of carbon fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 90:1941–1947
Cho C, Cho D, Park JK, Lee JY (2013) Effect of isothermal stabilization process and ultrasonic cleaning on the characteristics of rayon fabrics. Appl J Adhes Interface 14:21–27
Hall ME, Horrocks AR, Seddon H (1999) The flammability of Lyocell. Polym Degrad Stab 64:505–510
Kandola BK, Horrocks AR (1996) Complex char formation in flame-retarded fibre intumescent combinations-II. Thermal analytical studies. Polym Degrad Stab 54:289–303
Kandola BK, Horrocks AR, Price D, Coleman GV (1996) Flame-retardant treatments of cellulose and their influence on the mechanism of cellulose pyrolysis. Polym Rev 36:721–794
Wu QL, Gu SY, Gong JH, Pan D (2006) SEM/STM studies on the surface structure of a novel carbon fiber from Lyocell. Syn Met 156:792–795
Bai BC, Kim EA, Jeon YP, Lee CW, In SJ, Lee YS (2014) Improved flame-retardant properties of lyocell fiber achieved by phosphorus compound. Mater Lett 135(15):226–228
Price D, Horrocks AR, Akalin M, Faroq AA (1997) Influence of flame retardants on the mechanism of pyroysis of cotton (cellulose) fabrics in air. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 40–41:511–524
Jung JY, Lee YS (2018) Electrochemical properties of KOH-activated lyocell-based carbon fibers for EDLCs. Carbon Lett 27:112–116
Li H, Yang Y, Wen Y, Liu L (2007) A mechanism study on preparation of rayon based carbon fibers with (NH4)2SO4/NH4Cl/organosilicon composite catalyst system. Comp Sci Technol 67:2675–2682
Gronli MG, Varhegyi G, Di Blasi C (2002) Thermogravimetric analysis and devolatilization kinetics of wood. Ind Eng Chem Res 41:4201–4208
Nam S, Condon BD, Parikh DV, Zhao Q, Cintron MS, Madison C (2011) Effect of urea additive on the thermal decomposition of greige cotton nonwoven fabric treated with diammonium phosphate. Polym Deg Stab 96:2010–2018
Wang J, Xie H, Xin Z, Li Y, Chen L (2010) Enhancing thermal conductivity of palmitic acid based phase change materials with carbon nanotubes as fillers. Sol Energy 84:339–344
Hostler SR, Abramson AR, Gawryla MD, Bandi SA, Schiraldi DA (2009) Thermal conductivity of a clay-based aerogel. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:665–669
Guo B, Jia D, Cai C (2004) Effects of organo-montmorillonite dispersion on thermal stability of epoxy resin nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 40:1743–1748
Li XG (1999) High-resolution thermogravimetry of cellulose esters. J Appl Polym Sci 71(4):573–578
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP), funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE) of the Republic of Korea (20164010201070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H.G., Lee, YS. Effects of two different agents, H3PO4 and NaCl, to increase the flame-retardant properties of cellulose fibers. Carbon Lett. 29, 529–534 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-019-00087-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-019-00087-z