Abstract
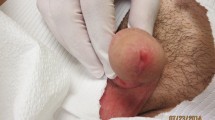
Sporotrichosis is a cosmopolitan subcutaneous mycosis caused by Sporothrix species. Recently, this mycosis has gained notoriety due to the appearance of new endemic areas, recognition of new pathogenic species, changes in epidemiology, occurrence of outbreaks, and increasing numbers of cases. The purpose of this study is to analyze the peculiarities of sporotrichosis cases in Brazil since its first report in the country until 2020. In this work, ecological, epidemiological, clinical, and laboratorial characteristics were compiled. A systematic review of human sporotrichosis diagnosed in Brazil and published up to December 2020 was performed on PubMed/MEDLINE, SciELO, Web of Science, and LILACS databases. Furthermore, animal sporotrichosis and environmental isolation of Sporothrix spp. in Brazil were also evaluated. The study included 230 papers, resulting in 10,400 human patients. Their ages ranged from 5 months to 92 years old and 55.98% were female. The lymphocutaneous form was predominant (56.14%), but systemic involvement was also notably reported (14.34%), especially in the lungs. Besides, hypersensitivity manifestations (4.55%) were described. Most patients had the diagnosis confirmed by isolation of Sporothrix spp., mainly from skin samples. Sporothrix brasiliensis was the major agent identified. HIV infection, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes were the most common comorbidities. Cure rate was 85.83%. Concerning animal sporotrichosis, 8538 cases were reported, mostly in cats (90.77%). Moreover, 13 Sporothrix spp. environmental strains were reported. This review highlights the burden of the emergent zoonotic sporotrichosis in Brazil, reinforcing the importance of “One Health” based actions to help controlling this disease.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are presented within the manuscript and/or its supplementary data.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Chakrabarti A, Bonifaz A, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, Mochizuki T, Li S (2015) Global epidemiology of sporotrichosis. Med Mycol 53:3–14
Marimon R, Cano J, Gene J, Sutton DA, Kawasaki M, Guarro J (2007) Sporothrix brasiliensis, S. globosa, and S. mexicana, three new Sporothrix species of clinical interest. J Clin Microbiol 45:3198–3206
Rodrigues AM, Cruz Choappa R, Fernandes GF, de Hoog GS, de Camargo ZP (2016) Sporothrix chilensis sp. nov. (Ascomycota: Ophiostomatales), a soil-borne agent of human sporotrichosis with mild-pathogenic potential to mammals. Fungal Biol 120:246–264
Rodrigues AM, Terra Della PP, Gremião ID, Pereira SA, Orofino-Costa R, de Camargo ZP (2020) The threat of emerging and re-emerging pathogenic Sporothrix species. Mycopathologia 185:813–842
Valeriano CAT, de Lima-Neto RG, Inácio CP, de Souza Rabello VB, Oliveira EP, Zancopé-Oliveira RM et al (2020) Is Sporothrix chilensis circulating outside Chile? PLoS Negl Trop Dis 14:e0008151
Dixon DM, Salkin IF, Duncan RA, Hurd NJ, Haines JH, Kemna ME et al (1991) Isolation and characterization of Sporothrix schenckii from clinical and environmental sources associated with the largest U.S. epidemic of sporotrichosis. J Clin Microbiol 29:1106–1113
McGuinness SL, Boyd R, Kidd S, McLeod C, Krause VL, Ralph AP (2015) Epidemiological investigation of an outbreak of cutaneous sporotrichosis, Northern Territory. Australia BMC Infect Dis 16:16
Gremião IDF, Miranda LHM, Reis EG, Rodrigues AM, Pereira AS (2017) Zoonotic epidemic of sporotrichosis: cat to human transmission. PLoS Pathogens 13(1):e100607
Gremião IDF, Oliveira MME, Monteiro de Miranda LH, Saraiva Freitas DF, Pereira AS (2020) Geographic expansion of sporotrichosis, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis 26:621–624
Rodrigues AM, de Melo Teixeira M, de Hoog GS, Schubach TMP, Pereira SA, Fernandes GF et al (2013) Phylogenetic analysis reveals a high prevalence of Sporothrix brasiliensis in feline sporotrichosis outbreaks. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 7:e2281
Singhai M, Rawat V, Verma P, Jha PK, Shree D, Goyal R et al (2012) Primary pulmonary sporotrichosis in a sub-Himalayan patient. J Lab Physicians 4:048–049
do Monte Alves M, Pipolo Milan E, da Silva Rocha WP, de Sena da Costa AS, Araújo Maciel B, Cavalcante Vale PH et al (2020) Fatal pulmonary sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis in northeast Brazil. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 14:e0008141
Zhang Y, Hagen F, Stielow B, Rodrigues AM, Samerpitak K, Zhou X et al (2015) Phylogeography and evolutionary patterns in Sporothrix spanning more than 14 000 human and animal case reports. Pers - Int Mycol J 35:1–20
Almeida-Paes R, de Oliveira LC, Oliveira MME, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, Nosanchuk JD (2015) Zancopé-Oliveira RM (2015) Phenotypic characteristics associated with virulence of clinical isolates from the Sporothrix complex rodrigo. Biomed Res Int 2:1–10
Freitas DF, Santos SS, Almeida-Paes R, de Oliveira MM, do Valle AC, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC et al (2015) Increase in virulence of Sporothrix brasiliensis over five years in a patient with chronic disseminated sporotrichosis. Virulence 6:112–120
Della Terra PP, Rodrigues AM, Fernandes GF, Nishikaku AS, Burger E, de Camargo ZP (2017) Exploring virulence and immunogenicity in the emerging pathogen Sporothrix brasiliensis. Xue C, editor. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 11:e0005903.
Cruz ILR, Freitas DFS, de Macedo PM, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, do Valle ACF, Almeida M de A, et al (2021) Evolution of virulence-related phenotypes of Sporothrix brasiliensis isolates from patients with chronic sporotrichosis and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Braz J Microbiol 52:5–18
Zancope-Oliveira RM, Almeida-Paes R, Oliveira MME, Freitas DF, Gutierrez Galhardo, Maria Clara (2011) New diagnostic applications in sporotrichosis. Skin Biopsy - Perspectives. InTech. p. 336.
Zancope-Oliveira RM, Almeida-Paes R, Ruiz-Baca E, Toriello C (2015) Diagnosis of sporotrichosis: current status and perspectives. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland
Orofino-Costa R, de Macedo PM, Rodrigues AM, Bernardes-Engemann AR (2017) Sporotrichosis: an update on epidemiology, etiopathogenesis, laboratory and clinical therapeutics. An Bras Dermatol 92:606–620
Gutierrez-Galhardo M, Barros M, Schubach A, Cuzzi T, Schubach T, Lazera M et al (2005) Erythema multiforme associated with sporotrichosis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venerol 19:507–509
Arinelli A, do Cuoto Aleixo ALQ, Freitas DFS, do Valle ACF, Almeida-Paes R, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC et al (2020) Ocular sporotrichosis: 26 cases with bulbar involvement in a hyperendemic area of zoonotic transmission. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 28:764–771
de Lima Barros MB, de Almeida Paes R, Schubach AO (2011) Sporothrix schenckii and sporotrichosis. Clinical Microbiology Review 24:633–654
Bernardes-Engemann AR, Costa RCO, Miguens BR, Penha CVL, Neves E, Pereira BAS et al (2005) Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the serodiagnosis of several clinical forms of sporotrichosis. Med Mycol 43:487–493
Almeida-Paes R, Pimenta MA, Pizzini CV, Monteiro PCF, Peralta JM, Nosanchuk JD et al (2007) Use of mycelial-phase Sporothrix schenckii exoantigens in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of sporotrichosis by antibody detection. CVI 14:244–249
Costa RO, de Macedo PM, Carvalhal A, Bernardes-Engemann AR (2013) Use of potassium iodide in dermatology: updates on an old drug. An Bras Dermatol 88:396–402
Bunce PE, Yang L, Chun S, Zhang SX, Trinkaus MA, Matukas LM (2012) Disseminated sporotrichosis in a patient with hairy cell leukemia treated with amphotericin B and posaconazole. Med Mycol 50:197–201
Paixão AG, Galhardo MCG, Almeida-Paes R, Nunes EP, Gonçalves MLC, Chequer GL et al (2015) The difficult management of disseminated Sporothrix brasiliensis in a patient with advanced AIDS. AIDS Res Ther 12:16
Ferreira CP, Galhardo MCG, Valle ACF (2011) Cryosurgery as adjuvant therapy in cutaneous sporotrichosis. Braz J Infect Dis 15:181–183
Costa RO, Bernardes-Engemann AR, Azulay-Abulafia L, Benvenuto F, de Lourdes PalermoNeves M, Lopes-Bezerra LM (2011) Sporotrichosis in pregnancy: case reports of 5 patients in a zoonotic epidemic in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. An Bras Dermatol 86:995–998
Fichman V, do Valle ACF, Freitas DFS, Sampaio FMS, Lyra MR, de Macedo PM et al (2019) Cryosurgery for the treatment of cutaneous sporotrichosis: experience with 199 cases. Br J Dermatol 180:1541–1542
García Duarte JM, Wattiez Acosta VR, Fornerón Viera PML, Aldama Caballero A, Gorostiaga Matiauda GA, Rivelli de Oddone VB et al (2017) Sporotrichosis transmitted by domestic cat. A family case report Rev Nac (Itauguá) 9:67–76
Córdoba S, Isla G, Szusz W, Vivot W, Hevia A, Davel G et al (2018) Molecular identification and susceptibility profile of Sporothrix schenckii sensu lato isolated in Argentina. Mycoses 61:441–448
Etchecopaz AN, Lanza N, Toscanini MA, Devoto TB, Pola SJ, Daneri GL et al (2020) Sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis in Argentina: case report, molecular identification and in vitro susceptibility pattern to antifungal drugs. Journal de Mycologie Médicale 30:100908
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097
Almeida F, Sampaio SAP, Lacaz C da S, Fernanades J de C (1955) Dados estatísticos sobre a Esporotricose. Aná1ise de 344 casos. X Reunião anual dos Dermato-sifilógrafos Brasileiros, Curitiba.
Castro LG, Belda Júnior W, Cucé LC, Sampaio SA, Stevens DA (1993) Successful treatment of sporotrichosis with oral fluconazole: a report of three cases. Br J Dermatol 128:352–356
Appenzeller S, Amaral TN, Amstalden EMI, Bertolo MB, Neto JFM, Samara AM et al (2006) Sporothrix schenckii infection presented as monoarthritis: report of two cases and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 25:926–928
Lutz A, Splendore A (1907) Sobre uma micose observada em homens e ratos: contribuição para o conhecimento das assim chamadas esporotricoses. Revista Médica de São Paulo 21:443–450
Rio de Janeiro (Estado). Secretaria de Estado de Saúde Resolução SES No 674 DE 12/07/2013. Diário Oficial [do] Estado do Rio de Janeiro, 2013.8p. [Portuguese]. http://www.rio.rj.gov.br/dlstatic/10112/4364979/4115670/ResolucaoSESN674DE12.07.2013.pdf. Accessed 07 september 2021.
Falcão EMM, de Lima Filho JB, Campos DP, Valle ACF, do Bastos FI, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC et al (2019) Hospitalizações e óbitos relacionados à esporotricose no Brasil. Cad Saúde Pública 35:e00109218
Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Portaria GM/MS nº 1.271 de 6 de junho de 2014. Diário Oficial [da] República Federativa do Brasil, 2014. 6p. [Portuguese] https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/gm/2014/prt1271_06_06_2014.html. Accessed 07september 2021.
Bove-Sevilla P, Mayorga-Rodríguez J, Hernández-Hernández O (2008) Sporotrichosis transmitted by a domestic cat. Case report Medicina Cutánea Ibero-Latino-Americana 36:33–35
Yegneswaran PP, Sripathi H, Bairy I, Lonikar V, Rao R, Prabhu S (2009) Zoonotic sporotrichosis of lymphocutaneous type in a man acquired from a domesticated feline source: report of a first case in southern Karnataka, India. Int J Dermatol 48:1198–1200
Rees RK, Swartzberg JE (2011) Feline-transmitted sporotrichosis: a case study from California. Dermatol Online J 17:2
Rios ME, Suarez J, Moreno J, Vallee J, Moreno JP (2018) Zoonotic sporotrichosis related to cat contact: first case report from Panama in Central America. Cureus 10:e2906
Tang MM, Tang JJ, Gill P, Chang CC, Baba R (2012) Cutaneous sporotrichosis: a six-year review of 19 cases in a tertiary referral center in Malaysia. Int J Dermatol 51:702–708
Etchecopaz A, Toscanini MA, Gisbert A, Mas J, Scarpa M, Iovannitti CA, et al. (2021) Sporothrix brasiliensis: a review of an emerging South American fungal pathogen, its related disease, presentation and spread in Argentina. J Fungi (Basel). 26;7(3):170.
Scheufen S, Strommer S, Weisenborn J, Prenger-Berninghoff E, Thom N, Bauer N et al (2015) Clinical manifestation of an amelanotic Sporothrix schenckii complex isolate in a cat in Germany. JMM. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmmcr.0.000039
Thomson J, Trott DJ, Malik R, Galgut B, McAllister MM, Nimmo J et al (2019) An atypical cause of sporotrichosis in a cat. Med Mycol Case Rep 23:72–76
Arrillaga-Moncrieff I, Capilla J, Mayayo E, Marimon R, Mariné M, Gené J et al (2009) Different virulence levels of the species of Sporothrix in a murine model. Clin Microbiol Infect 15:651–655
Duani H, Palmerston MF, Rosa Júnior JF, Ribeiro VT, Alcântara Neves PL (2019) Meningeal and multiorgan disseminated sporotrichosis: a case report and autopsy study. Medical Mycology Case Reports 26:47–52
Rodrigues AM, de Hoog GS, de Camargo ZP (2015) Molecular diagnosis of pathogenic Sporothrix species. Vinetz JM, editor. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 9:e0004190.
Zhang M, Li F, Li R, Gong J, Zhao F (2019) Fast diagnosis of sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix globosa, Sporothrix schenckii, and Sporothrix brasiliensis based on multiplex real-time PCR. Reynolds TB, editor. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 13:e0007219.
Oliveira MME, Muniz M de M, Almeida-Paes R, Zancope-Oliveira RM, Freitas AD, Lima MA, et al. (2020) Cerebrospinal fluid PCR: a new approach for the diagnosis of CNS sporotrichosis. Reynolds TB, editor. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 14:e0008196.
Costa RO, de Mesquita KC, Damasco PS, Bernardes-Engemann AR, Dias CMP, Silva IC et al (2008) Artritis infecciosa como única manifestación de la esporotricosis: serología de muestras de suero y líquido de la sinovia como recurso del diagnóstico. Rev Iberoam Micol 25:54–56
Lopes-Bezerra LM, Schubach A, Costa RO (2006) Sporothrix schenckii and sporotrichosis. An Acad Bras Cienc 78:293–308
Toriello C, Brunner-Mendoza C, Ruiz-Baca E, Duarte-Escalante E, Pérez-Mejía A, del Rocío R-M (2021) Sporotrichosis in Mexico. Braz. J Microbiol 52:49–62
Yao L, Song Y, Zhou J, Cui Y, Li S (2020) Epidemiological and clinical comparisons of paediatric and adult sporotrichosis in Jilin Province, China. Mycoses 63:308–313
Vismer HF, Hull PR (1997) Prevalence, epidemiology and geographical distribution of Sporothrix schenckii infections in Gauteng, South Africa. Mycopathologia 137:137–143
Song Y, Li S-S, Zhong S-X, Liu Y-Y, Yao L, Huo S-S (2013) Report of 457 sporotrichosis cases from Jilin province, northeast China, a serious endemic region: report of 457 sporotrichosis cases from China. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 27:313–318
Lima ÍMF, Ferraz CE, Gonçalves de Lima-Neto R, Takano DM (2020) Case report: sweet syndrome in patients with sporotrichosis: a 10-case series. Am J Trop Med Hyg 103:2533–2538
Procópio-Azevedo AC, Rabello VBS, Muniz MM, Figueiredo-Carvalho MHG, Almeida-Paes R, Zancopé-Oliveira RM, Silva JCAL, Macedo PM, Valle ACF, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, Freitas DFS (2021) Hypersensitivity reactions in sporotrichosis: a retrospective cohort of 325 patients from a reference hospital in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (2005–2018). Br J Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.20646
Freitas DFS, Valle ACF do, da Silva MBT, Campos DP, Lyra MR, de Souza RV, et al. (2014) Sporotrichosis: an emerging neglected opportunistic infection in HIV-infected patients in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Vinetz JM, editor. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8:e3110.
Arantes Ferreira GS, Watanabe ALC, Trevizoli NC, Jorge FMF, Cajá GON, Diaz LGG et al (2019) Disseminated sporotrichosis in a liver transplant patient: a case report. Transpl Proc 51:1621–1624
Fichman V, Marques de Macedo P, Francis Saraiva Freitas D, Francesconi C, do Valle A, Almeida-Silva FF, Reis Bernardes-Engemann A et al (2020) Zoonotic sporotrichosis in renal transplant recipients from Rio de Janeiro Brazil. Transpl Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.1111/tid.13485
Ramírez Soto MC (2015) Sporotrichosis: the story of an endemic region in Peru over 28 years (1985 to 2012). Ratner AJ, editor. PLoS ONE 10:e0127924.
Rubio G, Sánchez G, Porras L, Alvarado Z (2010) Esporotricosis: prevalencia, perfil clínico y epidemiológico en un centro de referencia en Colombia. Rev Iberoam Micol 27:75–79
Yao L, Song Y, Cui Y, Zhou J-F, Zhong S-X, Zhao D-Y et al (2020) Pediatric sporotrichosis in Jilin Province of China (2010–2016): a retrospective study of 704 cases. Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society 9:342–348
Larsson CE, de Almeida GonçalvesAraujo MVC, Dagli MLZ, Correa B, Fava Neto C (1989) Esporotricosis felina: aspectos clínicos e zoonóticos. Rev Inst Med trop S Paulo 31:351–358
de Lima Barros MB, Schubach TMP, Gutierrez Galhardo MC, de Oliveira Schubach A, Monteiro PCF, Reis RS et al (2001) Sporotrichosis: an emergent zoonosis in Rio de Janeiro. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 96:777–779
de Lima Barros MB, de Oliveira Schubach A, do Valle ACF, Gutierrez Galhardo MC, Conceição-Silva F, Schubach TMP et al (2004) Cat-transmitted sporotrichosis epidemic in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: description of a series of cases. Clin Infect Dis 38:529–535
Yeh H-Y, Chen K-H, Chen K-T (2018) Environmental determinants of infectious disease transmission: a focus on one health concept. IJERPH 15:1183
da Silva MBT, de Mattos Costa MM, da Silva Torres CC, Galhardo MCG, do Valle ACF, de Magalhães MAFM et al (2012) Esporotricose urbana: epidemia negligenciada no Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Cad Saúde Pública 28:1867–1880
Alzuguir CLC, Pereira SA, Magalhães MAFM, Almeida-Paes R, Freitas DFS, Oliveira LFA et al (2020) Geo-epidemiology and socioeconomic aspects of human sporotrichosis in the municipality of Duque de Caxias, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, between 2007 and 2016. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 114:99–106
Montenegro H, Rodrigues AM, Dias MAG, da Silva EA, Bernardi F, de Camargo ZP (2014) Feline sporotrichosis due to Sporothrix brasiliensis: an emerging animal infection in São Paulo. Brazil BMC Vet Res 10:269
Silva GM, Howes JCF, Leal CAS, Mesquita EP, Pedrosa CM, Oliveira AAF et al (2018) Surto de esporotricose felina na região metropolitana do Recife. Pesq Vet Bras 38:1767–1771
Miranda LHM, Silva JN, Gremião IDF, Menezes RC, Almeida-Paes R, Dos Reis ÉG et al (2018) Monitoring fungal burden and viability of Sporothrix spp in skin lesions of cats for predicting antifungal treatment response. J Fungi (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4030092
Schubach TMP, de Oliveira Schubach A, dos Reis RS, Cuzzi-Maya T, Blanco TCM, Monteiro DF et al (2002) Sporothrix schenckii isolated from domestic cats with and without sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Mycopathologia 153:83–86
Schubach A, Schubach TMP, de Lima Barros MB, Wanke B (2005) Cat-transmitted sporotrichosis, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis 11:1952–1954
Ramírez-Soto MC, Aguilar-Ancori EG, Tirado-Sánchez A, Bonifaz A (2018) Ecological determinants of sporotrichosis etiological agents. J Fungi (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4030095
Mattei AS, Madrid IM, Santin R, Silva FV, Carapeto LP, Meireles MCA (2011) Sporothrix schenckii in a hospital and home environment in the city of Pelotas/RS - Brazil. An Acad Bras Ciênc 83:1359–1362
Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, Zancopé-Oliveira RM, Monzón A, Rodriguez-Tudela JL, Cuenca-Estrella M (2010) Antifungal susceptibility profile in vitro of Sporothrix schenckii in two growth phases and by two methods: microdilution and E-test. Mycoses. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0507.2009.01701.x
Oliveira MME, Almeida-Paes R, Muniz MM, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, Zancope-Oliveira RM (2011) Phenotypic and molecular identification of Sporothrix isolates from an epidemic area of sporotrichosis in Brazil. Mycopathologia 172(4):257–267
Oliveira MME, Paula S, Almeida-Paes R, Pais C, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, Zancope-Oliveira RM (2012) Rapid identification of Sporothrix species by T3B fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol 50(6):2159–2162
Ottonelli Stopiglia CD, Magagnin CM, Castrillón MR, Mendes SDC, Heidrich D, Valente P, Scroferneker ML (2014) Antifungal susceptibilities and identification of species of the Sporothrix schenckii complex isolated in Brazil. Med Mycol 52(1):56–64
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Angelina Silva and Alessandra Pinheiro for their help in the search at Manguinhos Library.
Funding
RMZ-O was supported in part by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico [CNPq 302796/2017–7] and Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro [FAPERJ E-26/202.527/2019]. We also thank the support given by Fundação Oswaldo Cruz.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Vanessa Brito de Souza Rabello, Marcos de Abreu Almeida, Andrea Reis Bernardes-Engemann, Rodrigo Almeida-Paes, Priscila Marques de Macedo, and Rosely Maria Zancopé-Oliveira. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Vanessa Brito de Souza Rabello, Marcos de Abreu Almeida, Andrea Reis Bernardes-Engemann, Rodrigo Almeida-Paes, Priscila Marques de Macedo, and Rosely Maria Zancopé-Oliveira, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable. This article does not contain any studies with human participants and/or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest/Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabello, V.B.S., Almeida, M.A., Bernardes-Engemann, A.R. et al. The Historical Burden of Sporotrichosis in Brazil: a Systematic Review of Cases Reported from 1907 to 2020. Braz J Microbiol 53, 231–244 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-021-00658-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-021-00658-1