Abstract
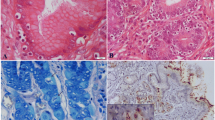
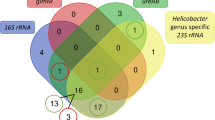
Helicobacter infection has been associated with hepatobiliary diseases in humans and animals. The aims of this study were to identify Helicobacter species in the hepatobiliary tract of dogs and to elucidate the possible association of these bacteria in liver diseases. Twenty-seven gastric and hepatobiliary samples were collected from 33 dogs with hepatic lesions and 17 dogs with no liver histological changes. Warthin-Starry staining, immunohistochemical assay, and PCR were performed to detect the presence of Helicobacter. Helicobacter genus was detected in 21.2% of the samples with hepatic lesions. The main lesion was chronic hepatitis. Immunohistochemistry revealed infection in liver (1/5) and gallbladder (1/3) 32 samples. The sequence analysis of seven amplicons of the 16S rRNA gene of Helicobacter genus from hepatobiliary samples showed 97.8 to 100% of nucleotide identity with gastric helicobacter. One amplicon of the ureA and ureB gene of Helicobacter genus from the stomach showed 89.1 to 90.7% nucleotide identity with H. heilmannii. The presence of Helicobacter genus in liver samples showing hepatic lesions suggests the involvement of these bacteria in the etiology of hepatobiliary disease in dogs. DNA sequences were similar to gastric Helicobacter species, reinforcing the hypothesis of bacterial translocation from the stomach to liver by the biliary pathway.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ito T, Kobayashi D, Uchida K, Takemura T, Nagaoka S, Kobayahi I et al (2008) Helicobacter pylori invades the gastric mucosa and translocates to the gastric lymph nodes. Lab Investig 88:664–681
Bento-Miranda M, Figueiredo C (2014) Helicobacter heilmannii sensu lato: an overview of the infection in humans. World J Gastroenterol 20:17779–17787
Haesebrouck F, Pasmans F, Flahou B, Smet A, Vandamme P, Ducatelle R (2011) Non-Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter species in the human gastric mucosa: a proposal to introduce the terms H. heilmannii sensu lato and sensu stricto. Helicobacter 16:339–340
Owen RJ (1998) Helicobacter-species classification and identification. Br Med Bull 54:17–30
Karagin PH, Stenram U, Wadstrom T, Ljungh A (2010) Helicobacter species and common gut bacterial DNA in gallbladder with cholecystitis. World J Gastroenterol 16:4817–4822
Xuan SY, Li N, Qiang X, Zhou RR, Shi YX (2006) Helicobacter infection in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue. World J Gastroenterol 12:2335–2340
Maurer KJ, Ihrig MM, Rogers AB, Ng V, Bouchard G, Leonard MR et al (2005) Identification of cholelithogenic enterohepatic helicobacter species and their role in murine cholesterol gallstone formation. Gastroenterology 128:1023–1033
Rogers AB, Boutin SR, Whary MT, Sundina N, Ge Z (2004) Progression of chronic hepatitis and preneoplasia in Helicobacter hepaticus-infected A/JCr mice. Toxicol Pathol 32:668–677
Fox JG, Shen Z, Muthupalani S, Rogers AR, Kirchain SM, Dewhirst FE (2009) Chronic hepatitis, hepatic dysplasia, fibrosis, and biliary hyperplasia in hamsters naturally infected with a novel Helicobacter classified in the H. bilis cluster. J Clin Microbiol 47:3673–3681
Boomkens SY, Slump E, Egberink HF, Rothuizen J, Penning LC (2005) PCR screening for candidate etiological agents of canine hepatitis. Vet Microbiol 108:49–55
Garcia A, Erdman SE, Xu S, Feng Y, Rogers AB, Schrenzel MD et al (2002) Hepatobiliary inflammation, neoplasia, and argyrophilic bacteria in a ferret colony. Vet Pathol 39:173–179
Fox JG, Drolet R, Higgins R, Messier S, Yan L, Coleman BE et al (1996a) Helicobacter canis isolated from a dog liver with multifocal necrotizing hepatitis. J Clin Microbiol 34:2479–2482
Marcasso RA, Takemura LS, Camargo PL, Alfieri AA, Bracarense APFRL (2016) Presence of Helicobacter DNA in hepatic tissues in dogs with nonspecific hepatic lesions. Afr J Microbiol Res 10:93–99
Greiter-Wilke A, Scanziani E, Soldati S, McDonough SP, McDonough PL, Center SA et al (2006) Association of Helicobacter with cholangiohepatitis in cats. J Vet Int Med 20:822–827
Sjodin S, Trowald-Wigh G, Fredriksson M (2011) Identification of Helicobacter DNA in feline pancreas, liver, stomach, and duodenum: comparison between findings in fresh and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue samples. Res Vet Sci 91:e28–e30
Kandelaki S, Kordzaia D (2014) Helicobacter and hepatobiliary diseases: conceptual view and review of the literature. Georgian Med News 232-233:92–98
Fox JG, Yan L, Shames B, Campbell J, Murphy JC, Li X (1996b) Persistent hepatitis and enterocolitis in germfree mice infected with Helicobacter hepaticus. Infect Immun 64:3673–3681
Schauer DB (2001) Enterohepatic Helicobacter Species. In: Mobley HLT, Mendz GL, Hazell SL (eds) Helicobacter pylori: physiology and genetics. ASM Press, Washington, DC chapter 43
World Small Animal Veterinary Association (2006) WSAVA standards for clinical and histological diagnosis of canine and feline liver disease. Liver Standardization Group, Jan Rothuizen. Saunders Elsevier Press
Takemura LS, Camargo PL, Alfieri AA, Bracarense AP (2009) Helicobacter spp. in cats: association between infecting species and epithelial proliferation within the gastric lamina propria. J Comp Pathol 141:127–134
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:e2725–e2729
Strauss-Ayali D, Scanziani E, Deng D, Simpson KW (2001) Helicobacter spp. infection in cats: evaluation of the humoral immune response and prevalence of gastric Helicobacter spp. Vet Microbiol 79:253–265
Van den Bulck K, Decostere A, Baele M, Driessen A, Debongnie JC, Burette A et al (2005) Identification of non-Helicobacter pylori spiral organisms in gastric samples from humans, dogs, and cats. J Clin Microbiol 43:2256–2260
Nam C, Ohmachi Y, Kokubo T, Nishikawa T, Uchida K, Nakayama H (2013) Histopathological studies on cases of chronic mouse hepatitis by natural Helicobacter infections. J Vet Med Sci 75:1231–1235
Nilsson HO, Taneera J, Castedal M, Glatz E, Olsson R, Wadstrom T (2000) Identification of Helicobacter pylori and other Helicobacter species by PCR, hybridization, and partial DNA sequencing in human liver samples from patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis or primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Microbiol 38:1072–1076
Pellicano R, Mazzaferro V, Grigioni WF, Cutufia MA, Fagoonee S, Silengo L et al (2004) Helicobacter species sequences in liver samples from patients with and without hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 10:598–601
Beisele M, Shen Z, Parry N, Mobley M, Taylor NS, Bucley E et al (2011) Helicobacter marmotae and novel Helicobacter and Campylobacter species isolated from the livers and intestines of prairie dogs. J Med Microbiol 60:1366–1374
Avenaud P, Marais A, Monteiro L, Le Bail B, Bioulac Sage P, Balabaud C et al (2000) Detection of Helicobacter species in the liver of patients with and without primary liver carcinoma. Cancer 89:1431–1439
O'Rourke JL, Solnick JV, Neilan BA, Seidel K, Hayter R, Hansen LM et al (2004) Description of 'Candidatus Helicobacter heilmannii' based on DNA sequence analysis of 16S rRNA and urease genes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:2203–2211
Yamanaka H, Arita M, Oi R, Ohsawa M, Mizushima M, Takagi T et al (2013) Prevalence of an unidentified Helicobacter species in laboratory mice and its distribution in the hepatobiliary system and gastrointestinal tract. Exp Anim 62:109–116
Tiwari SK, Khan AA, Ibrahim M, Habeeb MA, Habibullah CM (2006) Helicobacter pylori and other Helicobacter species DNA in human bile samples from patients with various hepato-biliary diseases. World J Gastroenterol 12:2181–2186
O'Boyle CJ, MacFie J, Mitchell CJ, Johnstone D, Sagar PM et al (1998) Microbiology of bacterial translocation in humans. Gut 42:29–35
Pellicano R, Menard A, Rizzetto M, Megraud F (2008) Helicobacter species and liver diseases: association or causation? Lancet Infect Dis 8:254–260
Van den Bulck K, Decostere A, Baele M, Vandamme P, Mast J, Ducatelle R et al (2006) Helicobacter cynogastricus sp. nov., isolated from the canine gastric mucosa. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1559–1564
Hamada T, Yokota K, Ayada K, Hirai K, Kamada T, Haruma K et al (2009) Detection of Helicobacter hepaticus in human bile samples of patients with biliary disease. Helicobacter 14:545–551
Wilson IG (1997) Inhibition and facilitation of nucleic acid amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3741–3751
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Annemieke Smet, Ghent University, Belgium, for positive controls of H. baculiformis, H. salomonis, and H. cynogastricus.
Funding
This study was financially supported by CNPq and Fundação Araucária, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jorge Sampaio
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takemura, L.S., Marcasso, R.A., Lorenzetti, E. et al. Helicobacter infection in the hepatobiliary system and hepatic lesions: a possible association in dogs. Braz J Microbiol 50, 297–305 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-018-0003-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-018-0003-8