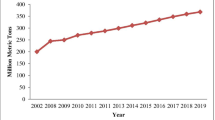
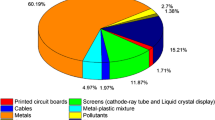
Abstract
This review looks over the current construction and demolition waste management (C&DWM) situations by scrutinizing the definition, classification, components, compositions, generated sources and causes, impacts of generated construction and demolition wastes (C&DWs), waste management hierarchy (WMH), 3R principles (Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle), Circular Economy (CE), frameworks, tools, and approaches of C&DWM. After reviewing the literature this study contributes to the literature by the following means: (a) suitable working definitions of C&DW and C&DWM are provided, (b) an expanded WMH for construction and demolition operations is presented, (c) frameworks of C&DWM are identified and listed as follows: frameworks based on WMH, including 3R principles and CE concept, frameworks focusing on the quantification, estimation, and prediction of generated C&DW, frameworks focusing on effective and sustainable C&DWM, frameworks focusing economic, social, and environmental performance assessment, frameworks based on multi-criteria analysis (MCA), frameworks based on post-disaster recovery period, and other miscellaneous frameworks, and (d) four categories of tools utilized in C&DWM are identified and explained, namely, approaches employed in C&DWM, information technology (IT) tools employed in C&DWM, multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) tools employed in C&DWM, and C&DWM technologies. Moreover, this study also found that CE, and green rating system (GRS) are widely used approaches, Building Information Modeling (BIM), Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Geographic Information System, and Big Data are the extensively used IT tools, Analytical Hierarchy Process, FUZZY, TOPSIS (Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to the Ideal Solution), Weighted Summation, Elimination and Choice Expressing the Reality II, Elimination and Choice Expressing the Reality III, Evaluation of Mixed Data, and REGIME (REG) are the widely used MCA tools in C&DWM, and Prefabricated Construction and Modular Construction are broadly used C&DWM technologies. Furthermore, it has been observed that the application of the Analytic Networking Process (ANP) and hybridization of ANP, FUZZY, and TOPSIS tools do not catch considerable attention in the literature for conducting MCA, although it yields more precise outcomes. Additionally, most previous research has focused on the estimation of generated C&DW, but less attention has been given to forecasting the generated C&DW due to inadequate available C&DW data. This review article also assists C&DWM practitioners, academics, stakeholders, and contractors in choosing appropriate frameworks and tools for C&DWM while managing C&DW.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting this study’s outcomes will be provided by the corresponding author DSAR upon request.
References
Li, Q., and Sun, P. 2009. Research trend of construction debris reclamation home and abroad. China Building Materials Sciences & Technology 4: 119–122.
Pacheco-Torgal, F., and Ding, Y. 2013. Handbook of recycled concrete and demolition waste. Amsterdam: Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857096906.3.424.
Roach, I. 2001. Diverting lightweight C and D waste from landfill. Wastes Management 23: 23–25.
Ali, A. 2018. Development of a framework for sustainable construction waste management. A case study of three major Libyan cities. University of Wolverhampton. p. 300. Available at: https://wlv.openrepository.com/handle/2436/622080. Accessed 14 Aug 2021.
Lu, W., Webster, C., Peng, Y., et al. 2016. Estimating and calibrating the amount of building-related construction and demolition waste in urban China. International Journal of Construction Management 17 (1): 13–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/15623599.2016.1166548.
Akhtar, A., and Sarmah, A.K. 2018. Construction and demolition waste generation and properties of recycled aggregate concrete: A global perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production 186: 262–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.085.
Faruqi, M.H.Z., and Siddiqui, F.Z. 2020. A mini review of construction and demolition waste management in India. Waste Management & Research 38 (7): 708–716. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X2091.
Menegaki, M., and Damigos, D. 2018. A review on current situation and challenges of construction and demolition waste management. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry 13: 8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2018.02.010.
Aslam, M.S., Huang, B., and Cui, L. 2020. Review of construction and demolition waste management in China and USA. Journal of Environmental Management 264: 110445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110445.
Perry, G., and VanderPol, M. 2014. Characterization & management of construction, renovation & demolition waste in Canada. In 2014 Recycling council of Alberta conference. Available at: https://recycle.ab.ca/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/VanderPol_Perry.pdf. Accessed 3 Sept 2021.
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME). 2019. Guide for identifying, evaluating and selecting policies for influencing construction, renovation and demolition waste management. pp. 1–151. Available at: https://ccme.ca/en/res/crdguidance-secured.pdf. Accessed 3 Sept 2021.
Yeheyis, M., Hewage, K., Alam, M.S., et al. 2013. An overview of construction and demolition waste management in Canada: A lifecycle analysis approach to sustainability. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy 15 (1): 81–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0481-6.
Pickin, J., Randell, P., Trinh, J., et al. 2018. National waste report 2018. Department of the Environment and Energy, Australia and Blue Environment Pty Ltd. pp. 1–126. Available at: https://www.dcceew.gov.au/environment/protection/waste/publications/national-waste-reports/2018. Accessed 3 Sept 2021.
Shooshtarian, S., Maqsood, T., Khalfan, M., et al. 2020. Landfill levy imposition on construction and demolition waste: Australian stakeholders’ perceptions. Sustainability 12 (11): 4496. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114496.
Ouda, O.K.M., Peterson, H.P., Rehan, M., et al. 2017. A case study of sustainable construction waste management in Saudi Arabia. Waste and Biomass Valorization 9 (12): 2541–2555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0174-9.
Blaisi, N.I. 2019. Construction and demolition waste management in Saudi Arabia: Current practice and roadmap for sustainable management. Journal of Cleaner Production 221: 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.264.
Yuan, H., Chini, A.R., Lu, Y., et al. 2012. A dynamic model for assessing the effects of management strategies on the reduction of construction and demolition waste. Waste Management 32 (3): 521–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.11.006.
Jin, R., Li, B., Zhou, T., et al. 2017. An empirical study of perceptions towards construction and demolition waste recycling and reuse in China. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 126: 86–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.07.034.
Kabirifar, K., Mojtahedi, M., Wang, C., et al. 2020. Construction and demolition waste management contributing factors coupled with reduce, reuse, and recycle strategies for effective waste management: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production 263: 121265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121265.
Deng, X., Liu, G., and Hao, J. 2008. A study of construction and demolition waste management in Hong Kong. In 2008 4th International conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/WiCom.2008.1745.
Chen, X., and Lu, W. 2017. Identifying factors influencing demolition waste generation in Hong Kong. Journal of Cleaner Production 141: 799–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.164.
Hossain, M.U., Wu, Z., and Poon, C.S. 2017. Comparative environmental evaluation of construction waste management through different waste sorting systems in Hong Kong. Waste Management 69: 325–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.07.043.
Mah, C.M., Fujiwara, T., and Ho, C.S. 2016. Construction and demolition waste generation rates for high-rise buildings in Malaysia. Waste Management & Research 34 (12): 1224–1230. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X16666944.
Hoang, N.H., Ishigaki, T., Kubota, R., et al. 2019. A review of construction and demolition waste management in Southeast Asia. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management 22 (2): 315–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00914-5.
Umar, U.A., Shafiq, N., and Ahmad, F.A. 2021. A case study on the effective implementation of the reuse and recycling of construction & demolition waste management practices in Malaysia. Ain Shams Engineering Journal 12 (1): 283–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2020.07.005.
Jamal, M.S., and Sobuz, M.H.R. 2017. A sustainable approach of demolition, reconstruction, reuses and recycling construction materials in Bangladesh. BAUET Journal 1 (1): 83–90.
Ashikuzzaman, M., and Howlader, M.H. 2020. Sustainable solid waste management in Bangladesh: Issues and challenges. Sustainable waste management challenges in developing countries. 35–55. https://www.igi-global.com/chapter/sustainable-solid-waste-management-in-bangladesh/240071
Fatemi, M.N. 2012. Strategies to reduce construction and demolition (C&D) waste for sustainable building design in Dhaka: Role of architects. In Proceedings of international seminar on architecture: Education, Practice and research. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nawrose-Fatemi/publication/268524277.
Chowdhury, F.H., Raihan, M.T., Islam, G.M.S., et al. 2016. Construction waste management practice: Bangladesh perception. In Proceedings of 3rd international conference on advances in civil engineering. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Fazlul-Chowdhury-2/publication/320596439. Accessed 3 Sept 2021.
Islam, R., Nazifa, T.H., Yuniarto, A., et al. 2019. An empirical study of construction and demolition waste generation and implication of recycling. Waste Management 95: 10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.05.049.
Elshaboury, N., Al-Sakkaf, A., Mohammed Abdelkader, E., et al. 2022. Construction and demolition waste management research: A science mapping analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research Public Health 19 (8): 4496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084496.
Wu, H., Zuo, J., Zillante, G., et al. 2019. Status quo and future directions of construction and demolition waste research: A critical review. Journal of Cleaner Production 240: 118163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118163.
Wu, H., Zuo, J., Yuan, H., et al. 2019. A review of performance assessment methods for construction and demolition waste management. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 150: 104407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104407.
Chen, J., Su, Y., Si, H., et al. 2018. Managerial areas of construction and demolition waste: A scientometric review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15 (11): 2350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112350.
Yuan, H., and Shen, L. 2011. Trend of the research on construction and demolition waste management. Waste Management 31 (4): 670–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.10.030.
Shen, L.Y., Tam, V.W., Tam, C.M., et al. 2004. Mapping approach for examining waste management on construction sites. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 130 (4): 472–481. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9364(2004)130:4(472).
Tam, V.W., and Tam, C.M. 2008. Waste reduction through incentives: A case study. Building Research & Information 36 (1): 37–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/09613210701417003.
Yuan, H.P., Shen, L.Y., Hao, J.J., et al. 2011. A model for cost–benefit analysis of construction and demolition waste management throughout the waste chain. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 55 (6): 604–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.06.004.
Park, J., and Tucker, R. 2016. Overcoming barriers to the reuse of construction waste material in Australia: A review of the literature. International Journal of Construction Management 17 (3): 228–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/15623599.2016.1192248.
Tchobanoglous, G., Eliassen, R., and Theisen, H. 1977. Solid Wastes: Engineering Principles and Management Issues. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Gavilan, R.M., and Bernold, L.E. 1994. Source evaluation of solid waste in building construction. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 120 (3): 536–552. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9364(1994)120:3(536).
Poon, C. 2007. Reducing construction waste. Waste Management 12: 1715–1716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2007.08.013.
Poon, C.-S., and Chan, D. 2007. The use of recycled aggregate in concrete in Hong Kong. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 50 (3): 293–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2006.06.005.
Arslan, H., Coşgun, N., and Salgin, B. 2012. Construction and demolition waste management in Turkey. In Waste management—An integrated vision, Rebellon, L.F.M. (ed.), 313–332. London: InTech. https://doi.org/10.5772/46110.
Domingo, N., and Luo, H. 2017. Canterbury earthquake construction and demolition waste management: Issues and improvement suggestions. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 22: 130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2017.03.003.
Yahya, K., and Boussabaine, A.H. 2006. Eco-costing of construction waste. Management of Environmental Quality: An International Journal 17 (1): 6–19. https://doi.org/10.1108/14777830610639404.
Lu, W., and Yuan, H. 2011. A framework for understanding waste management studies in construction. Waste Management 31 (6): 1252–1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.01.018.
Elgizawy, S.M., El-Haggar, S.M., and Nassar, K. 2016. Approaching sustainability of construction and demolition waste using zero waste concept. Low Carbon Economy 7 (1): 1–11. https://doi.org/10.4236/lce.2016.71001.
Spivey, D.A. 1974. Environment and construction management engineers. Journal of the Construction Division 100 (3): 395–401. https://doi.org/10.1061/JCCEAZ.0000443.
Skoyles, E. 1976. Materials wastage—A misuse of resources. Batiment International, Building Research and Practice 4 (4): 232. https://doi.org/10.1080/09613217608550498.
Skoyles, E. 1976. Waste of materials and the contractors quantity surveyor. The Quantity Surveyor 209–211.
Fatta, D., Papadopoulos, A., Avramikos, E., et al. 2003. Generation and management of construction and demolition waste in Greece—An existing challenge. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 40 (1): 81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-3449(03)00035-1.
Nagapan, S., Ismail, A., and Ade, A. 2012. Construction waste and related issues in Malaysia. Diges FKAAS 1: 15–20.
Government of UK. 2021. Waste and environmental impact. Classify different types of waste 2021. Available at: https://www.gov.uk/how-to-classify-different-types-of-waste/construction-and-demolition-waste. Accessed 24 Aug 2021.
Polat, G., Damci, A., Turkoglu, H., et al. 2017. Identification of root causes of construction and demolition (C&D) waste: The case of Turkey. Procedia Engineering 196: 948–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.08.035.
Graham, P., and Smithers, G. 1996. Construction waste minimisation for Australian residential development. Asia Pacific Building and Construction Management Journal 2 (1): 14–19.
Ofori, G., and Ekanayake, L. 2000. Construction material waste source evaluation. In Proceedings of the second southern African conference on sustainable development in the built environment, Pretoria. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:108020913.
Al-Ansary, M., El-Haggar, S., and Taha, M. 2004. Proposed guidelines for construction waste management in Egypt for sustainability of construction industry. In Proceedings of the international conference on sustainable construction waste management, Singapore.
Duan, H., Wang, J., and Huang, Q. 2015. Encouraging the environmentally sound management of C&D waste in China: An integrative review and research agenda. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 43: 611–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.11.069.
Ruiz, L.A.L., Ramón, X.R., and Domingo, S.G. 2020. The circular economy in the construction and demolition waste sector—A review and an integrative model approach. Journal of Cleaner Production 248: 119238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119238.
Duan, H., Miller, T.R., Liu, G., et al. 2019. Construction debris becomes growing concern of growing cities. Waste Management 83: 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.10.044.
Yang, K., Xu, Q., Townsend, T.G., et al. 2006. Hydrogen sulfide generation in simulated construction and demolition debris landfills: Impact of waste composition. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association 56 (8): 1130–1138. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2006.10464544.
Marinković, S., Radonjanin, V., Malešev, M., et al. 2010. Comparative environmental assessment of natural and recycled aggregate concrete. Waste Management 30 (11): 2255–2264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.04.012.
Begum, R.A., Siwar, C., Pereira, J.J., et al. 2006. A benefit–cost analysis on the economic feasibility of construction waste minimisation: The case of Malaysia. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 48 (1): 86–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2006.01.004.
Ghisellini, P., Ripa, M., and Ulgiati, S. 2018. Exploring environmental and economic costs and benefits of a circular economy approach to the construction and demolition sector. A literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production 178: 618–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.207.
Ye, G., Yuan, H., Shen, L., et al. 2012. Simulating effects of management measures on the improvement of the environmental performance of construction waste management. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 62: 56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2012.01.010.
Guerrero, L.A., Maas, G., and Hogland, W. 2013. Solid waste management challenges for cities in developing countries. Waste Management 33 (1): 220–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.09.008.
Huang, B., Wang, X., Kua, H., et al. 2018. Construction and demolition waste management in China through the 3R principle. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 129: 36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.09.029.
Ferguson, J., Kermode, N., Nash, C.L., et al. 1995. Managing and minimizing construction waste. A practical guide. London: Thomas Telford. https://doi.org/10.1680/mamcwapg.20238.
Ashford, S.A., Visvanathan, C., Husain, N., et al. 2000. Design and construction of engineered municipal solid waste landfills in Thailand. Waste Management & Research 18 (5): 462–470. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X0001800507.
Marchettini, N., Ridolfi, R., and Rustici, M. 2007. An environmental analysis for comparing waste management options and strategies. Waste Management 27 (4): 562–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2006.04.007.
Jalali, S. 2007. Quantification of construction waste amount. Available at: https://hdl.handle.net/1822/9105. Accessed 5 Sept 2021.
Won, J., and Cheng, J.C. 2017. Identifying potential opportunities of building information modeling for construction and demolition waste management and minimization. Automation in Construction 79: 3–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2017.02.002.
Esa, M.R., Halog, A., and Rigamonti, L. 2017. Developing strategies for managing construction and demolition wastes in Malaysia based on the concept of circular economy. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management 19 (3): 1144–1154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-016-0516-x.
European Commission. 2016. Construction and demolition waste management in United Kingdom. pp. 1–68. Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/pdf/waste/studies/deliverables/CDW_UK_Factsheet_Final.pdf. Accessed 21 Aug 2021.
Hunt, N., and Shields, J. 2020. Waste management strategy 2020–2025. Loughborough University, UK. pp. 1–17. Available at: https://www.lboro.ac.uk/media/media/services/sustainability/downloads/Waste-Management-Strategy-2020-2025.pdf. Accessed 19 Sept 2021.
Couto, A., and Couto, J.P. 2010. Guidelines to improve construction and demolition waste management in Portugal. In Process management, 285–308. London, UK: IntechOpen.
Hao, J., Shen, L., Devapriya, K., et al. 2006. Construction and demolition waste management in Hong Kong. Hong Kong, China: SDP Research Group, Dept of Building & Real Estate, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University.
Li, Y. 2013. Developing a sustainable construction waste estimation and management system. Hong Kong, China: Hong Kong University of Science and Technology.
US-EPA. 2021. Sustainable materials management: Non-hazardous materials and waste management hierarchy. Available at: https://www.epa.gov/smm/sustainable-materials-management-non-hazardous-materials-and-waste-management-hierarchy. Accessed 2 Oct 2021.
Chung, S.-S., and Lo, C.W. 2003. Evaluating sustainability in waste management: The case of construction and demolition, chemical and clinical wastes in Hong Kong. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 37 (2): 119–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-3449(02)00075-7.
Covaciu, M., Soproni, V.D., Hathazi, F.I., et al. 2019. Decontamination, drying and sterilization assisted by the high frequency electromagnetic field for the processing of construction waste used on driveways. In 2019 15th International conference on engineering of modern electric systems (EMES). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMES.2019.8795092.
Defra, U. 2011. Guidance on applying the waste hierarchy. London, UK. Available at: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/69403/pb13530-waste-hierarchy-guidance.pdf. Accessed 2 Oct 2021.
Rodríguez, D. 2016. Ceramic and mixed construction and demolition wastes (CDW): A technically viable and environmentally friendly source of coarse aggregates for the concrete manufacture. Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Ghent University. Available at: http://hdl.handle.net/1854/LU-7238813. Accessed 5 Oct 2021.
Jin, R., Yuan, H., and Chen, Q. 2019. Science mapping approach to assisting the review of construction and demolition waste management research published between 2009 and 2018. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 140: 175–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.09.029.
Kirchherr, J., Reike, D., and Hekkert, M. 2017. Conceptualizing the circular economy: An analysis of 114 definitions. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 127: 221–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.09.005.
Mahpour, A. 2018. Prioritizing barriers to adopt circular economy in construction and demolition waste management. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 134: 216–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.01.026.
Mignacca, B., Locatelli, G., and Velenturf, A. 2020. Modularisation as enabler of circular economy in energy infrastructure. Energy Policy 139: 111371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111371.
Ghaffar, S.H., Burman, M., and Braimah, N. 2020. Pathways to circular construction: An integrated management of construction and demolition waste for resource recovery. Journal of Cleaner Production 244: 118710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118710.
Bogoviku, L., and Waldmann, D. 2021. Modelling of mineral construction and demolition waste dynamics through a combination of geospatial and image analysis. Journal of Environmental Management 282: 111879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111879.
Zhang, C., Hu, M., Di Maio, F., et al. 2022. An overview of the waste hierarchy framework for analyzing the circularity in construction and demolition waste management in Europe. Science of the Total Environment 803: 149892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149892.
Lu, Y., Wu, Z., Chang, R., et al. 2017. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for green buildings: A critical review and future directions. Automation in Construction 83: 134–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2017.08.024.
Lu, W., Chen, X., Peng, Y., et al. 2018. The effects of green building on construction waste minimization: Triangulating ‘big data’with ‘thick data.’ Waste Management 79: 142–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.07.030.
Mcdonald, B., and Smithers, M. 1998. Implementing a waste management plan during the construction phase of a project: A case study. Construction Management & Economics 16 (1): 71–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/014461998372600.
Esa, M.R., Halog, A., and Rigamonti, L. 2017. Strategies for minimizing construction and demolition wastes in Malaysia. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 120: 219–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.12.014.
Gupta, S., Jha, K.N., and Vyas, G. 2020. Proposing building information modeling-based theoretical framework for construction and demolition waste management: strategies and tools. International Journal of Construction Management. https://doi.org/10.1080/15623599.2020.1786908.
Ayarkwa, J., Agyekum, K., Adinyira, E., et al. 2012. Perspectives for the implementation of lean construction in the Ghanaian construction industry. Journal of Construction Project Management and Innovation 2 (2): 345–359. https://doi.org/10.10520/EJC131245.
Desale, S.V., and Deodhar, S.V. 2014. Identification and eliminating waste in construction by using lean and six sigma principles. International Journal of innovative Research in Science, Engineering and technology 3 (4): 285–296.
Amade, B., Ononuju, C.N., Obodoh, D., et al. 2019. Barriers to lean adoption for construction projects. Pacific Journal of Science and Technology 20: 153–166.
Bajjou, M.S., Chafi, A., and Ennadi, A. 2019. Development of a conceptual framework of lean construction Principles: An input–output model. Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Systems 18 (01): 1–34. https://doi.org/10.1142/S021968671950001X.
Babalola, O., Ibem, E.O., and Ezema, I.C. 2019. Implementation of lean practices in the construction industry: A systematic review. Building and Environment 148: 34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2018.10.051.
Ahmed, S., and Sobuz, M.H.R. 2019. Challenges of implementing lean construction in the construction industry in Bangladesh. Smart and Sustainable Built Environment 9: 174–207. https://doi.org/10.1108/SASBE-02-2019-0018.
Ahmed, S., Hossain, M.M., and Haq, I. 2020. Implementation of lean construction in the construction industry in Bangladesh: Awareness, benefits and challenges. International Journal of Building Pathology and Adaptation 39: 368–406. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBPA-04-2019-0037.
Hussein, M., and Zayed, T. 2021. Critical factors for successful implementation of just-in-time concept in modular integrated construction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production 284: 124716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124716.
Cheng, J.C., and Ma, L.Y. 2013. A BIM-based system for demolition and renovation waste estimation and planning. Waste Management 33 (6): 1539–1551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.01.001.
Hamidi, B., Bulbul, T., Pearce, A., et al. 2014. Potential application of BIM in cost-benefit analysis of demolition waste management. In: Construction research congress 2014: Construction in a global network. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784413517.029.
Liu, Z., Osmani, M., Demian, P., et al. 2015. A BIM-aided construction waste minimisation framework. Automation in Construction 59: 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2015.07.020.
Akinade, O.O., Oyedele, L.O., Bilal, M., et al. 2015. Waste minimisation through deconstruction: A BIM based deconstructability assessment score (BIM-DAS). Resources, Conservation and Recycling 105: 167–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.10.018.
Wong, J.K.W., and Zhou, J. 2015. Enhancing environmental sustainability over building life cycles through green BIM: A review. Automation in Construction 57: 156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2015.06.003.
Won, J., Cheng, J.C., and Lee, G. 2016. Quantification of construction waste prevented by BIM-based design validation: Case studies in South Korea. Waste Management 49: 170–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.12.026.
Kim, Y.C., Hong, W.H., Park, J.W., et al. 2017. An estimation framework for building information modeling (BIM)-based demolition waste by type. Waste Management & Research 35 (12): 1285–1295. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X17736381.
Li, C.Z., Zhong, R.Y., Xue, F., et al. 2017. Integrating RFID and BIM technologies for mitigating risks and improving schedule performance of prefabricated house construction. Journal of Cleaner Production 165: 1048–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.156.
Lu, W., Webster, C., Chen, K., et al. 2017. Computational Building Information Modelling for construction waste management: Moving from rhetoric to reality. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 68: 587–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.10.029.
Xu, J., Shi, Y., Xie, Y., et al. 2019. A BIM-Based construction and demolition waste information management system for greenhouse gas quantification and reduction. Journal of Cleaner Production 229: 308–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.158.
Ratnasabapathy, S., Perera, S., and Alashwal, A. 2019. A review of smart technology usage in construction and demolition waste management. In Proceedings of the 8th World Construction Symposium, Sandanayake, Y.G., Gunatilake, S. and Waidyasekara, eds. Colombo, Sri Lanka, 8–10 November 2019, pp. 45–55. https://doi.org/10.31705/WCS.2019.5.
Liu, H., Sydora, C., Altaf, M.S., et al. 2019. Towards sustainable construction: BIM-enabled design and planning of roof sheathing installation for prefabricated buildings. Journal of Cleaner Production 235: 1189–1201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.07.055.
Farooq, U., Rehman, S.K.U., Javed, M.F., et al. 2020. Investigating BIM implementation barriers and issues in Pakistan using ISM approach. Applied Sciences 10 (20): 7250. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207250.
Li, C.Z., Zhao, Y., Xiao, B., et al. 2020. Research trend of the application of information technologies in construction and demolition waste management. Journal of Cleaner Production 263: 121458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121458.
Lu, W., Huang, G.Q., and Li, H. 2011. Scenarios for applying RFID technology in construction project management. Automation in Construction 20 (2): 101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2010.09.007.
Cheng, J.C., and Ma, L.Y. 2011. RFID supported cooperation for construction waste management. In International conference on cooperative design, visualization and engineering. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23734-8_20.
You, Z., Wu, C., Zheng, L., et al. 2020. An informatization scheme for construction and demolition waste supervision and management in China. Sustainability 12 (4): 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041672.
Li, H., Chen, Z., Yong, L., et al. 2005. Application of integrated GPS and GIS technology for reducing construction waste and improving construction efficiency. Automation in Construction 14 (3): 323–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2004.08.007.
Gorsevski, P.V., Donevska, K.R., Mitrovski, C.D., et al. 2012. Integrating multi-criteria evaluation techniques with geographic information systems for landfill site selection: A case study using ordered weighted average. Waste Management 32 (2): 287–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.09.023.
Ding, Z., Zhu, M., Wu, Z., et al. 2018. Combining AHP-entropy approach with GIS for construction waste landfill selection—A case study of Shenzhen. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15 (10): 2254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102254.
Seror, N., and Portnov, B.A. 2018. Identifying areas under potential risk of illegal construction and demolition waste dumping using GIS tools. Waste Management 75: 22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.01.027.
Biluca, J., de Aguiar, C.R., and Trojan, F. 2020. Sorting of suitable areas for disposal of construction and demolition waste using GIS and ELECTRE TRI. Waste Management 114: 307–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.07.007.
Lu, W., Chen, X., Peng, Y., et al. 2015. Benchmarking construction waste management performance using big data. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 105: 49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.10.013.
Lu, W., Chen, X., Ho, D.C., et al. 2016. Analysis of the construction waste management performance in Hong Kong: The public and private sectors compared using big data. Journal of Cleaner Production 112: 521–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.06.106.
Bilal, M., Oyedele, L.O., Akinade, O.O., et al. 2016. Big data architecture for construction waste analytics (CWA): A conceptual framework. Journal of Building Engineering 6: 144–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2016.03.002.
Chen, X., Lu, W., Xue, F., et al. 2018. A cost-benefit analysis of green buildings with respect to construction waste minimization using big data in Hong Kong. Journal of Green Building 13 (4): 61–76. https://doi.org/10.3992/1943-4618.13.4.61.
Lu, W. 2019. Big data analytics to identify illegal construction waste dumping: A Hong Kong study. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 141: 264–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.10.039.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., et al. 2016. Where is current research on blockchain technology?—A systematic review. PLoS ONE 11 (10): e0163477. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163477.
Wang, J., Wu, P., Wang, X., et al. 2017. The outlook of blockchain technology for construction engineering management. Frontiers of Engineering Management 4: 67–75. https://doi.org/10.15302/J-FEM-2017006.
Turk, Ž, and Klinc, R. 2017. Potentials of blockchain technology for construction management. Procedia Engineering 196: 638–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.08.052.
Yu, B., Wang, J., Li, J., et al. 2019. Prediction of large-scale demolition waste generation during urban renewal: A hybrid trilogy method. Waste Management 89: 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.03.063.
Di Maria, F., Bianconi, F., Micale, C., et al. 2016. Quality assessment for recycling aggregates from construction and demolition waste: An image-based approach for particle size estimation. Waste Management 48: 344–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.12.005.
Wang, H., Zhang, J., and Lin, H. 2019. Satellite-based analysis of landfill landslide: the case of the 2015 Shenzhen landslide. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1080/19386362.2019.1610605.
Li, H., Chen, Z., and Wong, C.T. 2003. Barcode technology for an incentive reward program to reduce construction wastes. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering 18 (4): 313–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8667.00320.
Khoshand, A., Khanlari, K., Abbasianjahromi, H., et al. 2020. Construction and demolition waste management: Fuzzy analytic hierarchy process approach. Waste Management & Research 38 (7): 773–782. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X20910468.
Zoghi, M., Rostami, G., Khoshand, A., et al. 2021. Material selection in design for deconstruction using Kano model, fuzzy-AHP and TOPSIS methodology. Waste Management & Research 40: 410–419. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X211013904.
Chen, Z., Li, H., and Wong, C.T. 2005. EnvironalPlanning: Analytic network process model for environmentally conscious construction planning. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 131 (1): 92–101. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9364(2005)131:1(92).
Zhang, F., Ju, Y., Gonzalez, E.D.S., et al. 2021. Evaluation of construction and demolition waste utilization schemes under uncertain environment: A fuzzy heterogeneous multi-criteria decision-making approach. Journal of Cleaner Production 313: 127907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127907.
Coronado, M., Dosal, E., Coz, A., et al. 2011. Estimation of construction and demolition waste (C&DW) generation and multicriteria analysis of C&DW management alternatives: A case study in Spain. Waste and Biomass Valorization 2 (2): 209–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-011-9064-8.
Dosal, E., Coronado, M., Muñoz, I., et al. 2012. Application of multi-criteria decision-making tool to locate construction and demolition waste (C&DW) recycling facilities in a northern spanish region. Environmental Engineering & Management Journal (EEMJ) 11 (3): 545–556.
Dosal, E., Viguri, J., and Andrés, A. 2013. Multi-criteria decision-making methods for the optimal location of construction and demolition waste (C&DW) recycling facilities. In Handbook of recycled concrete and demolition waste, 76–107. Amsterdam: Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857096906.1.76.
Roussat, N., Dujet, C., and Méhu, J. 2009. Choosing a sustainable demolition waste management strategy using multicriteria decision analysis. Waste Management 29 (1): 12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.04.010.
Banias, G., Achillas, C., Vlachokostas, C., et al. 2010. Assessing multiple criteria for the optimal location of a construction and demolition waste management facility. Building and Environment 45 (10): 2317–2326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2010.04.016.
Kourmpanis, B., Papadopoulos, A., Moustakas, K., et al. 2008. An integrated approach for the management of demolition waste in Cyprus. Waste Management & Research 26 (6): 573–581. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X08091554.
Marzouk, M., and Abd El-Razek, M. 2017. Selecting demolition waste materials disposal alternatives using fuzzy TOPSIS technique. International Journal of Natural Computing Research (IJNCR) 6 (2): 38–57. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJNCR.2017070103.
Eghbali-Zarch, M., Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R., Dehghan-Sanej, K., et al. 2021. Prioritizing the effective strategies for construction and demolition waste management using fuzzy IDOCRIW and WASPAS methods. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management 29: 1109–1138. https://doi.org/10.1108/ECAM-08-2020-0617.
Negash, Y.T., Hassan, A.M., Tseng, M.L., et al. 2021. Sustainable construction and demolition waste management in Somaliland: Regulatory barriers lead to technical and environmental barriers. Journal of Cleaner Production 297: 126717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126717.
Poon, C.S., Yu, A.T.W., Wong, S.W., et al. 2004. Management of construction waste in public housing projects in Hong Kong. Construction Management & Economics 22 (7): 675–689. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144619042000213292.
Tam, C.M., Tam, V.W., Chan, J.K., et al. 2005. Use of prefabrication to minimize construction waste—A case study approach. International Journal of Construction Management 5 (1): 91–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/15623599.2005.10773069.
Tam, V.W., Tam, C.M., Chan, J.K., et al. 2006. Cutting construction wastes by prefabrication. International Journal of Construction Management 6 (1): 15–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/15623599.2006.10773079.
Tam, V.W., Tam, C.M., Zeng, S.X., et al. 2007. Towards adoption of prefabrication in construction. Building and Environment 42 (10): 3642–3654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2006.10.003.
Jaillon, L., Poon, C.-S., and Chiang, Y.H. 2009. Quantifying the waste reduction potential of using prefabrication in building construction in Hong Kong. Waste Management 29 (1): 309–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.02.015.
Construction, M.H. 2011. Prefabrication and modularization: Increasing productivity in the construction industry. Smart Market Report. https://www.nist.gov/system/files/documents/el/economics/Prefabrication-Modularization-in-theConstruction-Industry-SMR-2011R.pdf. Accessed 6 Oct 2022.
Gálvez-Martos, J.L., Styles, D., Schoenberger, H., et al. 2018. Construction and demolition waste best management practice in Europe. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 136: 166–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.04.016.
Ajayi, S.O., Oyedele, L.O., Bilal, M., et al. 2015. Waste effectiveness of the construction industry: Understanding the impediments and requisites for improvements. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 102: 101–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.06.001.
Hardie, M., Khan, S., O'Donnell, A., et al. 2007. The efficacy of waste management plans in Australian commercial construction refurbishment projects. Construction Economics and Building 7 (2): 26–36. https://doi.org/10.5130/AJCEB.v7i2.2988.
Gulghane, A., and Khandve, P. 2015. Management for construction materials and control of construction waste in construction industry: A review. International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications 5 (4): 59–64.
Bandeira, S.R., Maciel, J.B.S., de Oliveira, J.C.S., et al. 2019. Construction and demolition waste management practices at construction sites. International Journal of Advanced Engineering Research and Science (IJAERS) 6 (10): 35–45.
Figueira, J.R., Mousseau, V., and Roy, B. 2016. ELECTRE methods. In Multiple criteria decision analysis: State of the art surveys, 155–185. New York: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3094-4_5.
Klang, A., Vikman, P.-Å., and Brattebø, H. 2003. Sustainable management of demolition waste—An integrated model for the evaluation of environmental, economic and social aspects. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 38 (4): 317–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-3449(02)00167-2.
Yuan, H. 2013. Key indicators for assessing the effectiveness of waste management in construction projects. Ecological Indicators 24: 476–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.07.022.
Calvo, N., Varela-Candamio, L., and Novo-Corti, I. 2014. A dynamic model for construction and demolition (C&D) waste management in Spain: Driving policies based on economic incentives and tax penalties. Sustainability 6 (1): 416–435. https://doi.org/10.3390/su6010416.
Zheng, L., Wu, H., Zhang, H., et al. 2017. Characterizing the generation and flows of construction and demolition waste in China. Construction and Building Materials 136: 405–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.01.055.
Qiao, L., Liu, D., Yuan, X., et al. 2020. Generation and prediction of construction and demolition waste using exponential smoothing method: A case study of Shandong Province, China. Sustainability 12 (12): 5094. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125094.
Ding, Z., Gong, W., Li, S., et al. 2018. System dynamics versus agent-based modeling: A review of complexity simulation in construction waste management. Sustainability 10 (7): 2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072484.
Ali, T.H., Akhund, M.A., Memon, N.A., et al. 2019. Application of artifical intelligence in construction waste management. In 2019 8th International Conference on Industrial Technology and Management (ICITM). Cambridge, UK: IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICITM.2019.8710680.
Wu, Z., Yu, A.T., and Poon, C.S. 2020. Promoting effective construction and demolition waste management towards sustainable development: A case study of Hong Kong. Sustainable Development 28 (6): 1713–1724. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2119.
Kim, S.Y., Nguyen, M.V., and Luu, V.T. 2020. A performance evaluation framework for construction and demolition waste management: Stakeholder perspectives. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/ECAM-12-2019-0683.
Kabirifar, K., Mojtahedi, M., Wang, C.C., et al. 2020. A conceptual foundation for effective construction and demolition waste management. Cleaner Engineering and Technology 1: 100019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2020.100019.
Kabirifar, K., Mojtahedi, M., Wang, C.C., et al. 2021. Effective construction and demolition waste management assessment through waste management hierarchy; a case of Australian large construction companies. Journal of Cleaner Production. 312: 127790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127790.
Stenis, J. 2005. Construction waste management based on industrial management models: A Swedish case study. Waste Management & Research 23 (1): 13–19. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X05050184.
Yuan, H. 2012. A model for evaluating the social performance of construction waste management. Waste Management 32 (6): 1218–1228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.01.028.
Yazdanbakhsh, A. 2018. A bi-level environmental impact assessment framework for comparing construction and demolition waste management strategies. Waste Management 77: 401–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.04.024.
Turkyilmaz, A., Guney, M., Karaca, F., et al. 2019. A comprehensive construction and demolition waste management model using PESTEL and 3R for construction companies operating in Central Asia. Sustainability 11 (6): 1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061593.
Karunasena, G., and Amaratunga, D. 2016. Capacity building for post disaster construction and demolition waste management: A case of Sri Lanka. Disaster Prevention and Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/DPM-09-2014-0172.
Shi, M., Cao, Q., Ran, B., et al. 2021. A conceptual framework integrating “building back better” and post-earthquake needs for recovery and reconstruction. Sustainability 13 (10): 5608. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105608.
Charles, S.H., Chang-Richards, A., and Yiu, T.W. 2022. Providing a framework for post-disaster resilience factors in buildings and infrastructure from end-users’ perspectives: Case study in Caribbean island states. International Journal of Disaster Resilience in the Built Environment. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJDRBE-02-2021-0020.
Mendis, N., Siriwardhana, S., and Kulatunga, U. 2022. Implementation of build back better concept for post-disaster reconstruction in Sri Lanka. In A system engineering approach to disaster resilience: Select proceedings of VCDRR 2021. Singapore: Springer. 33–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7397-9_3.
Acknowledgements
The Committee for Advanced Studies and Research (CASR) of Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET) is acknowledged for allowing us to conduct of a thesis on “Development and Evaluation of Construction and Demolition Waste Management Framework in the Context of Dhaka City”.
Funding
This study did not receive financial support or funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to generating the idea for this review article. Literature search, data analysis, and drafting were performed by DSAR. Reviewing, editing, and revising were performed by IUB.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rayhan, D.S.A., Bhuiyan, I.U. Review of construction and demolition waste management tools and frameworks with the classification, causes, and impacts of the waste. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 6, 95–121 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-023-00166-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-023-00166-y