Abstract
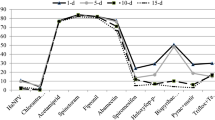
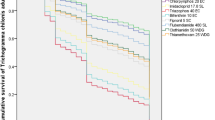
Selectivity of pesticides to the natural enemies in an agroecosystem is required for more effective integrated pest management. Trichogramma chilonis (Ishii) is an important natural enemy of lepidopteran pests, and is often exposed to pesticides. Effects of selected pesticides on acute mortality and parasitism when applied to parasitoids in egg, larval and pupal stages in their hosts were evaluated at 1x (field dose in Pakistan), 2x (double field dose) and 0.5x (half of field dose) doses. The parasitized host eggs were dipped in formulated solutions of pesticides when parasitoids were in different life stages. Parasitoid emergence from hosts treated with acetamiprid, fipronil and abamectin in the egg treatment and with spinetoram in all immature treatments were ≤ 33.9%. Treatment with acetamiprid (≤ 83.1 and ≤ 60.9%), fipronil (≤ 42.3and ≤ 72.7%), and abamectin (≤ 17.2 and ≤ 52.6%) yielded emergence in larval and pupal stage treatments, respectively. Spirotetramat, chlorantraniliprole, spiromesifen, haloxyfop-p-methyl, bispyribac sodium, nicosulfuron, chlorothalonil + procymidone, myclobutanil, pyraclostrobin + metiram, and trifloxystrobin + tebuconazole produced parasitoid emergence ≥ 80.1%.
Parasitoids emerged from hosts treated with spirotetramat, chlorantraniliprole, spiromesifen, bispyribac sodium, pyraclostrobin + metiram and trifloxystrobin + tebuconazole (except at 2 × dose in egg treatment) produced ≥ 84% parasitism in all treatments. Myclobutanil treatment of egg, and nicosulfuron and haloxyfop-p-methyl treatments of larvae and pupae, yielded > 90% parasitism. Acetamiprid and fipronil treatment of larvae and pupae, and abamectin treatment of pupae produced ≤ 78.46% and ≤ 10.76% parasitism, respectively. Over half of the pesticides caused no significant mortality to immature stages or exhibited little to no adverse impacts on parasitism and are promising for integration with these parasitoids.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar ZR, Tariq K, Handler AM, Ali A, Ullah F, Ali F, Zang L-S, Gulza A, Ali S (2021) Toxicological risk assessment of some commonly used insecticides on Cotesia flavipes, a larval parasitoid of the spotted stem borer Chilo partellus. Ecotoxico 30(3):448–458
Bale J, van Lenteren J, Bigler F (2008) Biological control and sustainable food production. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 363:761–776
Ballal CR, Srinivasan R, Jalali SK (2009) Evaluation of an endosulfan tolerant strain of Trichogramma chilonis on cotton, BioContr l54: 723–732
Beasley TM, Zumbo DB (2009) Aligned rank tests for interactions in split-plot designs: Distributional assumptions and stochastic homogeneity. J Mod Appli Statist Meth 8:16–50
Bellows T (2001) Restoring population balance through natural enemy introduction. Biol Cont 21:199–205
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Roy Statisti Socie Seri B 57:289–300
Biondi A, Campolo O, Desneux N, Siscaro G, Palmeri V, Zappala` L (2015) Life stage-dependent susceptibility of Aphytis melinus DeBach (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) to two pesticides commonly used in citrus orchards. Chemosph 128:142–147
Biondi A, Mommaerts V, Smagghe G, Viñuela E, Zappalà L, Desneux N (2012) The non-target impact of spinosyns on beneficial arthropods. Pest Manag Sci 68:1523–1536
Biondi A, Zappala` L, Stark JD, Desneux N (2013) Do biopesticides affect the demographic traits of a parasitoid wasp and its biocontrol services through sublethal effects? PLoS ONE 8:e76548
Bompard A, Amat I, Fauvergue X, Spataro T (2013) Host-parasitoid dynamics and the success of biological control when parasitoids are prone to allee effects. PLoS ONE 8(10):e76768. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076768
Brar KS, Varma GC, Shenhmar M (1991) Effect of insecticides on Trichogramma chilonis Ishii (hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae), an egg parasitoid of sugarcane borers and cotton bollworms. J Entomon 16:43–48
Brück E, Elbert A, Fischer R, Krueger S, Kühnhold J, Klueken AM, Nauen R, Niebes J-F, Reckmann U, Schnorbach H-J, Steffens R, van Waetermeulen X (2009) Movento®, an innovative ambimobile insecticide for sucking insect pest control in agriculture: Biological profile and field performance. Crop Prot 28:838–844
Brown RA (1989) Pesticides and non-target terrestrial invertebrates: an industrial approach. In: Jepson PC (ed) Pesticides and nontarget invertebrates. Intercept Ltd, Wimborne 19–42
Bueno A. de F, Bueno RCO de F, Parra JRP, Vieira SS (2008) Effects of pesticides used in soybean crops to the egg parasitoid Trichogramma pretiosum. Ciência Rural. Santa Maria 38(6):1495–1503
Bull DL, Coleman RJ (1985) Effects of pesticides on Trichogramma spp. Southwest Entomol (supplement) 8:156–168
Calvo B, Stantafe G (2016) Scmamp: An R software package for statistical comparison of multiple algorithms in multiple problems. https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/scmamp/versions/0.2.55 Version 0.2.55
Carmo EL, Bueno AF, Bueno RCOF (2010) Pesticide selectivity for the insect egg parasitoid Telenomus remus. BioCont 55:455–464
Carvalho GA, Reis PR, Rocha LCD, Moraes JC, Fuini LC, Ecole CC (2003) Side-effects of insecticides used in tomato fields on Trichogramma pretiosum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Maringa 25(2):275–279
Chang SC, Hu NT, Hsin CY, Sun CN (2001) Characterization of differences between two Trichogramma wasps by molecular markers. Biol Cont 21:75–78
Cheng S, Lin R, Wang L, Qiu Q, Qu M, Ren X, Zong F, Jiang H, Yu C (2018) Comparative susceptibility of thirteen selected pesticides to three different insect egg parasitoid Trichogramma species. Ecotoxic Environm Safety 166:86–91
Consoli FL, Parra JRP, Hassan SA (1998) Side-effects of insecticides used in tomato fields on the egg parasitoid Trichogramma pretiosum Riley (Hym., Trichogrammatidae), a natural enemy of Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lep., Gelechiidae). J Appl Entomol 122:43–47
Croft BA (1990) Arthropod biological control agents and pesticides. John Wiley and Sons, New York
de Mendiburu F (2020) Agricolae: An R software package for statistical procedures for agricultural research. https://tarwi.lamolina.edu.pe/~fmendiburu/ Version 1.2–8
de Paiva ACR, Beloti VH, Yamamoto PT (2018) Sublethal effects of insecticides used in soybean on the parasitoid Trichogramma pretiosum. Ecotoxico 27(4):448–456
de Paiva ACR, Filho FHI, Parro EA, Barbosa DPL, Yamamoto PT (2020) Do Ready-Mix Insecticides Cause Lethal and Sublethal Effects on Trichogramma pretiosum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) Pupa?. J Eco Entomol XX(XX) 1–7
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech JM (2007) The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 52:81–106
Desneux N, Pham-Dele`gue MH, Kaiser L (2004) Effects of sub-lethal and lethal doses of lambda-cyhalothrin on oviposition experience and host-searching behaviour of a parasitic wasp, Aphidius ervi. Pest Manag Sci 60:381–389
Desneux N, Ramirez-Romero R, Kaiser L (2006) Multistep bioassay to predict recolonization potential of emerging parasitoids after a pesticide treatment. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2675–2682
Engindeniz S, Engindeniz DY (2006) Economic analysis of pesticide use on greenhouse cucumber growing: A case 493 study for Turkey. J Plant Dis Prot 113:193–198
Firake DM, Thubru DP, Behere GT (2017) Eco-toxicological risk and impact of pesticides on important parasitoids of cabbage butterflies in cruciferous ecosystem. Chemosph 168:372–383
Fishel FM (2013) The EPA conventional reduced risk pesticide program. PI-224. University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, Gainesville
Ghorbani M, Saber M, Bagheri M, Vaez N (2016) Effects of diazinon and fipronil on different developmental stages of Trichogramma brassicae Bezdenko (Hym.; Trichogrammatidae). J Agric Sci Technol 18:1267–1278
Gill HK, Garg H (2014) Pesticide: Environmental Impacts and Management Strategies. Pesticides-Toxic Effects. Intech. Rijeka, Croatia, 187–230
Goulart RM, Volpe HX, Vacari AM, Thuler RT, De Bortoli SA (2011) Insecticide selectivity to two species of Trichogramma in three different hosts, as determined by IOBC/WPRS methodology. Pest Manag Sci 68(2):240–244
Guedes RN, Lima JOG, Zanuncio JC (1992) Seletividade dos inseticidas deltametrina, fenvalerato e fenitrotion para Podisus connexivus Bergroth, 1891 (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). An Soc Entomol Bras 21:339–346
Gurr GM, Wratten SD, Barbosa P (2000) Success in conservation biological control of arthropods. In: Gurr G, Wratten S (eds) Biological control: measures of success. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 105–132
Hagley EAC, Laing JE (1989) Effect of pesticides on parasitism of artificially distributed eggs of the codling moth Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) by Trichogramma sp. (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Proc Entomol Soc Ont 120:25–33
Hassan SA (1977) Standardized techniques for testing side-effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods in the laboratory. J Plant Dis Prot 84:158–163
Hassan SA (1989) Testing methodology and the concept of the IOBC/WPRS Working Group, in Pesticides and Non-Target Invertebrates, ed. By Jepson PC. Intercept, Andover, 1–18
Hassan SA (1992) Guideline of the side effects of plant protection products on Trichogramma chilonis. In guideline for testing the effects of pesticides on beneficial organisms: description of test method. Bull IOBC/WPRS 15:18–39
Hassan SA (1993) The mass rearing and utilization of Trichogramma to control lepidopterous pests: achievements and outlook. Pestic Sci 37(4):387–391
Hassan SA (1994) Strategies to select Trichogramma species for use in biological control. In: Wajnberg E, Hassan SA (eds) Biological Control With Egg Parasitoids. CAB International, Oxon, 55–71
Hassan SA (1997) Seleção de espécies de Trichogramma para uso em programas controle biológico. In: Parra JRP, Zucchi RA (eds) Trichogramma e o controle biológico aplicado. pp. 183–206
Hassan SA, Abdelgader H (2001) A sequential testing program to assess the side effects of pesticides on Trichogramma cacoeciae Marchal (Hym.Trichogrammatidae). IOBC/WPRS Bull 24:71–81
Hassan SA, Biglert H, Bogenschutz H, Boller E, Brun J, Callis JNM, CPelseneer J, Duso C, Grove A, Heimbach U, Helyer N, Hokkanen H, Lewis GB, Mansour F, Moreth L, Polgar L, S-Petersen L, Suphanor B, Staubli A, Stern G, Vainio A, Veire VDM, Viggiani G, Vogt H (1994) Results of the sixth joint pesticide testing programme of the IOBC/WPRS-working group “Pesticides and Beneficial Organisms.” Entomopha 39(1):107–119
Hassan SA, Hafes B, Degrande PE, Herai K (1998) The side-effects of pesticides on the egg parasitoid Trichogramma cacoeciae Marchal (Hym., Trichogrammatidae), acute dose response and persistence tests. J Appl Ent 122(1–5):569–57
Hewa-Kapuge S, Mcdougall S, Hoffmann AA (2003) Effects of methoxyfenozide, indoxacarb, and other insecticides on the beneficial egg parasitoid Trichogramma nr. Brassicae (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) under laboratory and field conditions. J Econ Entomol 96:1083–1090
Higgins JJ, Tashtoush S (1994) An aligned rank transform test for interaction. Nonline Wor 1:201–211
Hussain D, Akram M, Iqbal Z, Ali A, Saleem M (2010) Effect of insecticides on Trichogramma chilonis Ishii (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) immature and adult survival. J Agric Res 48:531–537
Hussain D, Ali A, M-ul-Hassan M, Ali S, Saleem M, Nadeem S (2012) Evaluation of Toxicity of Some New Insecticides against Egg Parasitoid Trichogramma chilonis (Ishii) (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Pakistan J Zool 44(4):1123–1127
Hutchison WD, Flood B, Wyman JA (2004) Advances in United States sweet corn and snap bean insect pest management. In: Insect pest management Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 247–278
Jacas J, Urbaneja A (2009) Origen de las plagas e historia del control Biológico. Control Biológico De. Plagas Agric. Phytoma, Esp. 3–13
Jalali SK, Singh SP (1993) Susceptibility of various stages of Trichogrammatoidea armigera Nagaraja to some pesticides and effect of residues on survival and parasitizing ability. Biocont Sci Technol 3:21–27
Jepson PC (1989) Pesticides and non-target invertebrates. (ed.) Intercept. Wimborne. Dorset, U.K
Jiang J, Liu X, Zhang Z, Liu F, Mu W (2019) Lethal and sublethal impact of sulfoxaflor on three species of Trichogramma parasitoid wasps (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Biol Cont 134:32–37
Jiang J, Ma D, Zhang Z, Yu C, Liu F, Mu W (2018) Favorable compatibility of nitenpyram with the aphid predator, Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Envir Sci Pollu Res, 25(27):27393–27401
Kay M, Wobbrock JO (2015) ARTool: An R software package for the aligned rank transform for nonparametric factorial ANOVAs. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ARTool Version 0.9.5
Khan MA (2017) Effect of selected baculoviruses on oviposition preference by Trichogramma chilonis (Trichogrammatidae: Hymenoptera). J King Saud Univ–Sci 29:214–220
Khan MA (2020) Lethal and parasitism effects of selected novel pesticides on adult Trichogramma chilonis (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). J Plant Dis Prot 127:81–90
Khan MA, Khan H, Farid A (2014) Assessment of the lethal and parasitism effects of Helicoverpa armigera Nucleopolyhedrovirus (HaNPV) on Trichogramma chilonis (Ishii) (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Sar J Agric 30(4):425–432
Khan MA, Khan H, Farid A, Ali A (2015a) Evaluation of Toxicity of some Novel Pesticides to Parasitism by Trichogramma chilonis (Hymenoptera: Trichogramm-atidae). J Agric Res 53(1):63–73
Khan MA, Khan H, Ruberson JR (2015b) Lethal and behavioral effects of selectednovel pesticides on adults of Trichogrammapretiosum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Pest Manag Sci 71:1640–1648
Khan MA, Ruberson JR (2017) Lethal effects of selected novel pesticides on immature stages of Trichogrammapretiosum (Hymenoptera:Trichogrammatidae). Pest Manag Sci 73(12):2465–2472
Landis DA, Wratten SD, Gurr GM (2000) Habitat management to conserve natural enemies of arthropod pests in agriculture. Ann Rev Ento 45:175–201
Leite GLD, de Paulo PD, Zanuncio JC, Tavares WD-S, Alvarenga AC, Dourado LR, Bispo EP, Soares MA (2017) Herbicide toxicity, selectivity and hormesis of nicosulfuron on 10 Trichogrammatidae (Hymenoptera) species parasitizing Anagasta ( = Ephestia) kuehniella(Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) eggs. J Environ Sci Health B 2:52(1):70–76
Lingathurai S PM, Raveen R, Priyatharsini PV, Sathikumaran R, Narayanan PCS (2015) Ecotoxicological performances and biochemical effect of selected pesticides on Trichogramma chilonis (Ishii) (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatid- ae). J Entom Zool Stud 3(1):109–114
Lou YG, Zhang GR, Zhang WQ, Huc Y, Zhang J (2013) Biological control of rice insect pests in China. Biol Cont 67:8–12
Mahankuda B, Sawai HR, Gawande RW, Neharkar PS, Nagdeote VG (2019) Effect of insecticide residues on the adult survival rate of Trichogramma chilonis under laboratory condition. J Entomol Zool Stud 7(2):1349–1351
Manzoni CG, Grutzmacher AD, Giolo FP, Harter WDR, Castilhos RV, Paschoal MDF (2007) Side-effects of pesticides used in integrated production of apples to parasitoids of Trichogramma pretiosum Riley and Trichogramma atopovirilia Oatman & Platner (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). BioAssay 2:1–11
Martinson T, Williams L III, English-Loeb G (2001) Compatibility of chemical disease and insect management practices used in New York vineyards with biological control by Anagrus spp Mymaridae Hymenoptera parasitoids of Erthroneura leafhoppers. Biol Cont 22:227–234
Moens J, Tirry L, Clercq PD (2012) Susceptibility of cocooned pupae and adults of the parasitoid Microplitis mediator to selected insecticides. Phytopara 40:5–9
Moura AP, Carvalho GA, Pereira AE, Rocha LCD (2006) Selectivity evaluation of insecticides used to control tomato pests to Trichogramma pretiosum. BioCont 51:769–778
Nascimento PT, Fadini MAM, Valicente FH, Ribeiro PEA (2018) Does Bacillus thuringiensis have adverse effects on the host egg location by parasitoid wasps? Revis Brasil De Entomol 62:260–266
Parra JRP, Zucchi RA (1997) Trichogramma e o Controle Biol´ogico Aplicado. FEALQ, Piracicaba, Brazil, pp. 324
Parreira DS, Cruz RA, Zanuncio JC, Lemes PG, Rolim GS, Barbosa LR, Leite GLD, Serrão JE (2018) Essential oils cause detrimental effects on biological parameters of Trichogramma galloi immatures, J Pest Sci 91(2):887–895
Peterson LS (1993) Effects of 45 insecticides, acaricides and molluscicides on the rove beetle Aleochara bilineata (col.: staphylinidae) in the laboratory. Entomopha 38 (3):371–382
Peterson LS (1995) Effects of 37 fungicides on the rove beetle Aleochara bilineata (coleop: staphylinidae) in the laboratory. Entomophaga 40(2):145–152
Pinto JD (2006) A review of the New World genera of Trichogrammatidae (Hymenoptera). J Hymen 15:38–163
Pinto JD, Stouthamer R (1994) Systematics of the Trichogrammatidae with emphasis on Trichogramma. In: Wajnberg E, Hassan SA (eds) Biological control with egg parasitoids. CAB International, Wallingford, pp. 1–36
Polaszek A (2010) Species diversity and host associations of Trichogramma in Eurasia. In: Cônsoli FL, Parra JR, Zucchi RA (eds) Egg Parasitoids in Agroecosystems with Emphasis on Trichogramma. Springer, Dordrecht, pp. 237–266
Pontes JP, Leite GLD, Bispo EPR, Tavares W de S, Menezes CWG de,Wilcken CF, Zanuncio JC (2020) A glyphosate‑based herbicide in a free-choice test on parasitism, emergence, and female‑biased sex ratio of 10 Trichogrammatidae. J Plant Dis Prot 127:73–79
R Core Team (2013) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Ruberson JR, Nemoto H, Hirose Y (1998) Pesticides and conservation of natural enemies in pest management. In: Barbosa P (ed) Conservation biological control. Academic Press, New York, pp 207–220
Sagheer M, Ashfaq M, M-ul H, Rana SA (2008) Integration of Some Biopesticides and Trichogramma chilonis for the Sustainable Management of Rice Leaf Folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guenee) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Pak J Agri Sci 45(1):69–74
Sattar S, Ullah F, Saljoqi AUR, Arif M, Qazi JI (2011) Toxicity of some new insecticides against Trichogramma chilonis (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) under laboratory and extended laboratory conditions. Pak J Zool 43:1117–1125
Schuld M, Schmuck UR (2000) Effects of Thiacloprid, a New Chloronicotinyl Insecticide, on the Egg Parasitoid Trichogramma cacoeciaev. Ecotoxicolo 9:197–205
Sheng S, Wang J, Zhang X-rui, Liu Z-xiang, Yan M-wen, Shao Y, Zhou J-cheng, Wu Fu-an, Wang J (2021) Evaluation of Sensitivity to Phoxim and Cypermethrin in an Endoparasitoid, Meteorus pulchricornis (Wesmael) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), and Its Parasitization Efficiency Under Insecticide Stress. J Insec Sci 21(1):10; 1–8
Singh PP, Varma GC (1986) Comparative toxicities of some pesticides to Chrysoperla carnea (Chrysopidae: Neuroptera) and Trichogrammabrasiliensis (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae), two arthropod natural enemies of cotton pests. Agric Ecosyst Environ 15:23–30
Smith SM (1996) Biological control with Trichogramma: advances, successes, and potential of their use. Annu Rev Entomol 41:375–406
Snyder WE (2019) Give predators a complement: conserving natural enemy biodiversity to improve biocontrol. Biol Cont 135:73–82
Stark JD, Banken JO (1999) Importance of population structure at the time of toxicant exposure. Ecotox Environ Safety 42:282–287
Stark JD, Vargas R, Banks JE (2007) Incorporating ecologically relevant measures of pesticides effect for estimating the compatibility of pesticides and biocontrol agents. J Econ Entomol 100:1027–1032
Steiner H (1977) Standardized field test to measure side-effects of pesticides in the tree level. J Plant Dise Prot 84(3):164–166
Sterk G, Hassan SA, Baillod M, Bakker F, Bigler F, Blümel S, Bogenschütz H, Boller E, Bromand, B, Brun J, Calis JNM, Coremans-Pelseneer J, Duso C, Garrido A, Grove A, Heimbach U, Hokkanen H, Jacas J, Lewis G, Moreth L, Polgar L, Rovesti L, Samsoe-Peterson L, Sauphanor B, Schaub L, Stäubli A, Tuset JJ, Vainio A, de Veire M.V, Viggiani G, Viñuela E, Vogt H (1999) Results of the seventh joint pesticide testing programme carried out by the IOBC/WPRS-Working Group ‘‘Pesticides and Beneficial Organisms’’. BioControl 44:99–117
Suinaga FA, Picanc¸o M, Zanuncio JC, Bastos CS (1996) Seletividade fisiólogica de inseticidas a Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas, 1851) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) predador de lagartas desfolhadoras de eucalipto. Rev Árvore 20:407–414
Tabebordbara F, Shishehbora P, Ziaeea M, Sohrabi F (2020) Lethal and sublethal effects of two new insecticides spirotetramat and flupyradifurone in comparison to conventional insecticide deltamethrin on Trichogramma evanescens (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). J Asia-Pacif Entom 23:1114–1119
Thomson LJ, Hoffmann AA (2010) Natural enemies responses and pest control importance of local vegetation. Biol Cont 52:160–166
Torres JB, Bueno A de F (2018) Conservation biological control using selective insecticides – A valuable tool for IPM. Bio Cont 126:53–64
You Y, Lin T, Wei H, Zeng Z, Fu J, Liu X, Lin R, Zhang Y (2016) Laboratory evaluation of the sublethal effects of four selective pesticides on the predatory mite Neoseiulus cucumeris (Oudemans). Syst Appl Acarol 21(11):1506–1514
Yu SJ (1998) Selectivity of insecticides to the spined soldier bug (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) and its lepidopterous prey. J Econ Entomol 81:119–122
van den Bosch R, Stern VM (1962) The integration of chemical and biological control of arthropods pests. Annu Rev Ent 7:367–386
Varma GC, Singh PP (1987) Effect of insecticides on the emergence of Trichogramma brasiliensis (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) from parasitized host eggs. Entomoph 32:443–448
Vieira A, Oliveira L, Garcia P (2001) Effects of conventional pesticides on the pre-imaginal developmental stages and on adults of Trichogramma cordubensis (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Biocont Sci Technol 11:527–534
Wahengbam J, Raut AM, Mandal SK, Banu AN (2018) Efficacy of new generation insecticides against Trichogramma chilonis Ishii and Trichogramma pretiosum Riley. J Ent Zool Stud 6(1):1361–1365
Wajnberg E, Hassan SA (1994) Biological Control with Egg Parasitoids.CAB International, Wallingford, Oxon, UK, pp. 286
Way MJ (1986) The role of biological control in integrated plant protection. In: Franz JM (ed) Biological Plant and Health Protection. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart, pp 289–303
Wang DS, He YR, Guo XL, Luo YL (2012) Acute toxicities and sublethal effects of some conventional insecticides on Trichogramma chilonis (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). J Econ Entomol 105(4):1157–1163
Wang D, Lü L, He Y, Shi Q, Wang G (2016) Effects of Insecticides on Oviposition and Host Discrimination Behavior in Trichogramma chilonis (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). J Econ Entomol 109(6):2380–2387
Wang D, Lü L, He Y (2017) Effects of insecticides on sex pheromone communication and mating behavior in Trichogramma chilonis. J Pest Sci 91(1):65–78
Willow J, Silva A, Veromann E, Smagghe G (2019) Acute effect of low-dose thiacloprid exposure synergised by tebuconazole in a parasitoid wasp. PlosOne 14(2):e0212456. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212456
Wobbrock JO, Findlater L, Gergle D, Higgins J (2011) The aligned rank transform for nonparametric factorial analyses using only ANOVA procedures. In Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '11), 143–146. URL: https://depts.washington.edu/aimgroup/proj/art/
Zucchi RA, Querino RB, Monteiro RC (2010) Diversity and hosts of Trichogramma in the New World, with emphasis in South America. In: Cônsoli FL, Parra JR, Zucchi RA (eds) Egg Parasitoids in Agroecosystems with Emphasis on Trichogramma. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 219–236
Acknowledgements
I gratefully acknowledged the Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan financial support under indigenous PhD fellowship. I also wish to offer special thanks to the administration of the Nuclear Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA), Tarnab, Peshawar (Pakistan) for permission and provision of laboratory facilities to conduct experiments. I am also very grateful to Dr John R Ruberson, Chairman Department of Entomology, University of Nebraska, Lincoln. Nebraska, USA for English editing of the manuscript. I am very thankful to Jos Feys, senior research fellow at the KU Leuven University (Catholic University of Leuven, Belgium) for statistical analysis of the data.
Funding
This study was funded by Higher Education Commission of Pakistan under the indigenous 5000 PhD fellowship program, Batch IV with research grant number (PIN) 074–3591-BM4-011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I am the sole author of the manuscript and declares no conflict of interest with any person, institution or organization.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.A. Lethal and parasitism effects of selected novel pesticides on the immature stages of Trichogramma chilonis (Trichogrammatidae: Hymenoptera). Int J Trop Insect Sci 42, 1077–1093 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-021-00580-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-021-00580-x