Abstract
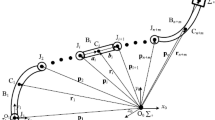
Multi-DOF flexible space robots play a significant role in the on-orbit service. The flexibility of the robots is mainly caused by the flexible links and some flexible drive elements in joints. The vibration generated by the component flexibility can affect the accuracy of control. In this paper, the dynamics and control issues of flexible-link flexible-joint (FLFJ) space robots considering joint friction are studied. Firstly, the Spong’s model is employed to depict flexible joints, and the Coulomb friction model is adopted to describe joint friction. Then based on the single direction recursive construction method and velocity variation principle, dynamic equations of the system are derived. Secondly, a trajectory of joint motion is given and a trajectory tracking controller with friction compensation is designed with the computed torque method. Finally, several numerical simulations are carried out to verify the accuracy of the dynamic model and illustrate the effect of joint friction and joint flexibility on the dynamic characteristics of space robots. Besides, simulation results suggest that the controller designed in this paper could effectively achieve the trajectory tracking control for the 6-DOF FLFJ space robot with joint friction.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devito CL (1996) A non-linear model for time. Astrophys Sp Sci 244(1–2):357–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00642306
Spong MW (1987) Modeling and control of elastic joint robots. J Dyn Syst Meas Control Trans ASME 109(4):310–319. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3143860
Bridges MM, Dawson DM (1995) Redesign of robust controllers for rigid-link flexible-joint robotic manipulators actuated with harmonic drive gearing. IEE Proc Control Theory Appl 142(5):508–514. https://doi.org/10.1049/ip-cta:19951970
Zavrazhina TV, Zavrazhina NM (2001) Influence of elastic and dissipative properties of hinge joints on dynamics of space manipulator. J Autom Inf Sci 33(9–12):53–63. https://doi.org/10.1615/JAutomatInfScien.v33.i10.50
Xu GY, Sun CM (2013) Dynamic modeling and stiffness coefficient analysis of a 3-DOF flexible joint space manipulator. In: Proceeding of 2013 5th International conference intelligent human–machine system cybernetics (IHMSC) 2:171–174. https://doi.org/10.1109/IHMSC.2013.188
Ferretti G, Magnani G, Rocco P (2004) Impedance control for elastic joints industrial manipulators. IEEE Trans Robot 20(3):488–498. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRA.2004.825472
Zhang Q, Liu GJ (2016) Precise control of elastic joint robot using an interconnection and damping assignment passivity-based approach. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 21(6):2728–2736. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMECH.2016.2578287
Xia K, Xing HJ, Ding L, Gao HB, Liu GJ, Deng ZQ (2019) Virtual decomposition-based modeling for multi-DOF manipulator with flexible joint. IEEE Access 7:91582–91592. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2919749
Talebi HA, Patel RV, Asmer H (2000) Neural network based dynamic modeling of flexible-link manipulators with application to the SSRMS. J Robot Syst 17(7):385–401. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4563(200007)17:7%3c385:AID-ROB4%3e3.0.CO;2-3
Yang T, Yan S, Han Z (2015) Nonlinear model of space manipulator joint considering time-variant stiffness and backlash. J Sound Vib 341:246–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2014.12.028
He X, Zhang S, Ouyang Y, Fu Q (2020) Vibration control for a flexible single-link manipulator and its application. IET Control Theory Appl 14(7):930–938. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cta.2018.5815
Korayem MH, Nikoobin A, Azimirad V (2009) Trajectory optimization of flexible link manipulators in point-to-point motion. Robotica 27(6):825–840. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0263574708005183
Cui L, Wang H, Chen W (2020) Trajectory planning of a spatial flexible manipulator for vibration suppression. Robot Auton Syst 123:103316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2019.103316
Korayem MH, Rahimi HN, Nikoobin A (2012) Mathematical modeling and trajectory planning of mobile manipulators with flexible links and joints. Appl Math Model 36(7):3229–3244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2011.10.002
Buondonno G, De Luca A (2015) A recursive Newton–Euler algorithm for robots with elastic joints and its application to control. IEEE Int Conf Intell Robot Syst 1:5526–5532. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2015.7354160
Tomei P (1991) A simple PD controller for robots with elastic joints. Autom Control IEEE Trans 36(10):1208–1213. https://doi.org/10.1109/9.90238
Caverly RJ, Zlotnik DE, Bridgeman LJ, Forbes JR (2014) Saturated proportional derivative control of flexible-joint manipulators. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 30(6):658–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2014.06.001
Yeon JS, Park JH (2008) Practical robust control for flexible joint robot manipulators. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference robotics and automation. 3377–3382, 2008 https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2008.4543726
Park CW (2004) Robust stable fuzzy control via fuzzy modeling and feedback linearization with its applications to controlling uncertain single-link flexible joint manipulators. J Intell Robot Syst Theory Appl 39(2):131–147. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JINT.0000015344.84152.dd
Chaoui H, Gueaieb W, Yagoub MCE, Sicard P (2006) Hybrid neural fuzzy sliding mode control of flexible-joint manipulators with unknown dynamics. In: Proceedings of industrial electronics conference (IECON) 4082–4087, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2006.348032
Chien MC, Huang AC (2007) Adaptive control for flexible-joint electrically driven robot with time-varying uncertainties. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 54(2):1032–1038. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2007.893054
Kim JY, Croft EA (2019) Full-state tracking control for flexible joint robots with singular perturbation techniques. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 27(1):63–73. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCST.2017.2756962
Li Y, Tong SC, Li TS (2012) Fuzzy adaptive dynamic surface control for a single-link flexible-joint robot. Nonlinear Dyn 70(3):2035–2048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0596-7
Li WP, Luo B, Huang H (2016) Active vibration control of flexible joint manipulator using input shaping and adaptive parameter auto disturbance rejection controller. J Sound Vib 363:97–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2015.11.002
Jia PX (2019) Control of flexible joint robot based on motor state feedback and dynamic surface approach. J Control Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5431636
Giusti A, Malzahn J, Tsagarakis NG, Althoff M (2018) On the combined inverse-dynamics/passivity-based control of elastic-joint robots. IEEE Trans Robot 34(6):1461–1471. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2018.2861917
Qi Z, Xu Y, Luo X et al (2010) Recursive formulations for multibody systems with frictional joints based on the interaction between bodies. Mult Syst Dyn 24(2):133–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-010-9213-z
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers 11772187, 11802174), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant numbers 2018M632104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Liu, X. & Cai, G. Dynamics and Control of a Flexible-Link Flexible-Joint Space Robot with Joint Friction. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 22, 415–432 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42405-020-00294-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42405-020-00294-3