Abstract
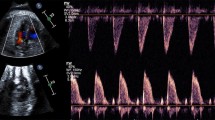
Pulse wave velocity (PWV) reflects blood pulse pressure. We attempted to determine whether commercially marketed ultrasound machine can accurately measure the PWV of the descending aorta of the human fetus. Thirty-two singleton pregnant women participated. Eight women (tocolysis group) were given ritodrine hydrochloride, and the other 24 women (normal group) were not. The descending aorta of the fetus was depicted in the longitudinal direction. Two distant sample volumes were set, and two Doppler waveforms were simultaneously obtained. The distance between the two sample volumes was divided by the time interval between the start of the two waveforms, and a PWV value was obtained. (1) Scatter diagrams for the gestational week and PWV were made, and a linear regression analysis was determined. (2) The PWV for the normal group was compared with the PWV for a group described in a previous report, one measured using ultrasonic phased-tracking. (3) The PWV values in the tocolysis group were compared with those in the normal group. (1) Significant correlations between PWV and gestational weeks were not found. (2) The mean (SE) of the PWV was 2.1 (0.12) m/s, which was similar to the PWV (2.2 (0.069) m/s) measured with ultrasonic phased-tracking. (3) The mean (SE) of the PWV (2.6 (0.25) m/s) in the tocolysis group was larger than that in the normal group (p = 0.032). The PWV of the descending fetal aorta could be accurately and conveniently measured with a commercially marketed ultrasound machine. In addition, PWV measurement with dual Doppler technique had ability to detect fetal cardio-vascular changes by ritodrine infusion.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The corresponding author is ready to show the data when required.
References
Fujita Y, Satoh S, Yumoto Y, Koga T, Kinukawa N, Nakano H. Fetal aortic distention waveforms for evaluating cardiac function and changes in blood pressure: Fetal lamb validation. J Obstet Gynecol Res. 2006;32:155–61.
Mori A, Trudinger B, Mori R, Reed V, Takeda Y. The fetal aortic pressure waveform in normal and compromised pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997;104:1255–61.
Struijk PC, Mathews VJ, Loupas T, Stewart PA, Clark EB, Steegers EAP, et al. Blood pressure estimation in the human fetal descending aorta. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008;32:673–81. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.6137.
Miyashita S, Murotsuki J, Muromoto J, Ozawa K, Yaegashi N, Hasegawa H, et al. Measurement of internal diameter changes and pulse wave velocity in fetal descending aorta using the ultrasonic phased-tracking method in normal and growth-restricted fetuses. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:1311–9.
Wang Z, Yang Y, Yuan L, Liu J, Duan Y, Cao T. Noninvasive method for measuring local pulse wave velocity by dual pulse wave Doppler: in vitro and in vivo studies. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0120482.
Jiang B, Liu B, Mcneill KL, Chowienczk PJ. Measurement of pulse wave velocity using pulse wave Doppler ultrasound: Comparison with arterial tonometry. Ultrsound Med Biol. 2008;34:509–12.
Gokay Z, Ozcan T, Copel JA. Changes in fetal hemodynamics with Ritodrine tocolysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001;18:44–6.
Räsänen J. The effect of ritodrine infusion on fetal myocardial function and fetal hemodynamics. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1990;69:487–92.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Takuya Ayabe for his support, and we appreciate language help by Mr. Howard Stacey.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ER; planning the study, writing the manuscript, MS; collecting and interpreting the data, KY; collecting the data, MM; collecting the data, HK; collecting the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Teikyo University. Written informed consent was obtained by all women before participating in the study.
Consent for Publication
All authors consent to publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Medicine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryo, E., Seto, M., Yatsuki, K. et al. Measurement of Pulse Wave Velocity in Fetal Descending Aorta with Dual Doppler Method: a Preliminary Study. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 3, 1133–1136 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-021-00867-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-021-00867-7