Abstract
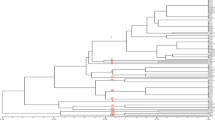
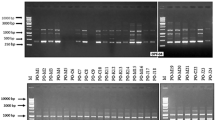
Blast disease caused by a filamentous heterothallic ascomycetous fungus Magnaporthe oryzae is one of the most devastating diseases of rice crop in different parts of the world. A variety of DNA markers are used for understanding the diversity and virulence spectrum of this fungus. In our current investigation, 21 simple sequence repeat markers are taken to analyse genetic diversity among 72 M. oryzae isolates obtained from different geographical locations of Karnataka, India. Results showed that there is significant variation among the isolates of M. oryzae with 92 polymorphic bands with an average of 4.38 bands for each marker. Average locus heterozygosity and polymorphic information content (PIC) of total markers were 0.73 and 0.60 respectively; Cluster analysis interestingly indicated a correlation of grouping with the geographical boundaries. We have also plotted virulence spectrum for each group and found out mixed types of reaction pattern in each group. SSR based genetic diversity of the pathogen is evolved as per the geographical boundaries and the extent of diversity might help the pathogen significantly in adapting to the changed environment. Hence during breeding program locus heterozygosity, PIC and virulence spectrum have to be considered for obtaining stable resistance cultivars.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Chadha S, Gopalakrishna T (2009) Informativeness of dinucleotide repeat-based primers in fungal pathogen of rice Magnaporthe grisea. Microbiol Res 164:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2006.11.019
Chen QH, Wang YC, Li AN, Zhang ZG, Zheng XB (2007) Molecular mapping of two cultivar-specific avirulence genes in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Genet Genom 277:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0179-8
Consolo VF, Cordo CA, Salerno GL (2008) DNA fingerprint and pathotype diversity of Pyricularia oryzae populations from Argentina. Australas Plant Pathol 37:357–364. https://doi.org/10.1071/AP08010
Couch BC, Kohn LM (2002) A multilocus gene genealogy concordant with host preference indicates segregation of a new species, Magnaporthe oryzae, from M. grisea. Mycologia 94:683–693. https://doi.org/10.1080/15572536.2003.11833196
Dean R, Van Kan JA, Pretorius ZA, Hammond-Kosack KE, Di Pietro A, Spanu PD et al (2012) The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:414–430. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00783.x
Dubina EV, Alabushev AV, Kostylev PI, Kharchenko ES, Ruban MG et al (2020) Biodiversity of Pyricularia oryzae Cav. in rice-growing regions of the south of Russia using PCR method. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:289–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00737-6
El-Wahsh SM, El-Raee YZ, Emeran AA, Mashaal SF, Arafa RA (2016) Genetic diversity of rice blast fungus populations (Pyricularia grisea) using molecular markers. J Agric Chem Biotechnol 7:57–65
IRRI (1996) Standard evaluation system for rice, 4th edn. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, p 62
Jagadeesh D, Kumar MP, Chandrakanth R, Devaki NS (2018a) Molecular diversity of internal transcribed spacer among the monoconidial isolates of Magnaporthe oryzae isolated from rice in Southern Karnataka, India. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 16:631–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2018.05.008
Jagadeesh D, Kumar MP, Devaki NS (2018b) Status of Magnaporthe oryzae infection in different districts of Karnataka, India and establishment of monoconidial cultures for understanding genetic diversity. Int J Agric Environ Biotechnol 11:345–355. https://doi.org/10.30954/0974-1712.04.2018.16
Jagadeesh D, Prasanna Kumar MK, Devaki NS (2018c) A simple and reliable method for obtaining monoconidial culture and storage of Magnaporthe oryzae. Int J Life Sci 6:540–543
Jagadeesh D, Kumar MP, Devaki NS (2018d) Population analysis of Magnaporthe oryzae by using endogenous repetitive DNA sequences and mating-type alleles in different districts of Karnataka, India. J Appl Genet 59:365–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-018-0453-6
Karaoglu H, Lee CM, Meyer W (2005) Survey of simple sequence repeats in completed fungal genomes. Mol Biol Evol 22:639–649. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msi057
Kaye C, Milazzo J, Rozenfeld S, Lebrun MH, Tharreau D (2003) The development of simple sequence repeat markers for Magnaporthe grisea and their integration into an established genetic linkage map. Fungal Genet Biol 40:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2003.08.001
Li T, Wen J, Zhang Y, Correll J, Wang L, Pan Q (2018) Reconstruction of an SSR-based Magnaporthe oryzae physical map to locate avirulence gene AvrPi12. BMC Microbiol 18:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-018-1192-x
Liu BH (1998) Statistical genomics: linkage, mapping and QTL analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 611
Longya A, Talumphai S, Jantasuriyarat C (2020) Morphological characterization and genetic diversity of rice blast fungus, Pyricularia oryzae, from Thailand using ISSR and SRAP markers. J Fungi 6:38. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6010038
Lopez ALC, Yli-Matilla T, Cumagun CJR (2019) Geographic distribution of avirulence genes of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae in the Philippines. Microorganisms 7:23. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7010023
Mahesh HB, Meghana S, Shailaja H, Prasannakumar MK, Mahadevu P, Channabyregowda MV, Malali G (2016) Acquisition of the grasshopper retro transposon by rice Magnaporthe isolates indicates a dynamic gene flow between rice and non-rice Magnaporthe population. J Pathol Microbiol 1:1011
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27(2 Part 1):209–220
Meng X, Xiao G, Telebanco-Yanoria MJ, Siazon PM, Padilla J et al (2020) The broad-spectrum rice blast resistance (R) gene Pita2 encodes a novel R protein unique from Pita. Rice 13:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-020-00377-5
Miah G, Rafii MY, Ismail MR, Puteh AB, Rahim HA, Islam K, Latif MA (2013) A review of microsatellite markers and their applications in rice breeding programs to improve blast disease resistance. Int J Mol Sci 14:22499–22528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122499
Milbourne D, Meyer R, Bradshaw JE, Baird E, Bonar N, Provan J et al (1997) Comparison of PCR-based marker systems for the analysis of genetic relationships in cultivated potato. Mol Breed 3:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009633005390
Motlagh MRS, Habibi F, Ebadi AA (2015) Genetic and molecular characterization of population of Pyricularia oryzae from rice blast by SRR. Acta Sci Pol Hortorum Cultus 14:15–28
Nagaraju J, Reddy KD, Nagaraja GM, Sethuraman BN (2001) Comparison of multilocus RFLPs and PCR-based marker systems for genetic analysis of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Heredity 86:588–597. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2540.2001.00861.x
Nalley L, Tsiboe F, Durand-Morat A, Shew A, Thoma G (2016) Economic and environmental impact of rice blast pathogen (Magnaporthe oryzae) alleviation in the United States. PLoS ONE 11(12):e0167295
Orasen G, Greco R, Puja E, Pozzi C, Stile MR (2020) Blast resistance R genes pyramiding in temperate japonica rice. Euphytica 216:40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-2575-2
Rolf FJ (1998) Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system ver. 2.02. Applied Biostatics Inc., New York
Shen Y, Frouin J, He Y, Kaye C, Xiao F, Notteghem LJ, Liu E et al (2004) The perfect stage and SSR analysis of Magnaporthe griseain the Yanxi blast Nursery, Hunan Prvince. Zhongguo Shuidao Kexue 18:262–268
Suzuki F, Suga H, Tomimura K, Fuji S, Arai M, Koba A, Nakajima T (2009) Development of simple sequence repeat markers for Japanese isolates of Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Ecol Resour 9:588–590. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2008.02446.x
Thon MR, Pan H, Diener S, Papalas J, Taro A, Mitchell TK, Dean RA (2006) The role of transposable element clusters in genome evolution and loss of synteny in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Genome Biol 7:R16. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2006-7-2-r16
Viji G, Gnanamanickam SS, Levy M (2000) DNA polymorphisms of isolates of Magnaporthe grisea from India that are pathogenic to finger millet and rice. Mycol Res 104:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1017/S095375629900194X
Wang JC, Correll JC, Jia Y (2015) Characterization of rice blast resistance genes in rice germplasm with monogenic lines and pathogenicity assays. Crop Prot 72:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2015.03.014
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR Protocols. A guide to methods and applications. Academic, San Diego, pp 315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-372180-8.50042-1
Zheng Y, Zhang G, Lin F, Wang Z, Jin G, Yang L et al (2008) Development of microsatellite markers and construction of genetic map in rice blast pathogen Magnaporthe grisea. Fungal Genet Biol 45:1340–1347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2008.07.012
Acknowledgements
We thank University Grants Commission, New Delhi for the financial support by sanctioning Major Research Project (F. No. 41-408/2012 (SR) dated July 2012) to carry out this investigation. Authors are also grateful to Department of Plant Pathology, GKVK, UAS, Bangalore for providing instrumentation facility to carry out molecular work. We are also thankful to Yuvaraja’s College, University of Mysore, Mysuru for providing facilities for carrying out this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jagadeesh, D., Kumar, M.K.P., Amruthavalli, C. et al. Genetic diversity of Magnaporthe oryzae, the blast pathogen of rice in different districts of Karnataka, India determined by simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Indian Phytopathology 73, 713–723 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-020-00257-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-020-00257-4